Deposition Date
2021-01-26
Release Date
2021-05-12
Last Version Date
2023-10-18
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7LHZ
Keywords:
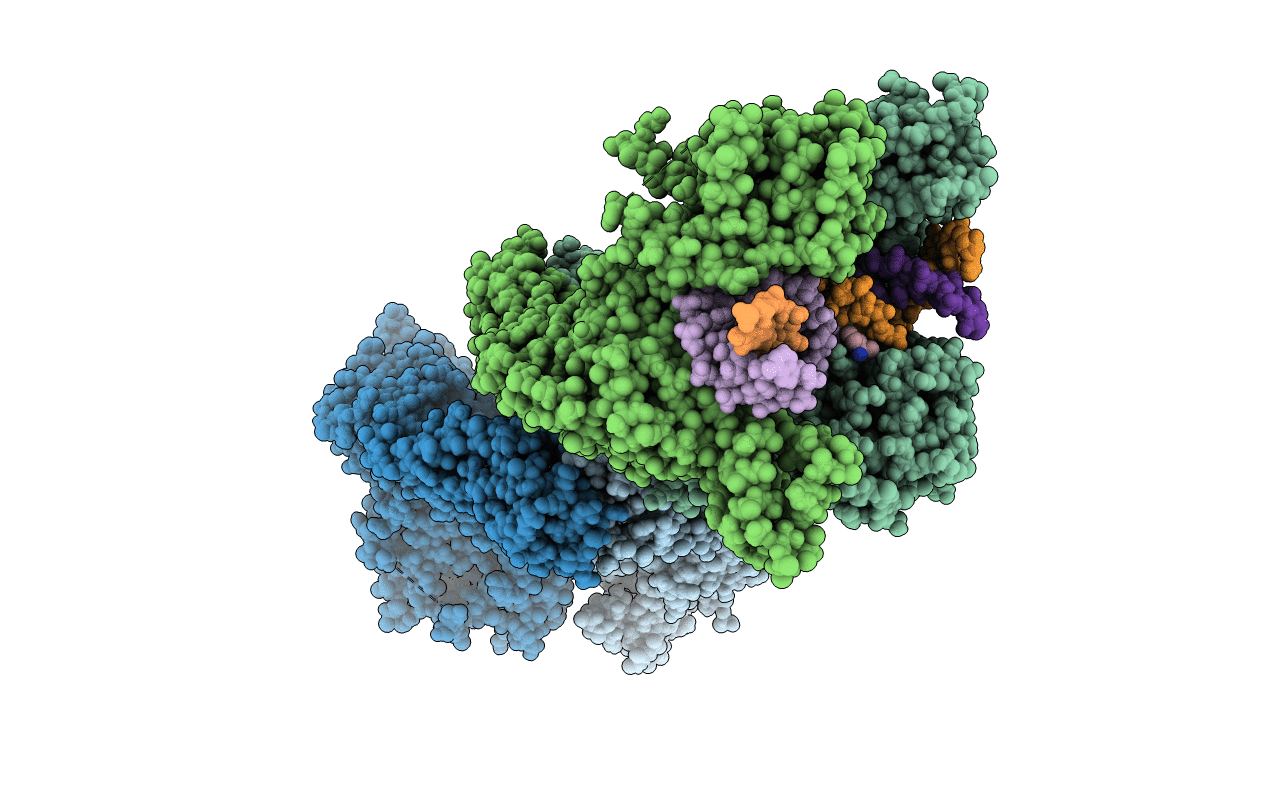
Title:
K. pneumoniae Topoisomerase IV (ParE-ParC) in complex with DNA and (3S)-10-[(3R)-3-(1-aminocyclopropyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]-9-fluoro-3-methyl-5-oxo-2,3-dihydro-5H-[1,4]oxazino[2,3,4-ij]quinoline-6-carboxylic acid (compound 25)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Klebsiella pneumoniae 342 (Taxon ID: 507522)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.30
R-Value Work:
0.28
R-Value Observed:
0.28
Space Group:
P 1 21 1


