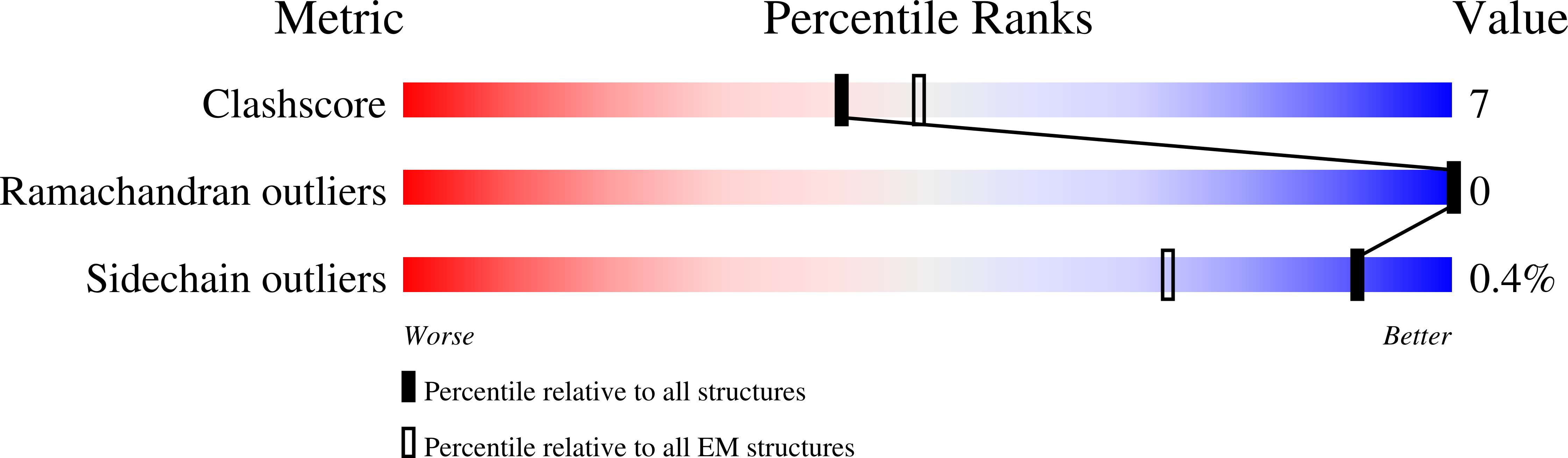
Deposition Date
2021-04-18
Release Date
2021-06-02
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7MIZ
Keywords:
Title:
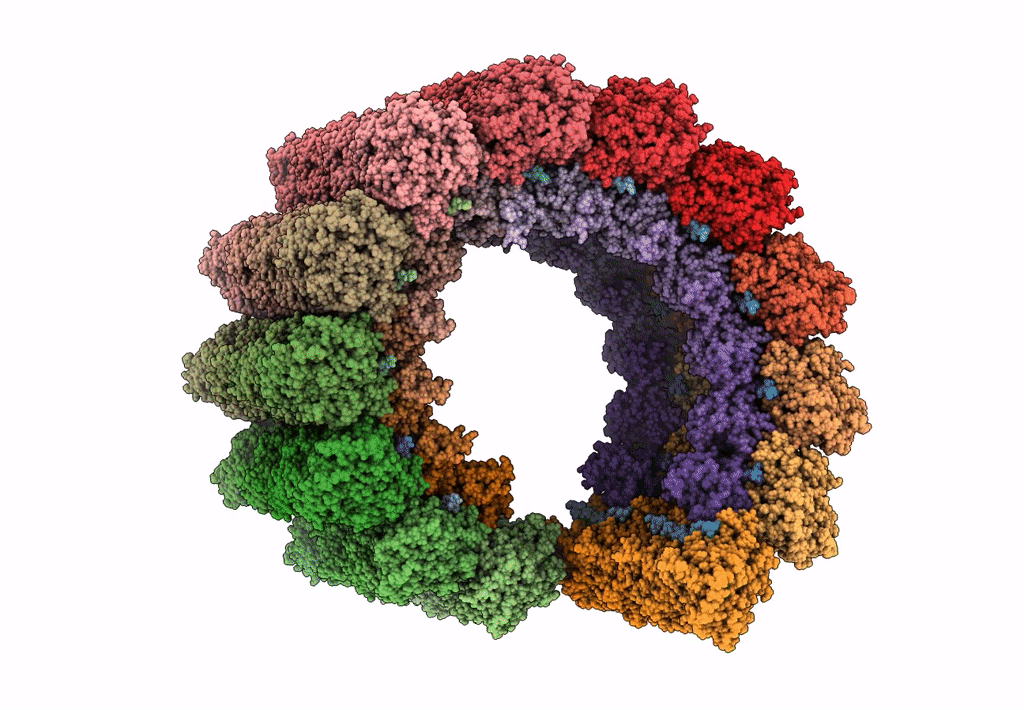