Deposition Date
2021-01-20
Release Date
2021-08-18
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7LGQ
Keywords:
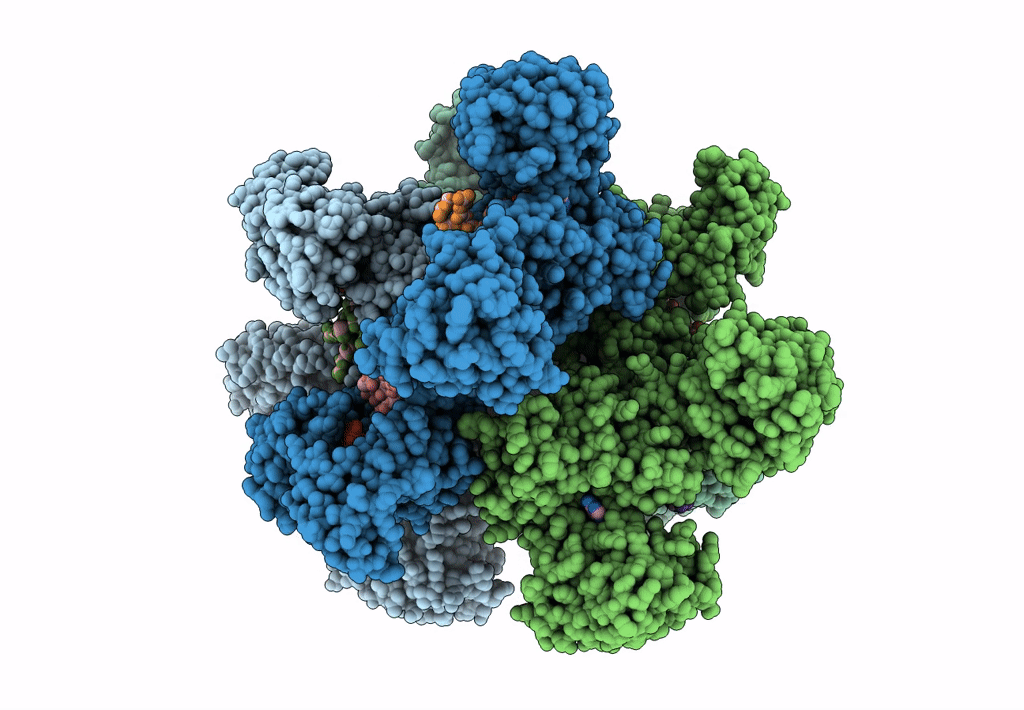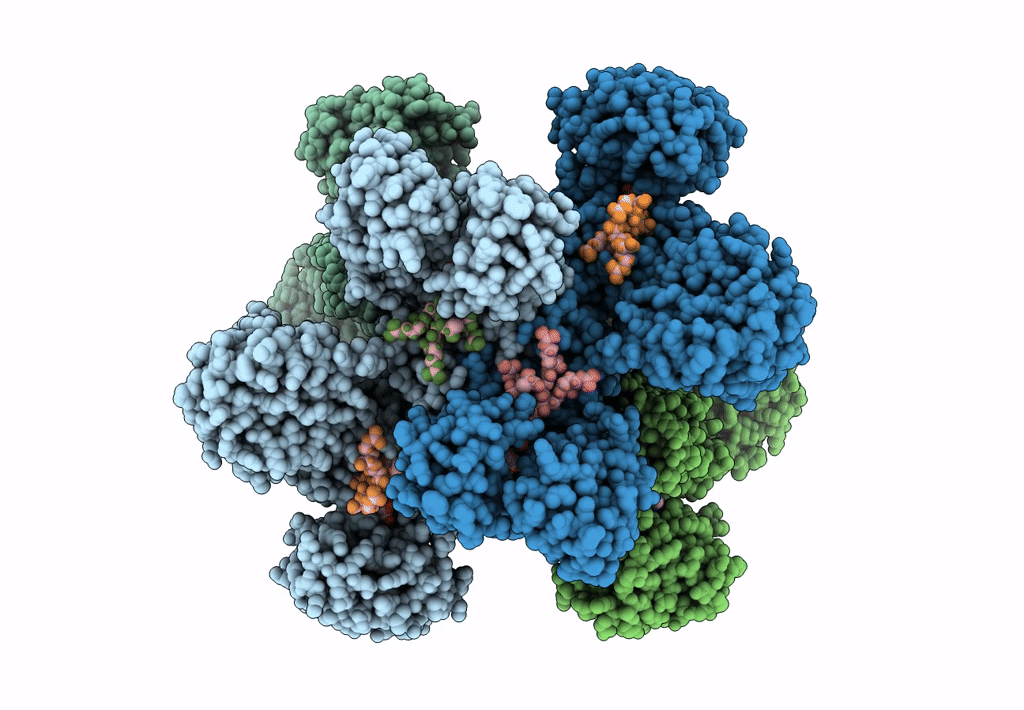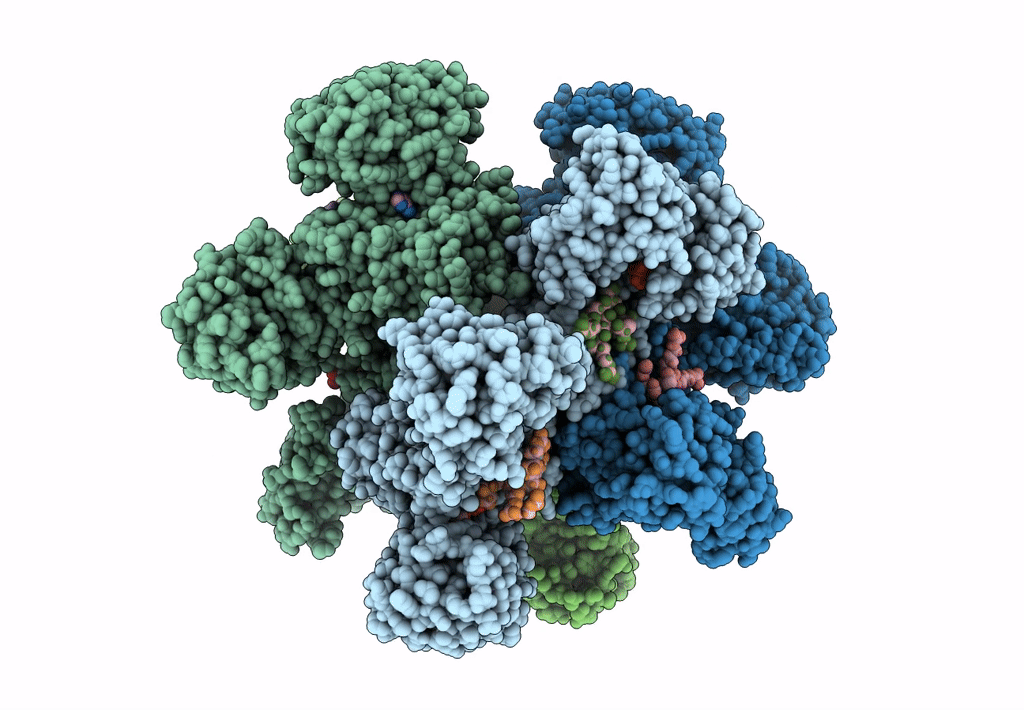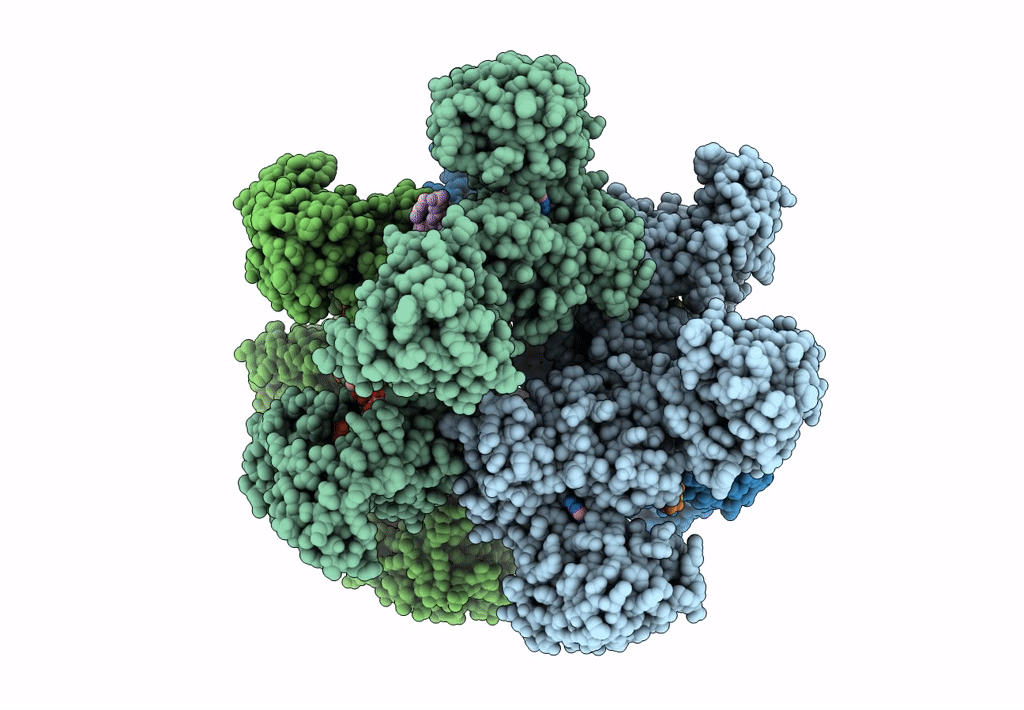
Title:
Cyanophycin synthetase 1 from Synechocystis sp. UTEX2470 with ATP and 8x(Asp-Arg)-Asn
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Synechocystis sp. (strain PCC 6714) (Taxon ID: 1147)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.70 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


