Deposition Date
2021-02-23
Release Date
2021-07-28
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7LUU
Keywords:
Title:
Kinetic and Structural Characterization of the First B3 Metallo-beta-Lactamase with an Active Site Glutamic Acid
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
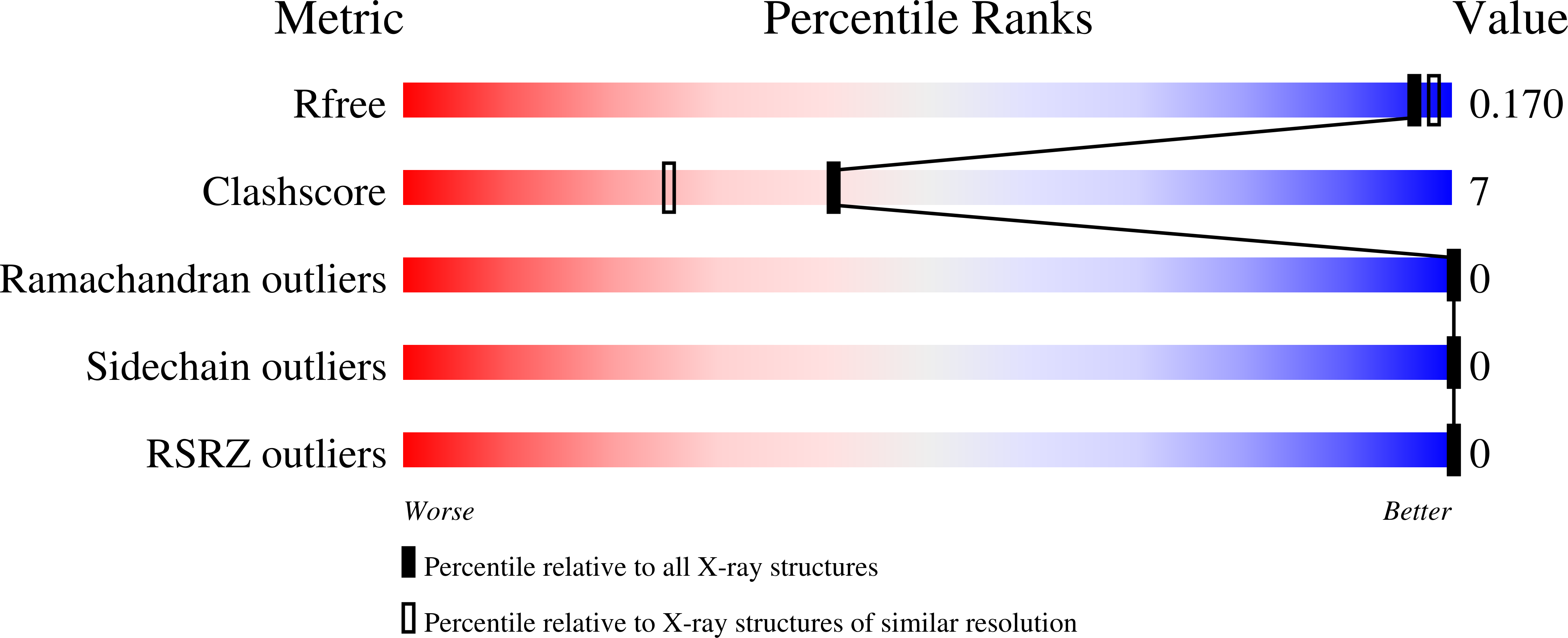
Resolution:
1.68 Å
R-Value Free:
0.16
R-Value Work:
0.14
R-Value Observed:
0.14
Space Group:
P 21 21 2