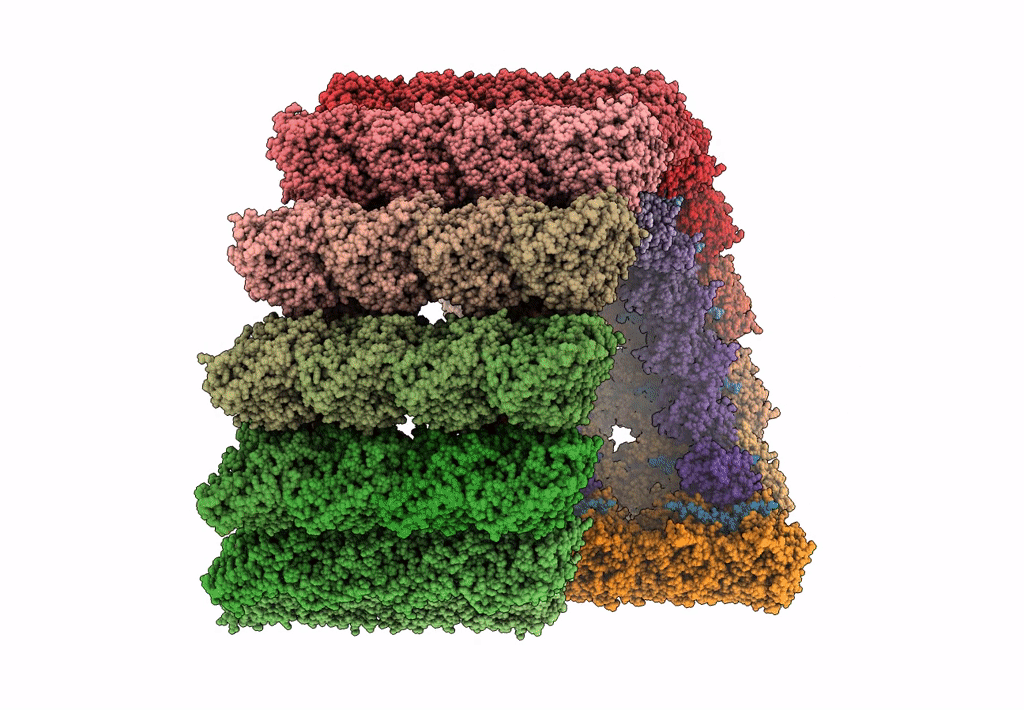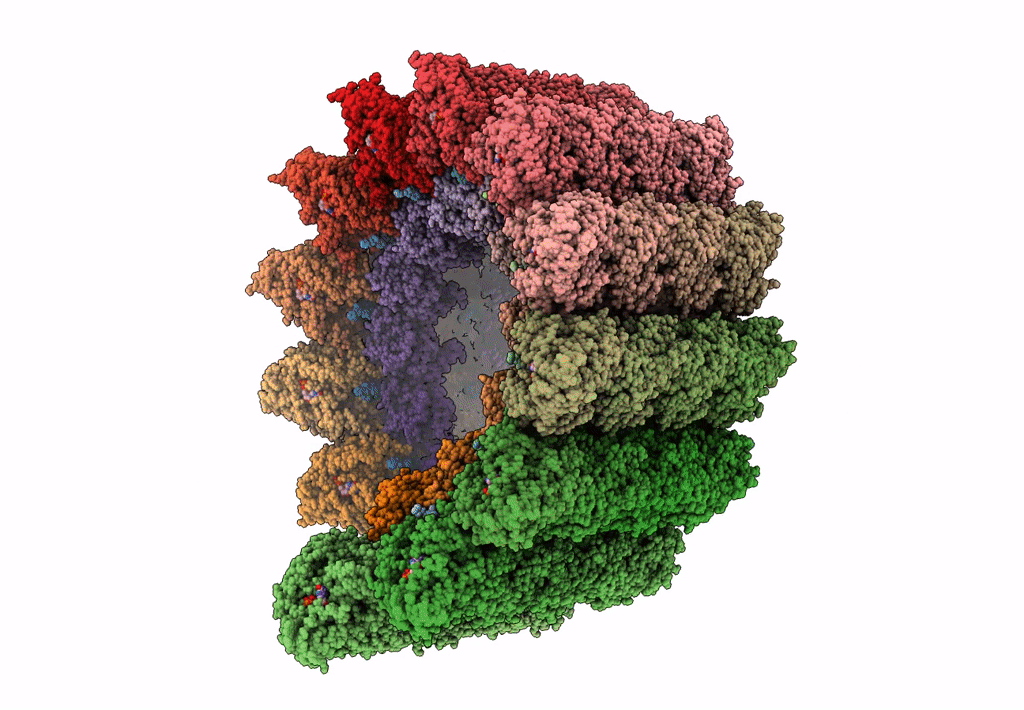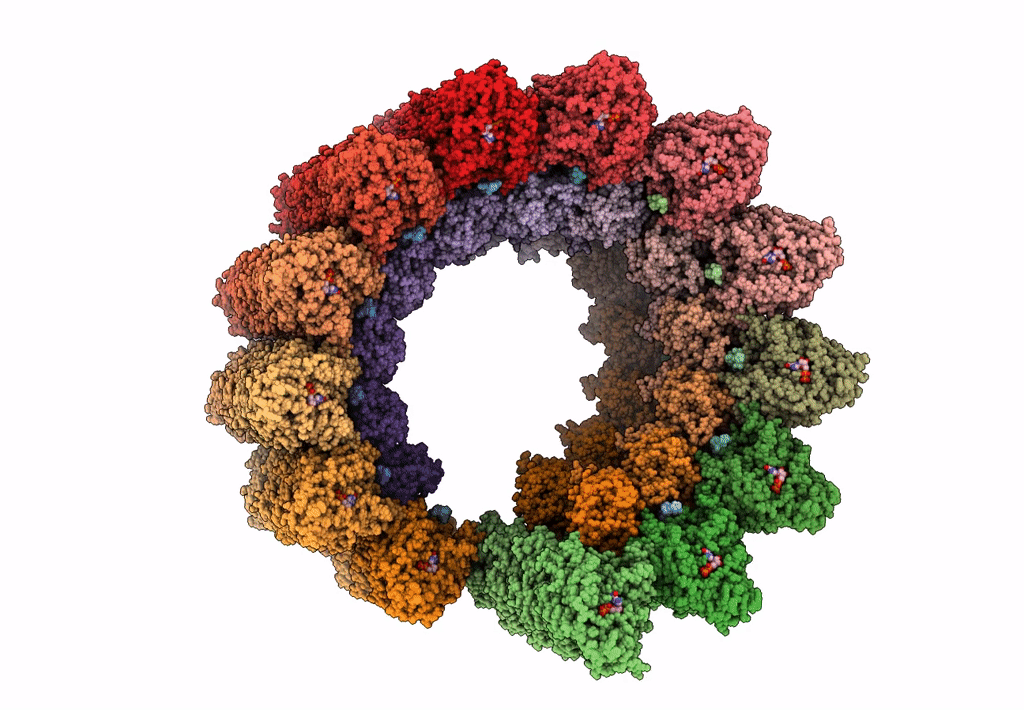
Atomic structure of cortical microtubule from Toxoplasma gondii
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Toxoplasma gondii (Taxon ID: 5811)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.40 Å
Aggregation State:
FILAMENT
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE