Deposition Date
2021-03-08
Release Date
2021-08-04
Last Version Date
2024-05-29
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7LYS
Keywords:
Title:
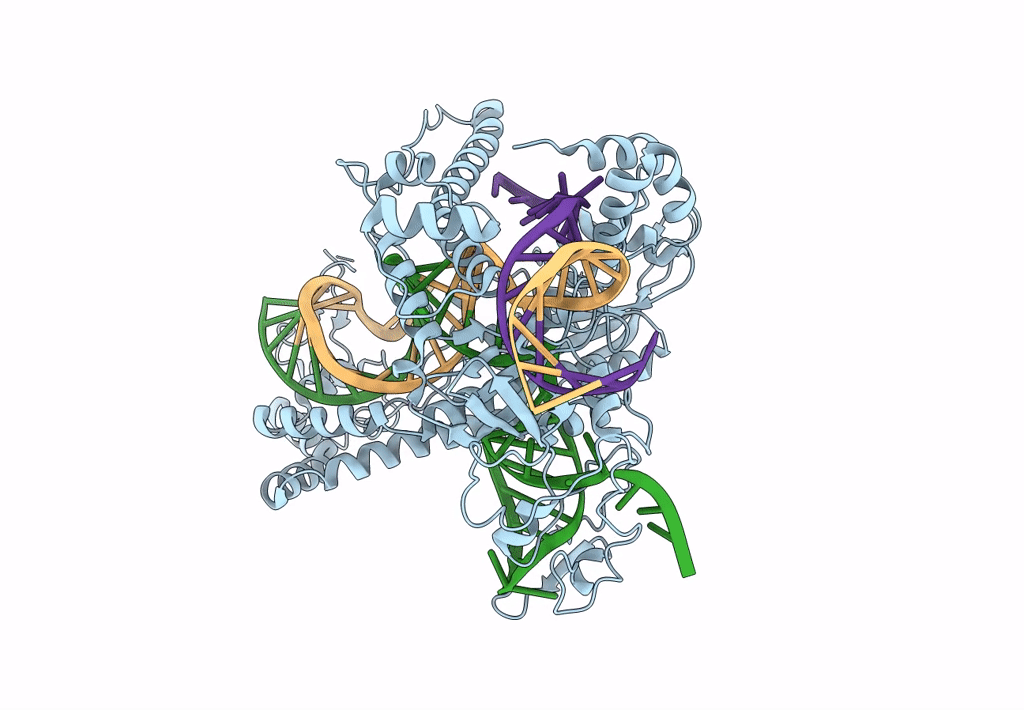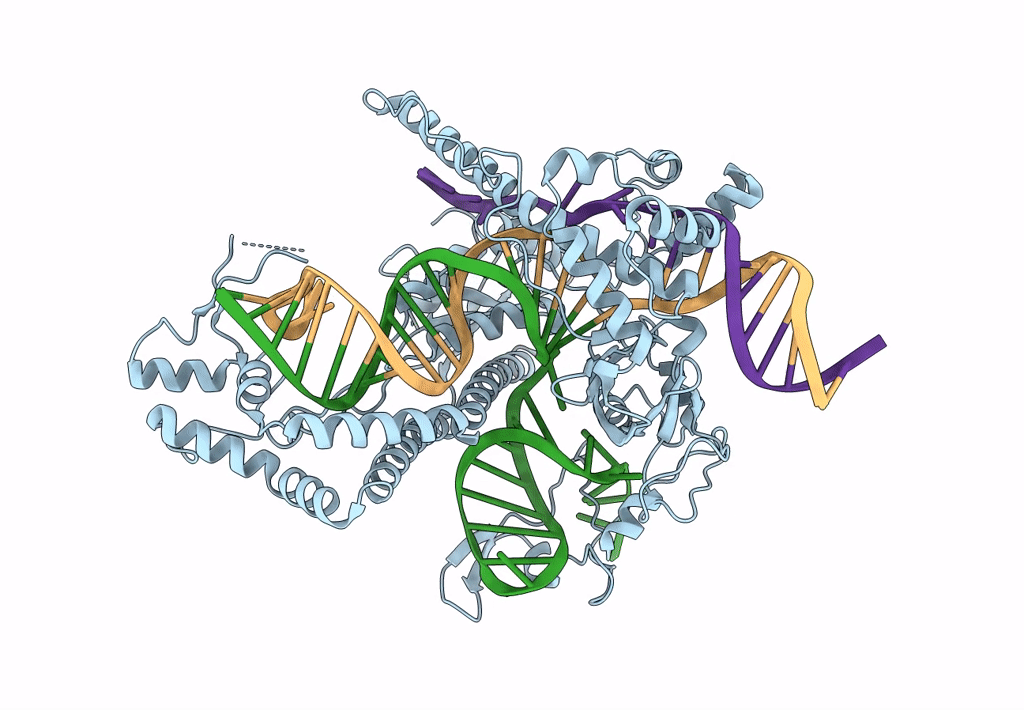