Deposition Date
2021-01-26
Release Date
2021-09-08
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7LHY
Keywords:
Title:
Caenorhabditis elegans SWSN-4 (SMARCA4-BRG1) ATPase Bromodomain in complex with a modified histone H3, N6-epsilon-acetyl-L-lysine 14 (H3K14ac) polypeptide
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Caenorhabditis elegans (Taxon ID: 6239)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
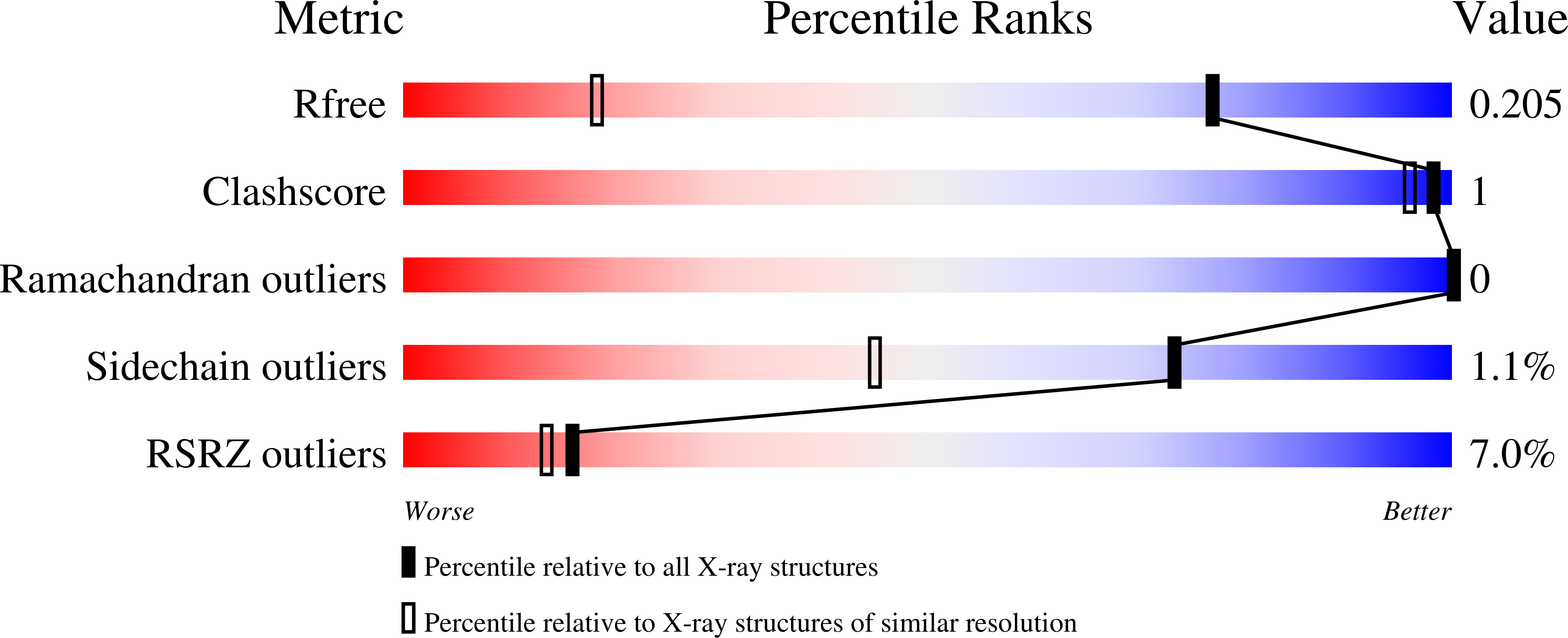
Resolution:
1.30 Å
R-Value Free:
0.19
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 41 21 2