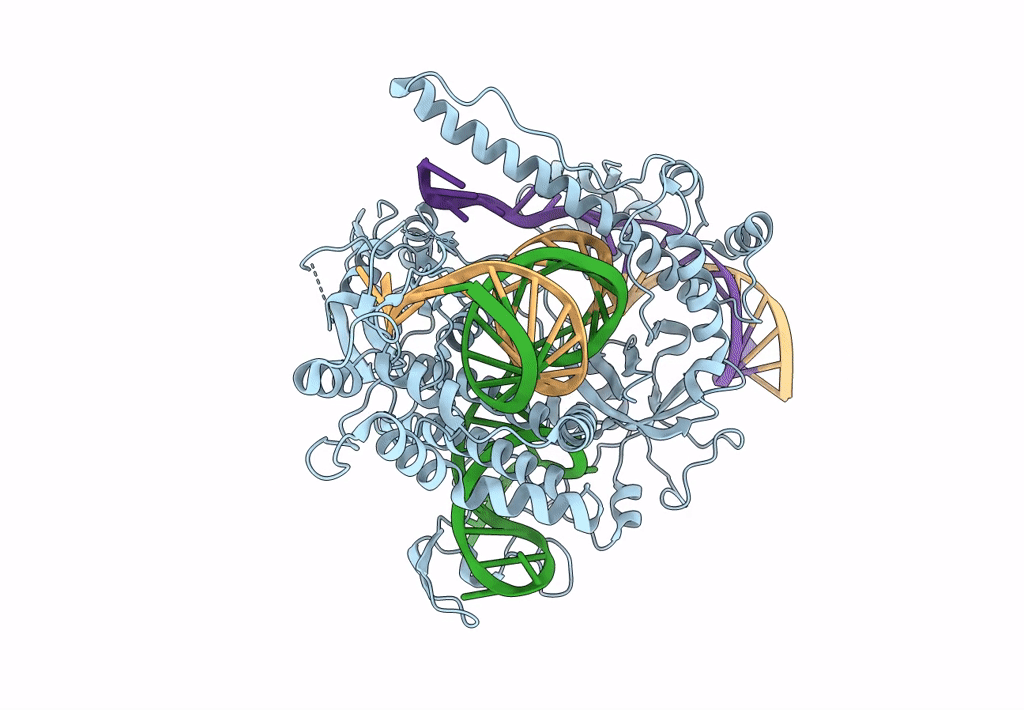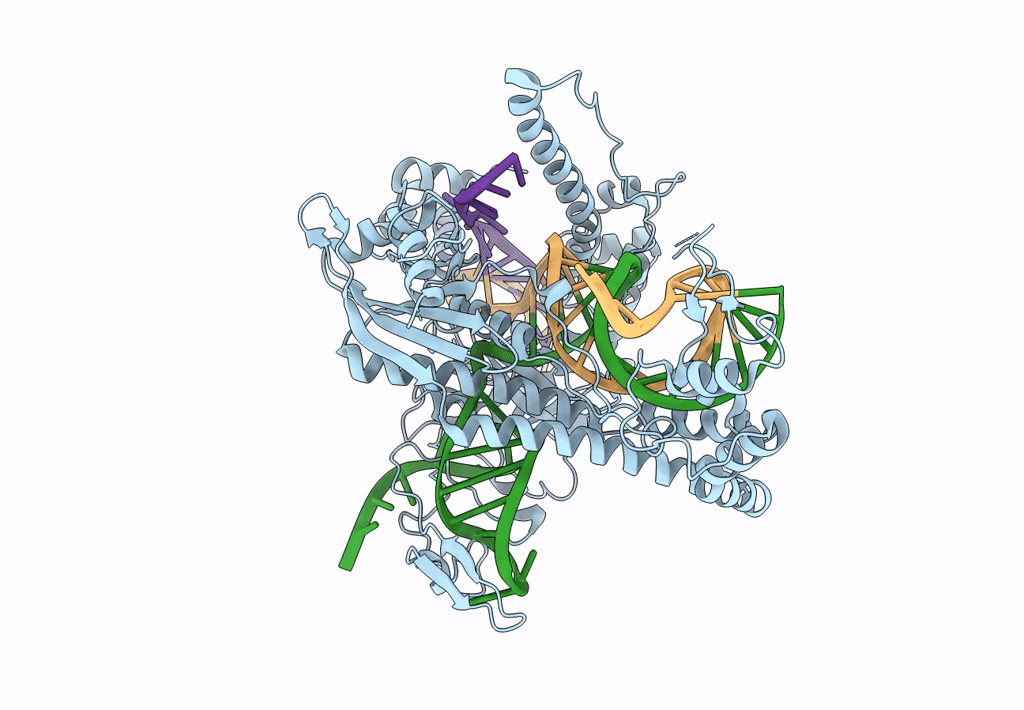
Cryo-EM structure of CasPhi-2 (Cas12j) bound to crRNA and DNA
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Biggievirus Mos11 (Taxon ID: 1925777)
Phage #D (Taxon ID: 77920)
Phage #D (Taxon ID: 77920)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
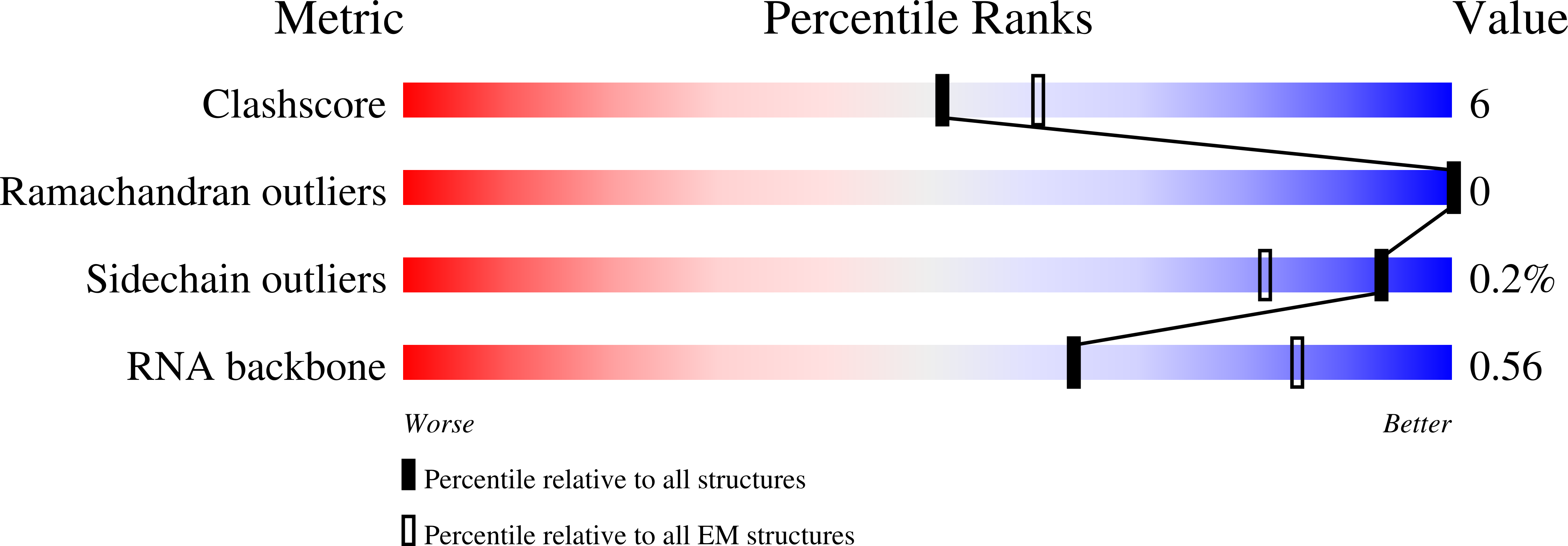
Resolution:
3.05 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE