Deposition Date
2020-11-29
Release Date
2021-03-24
Last Version Date
2024-04-03
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7KW2
Keywords:
Title:
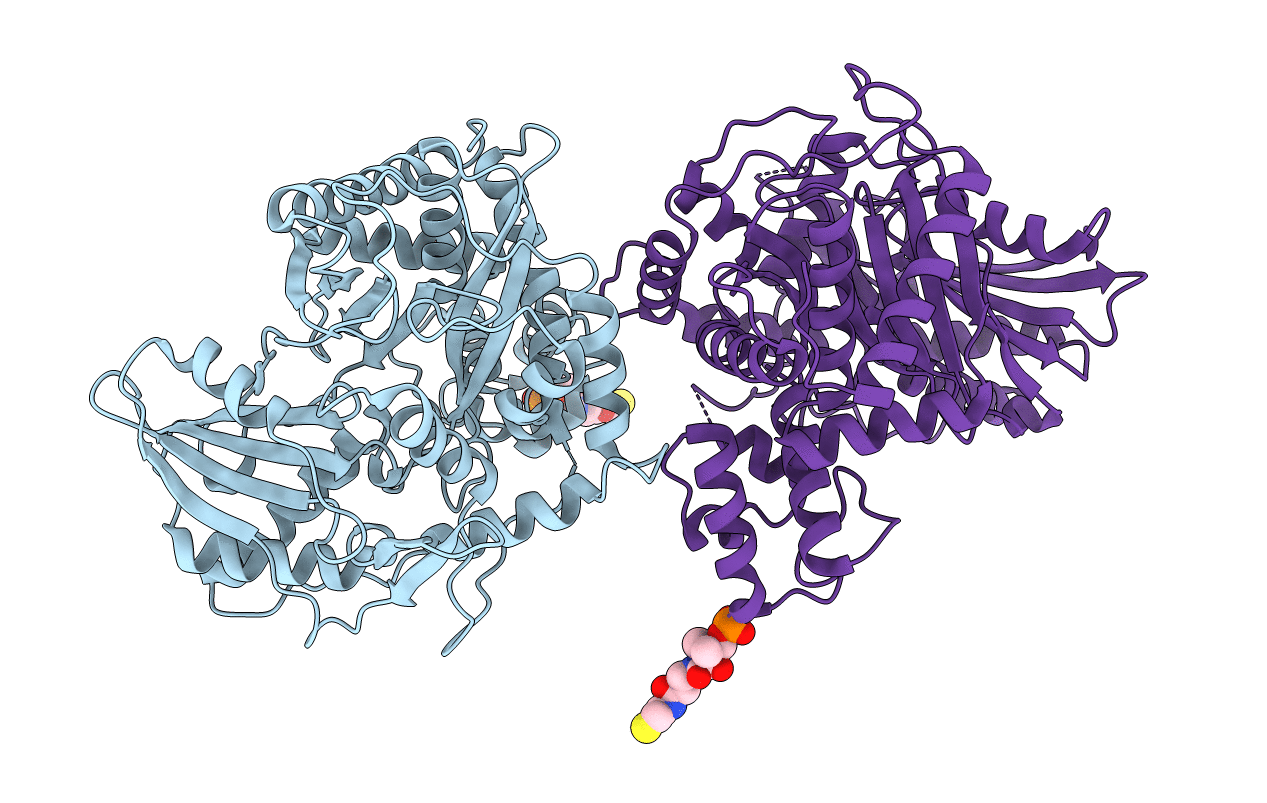
Non-ribosomal didomain (holo-PCP-C) acceptor bound state, R2577G
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Thermobifida fusca (Taxon ID: 269800)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
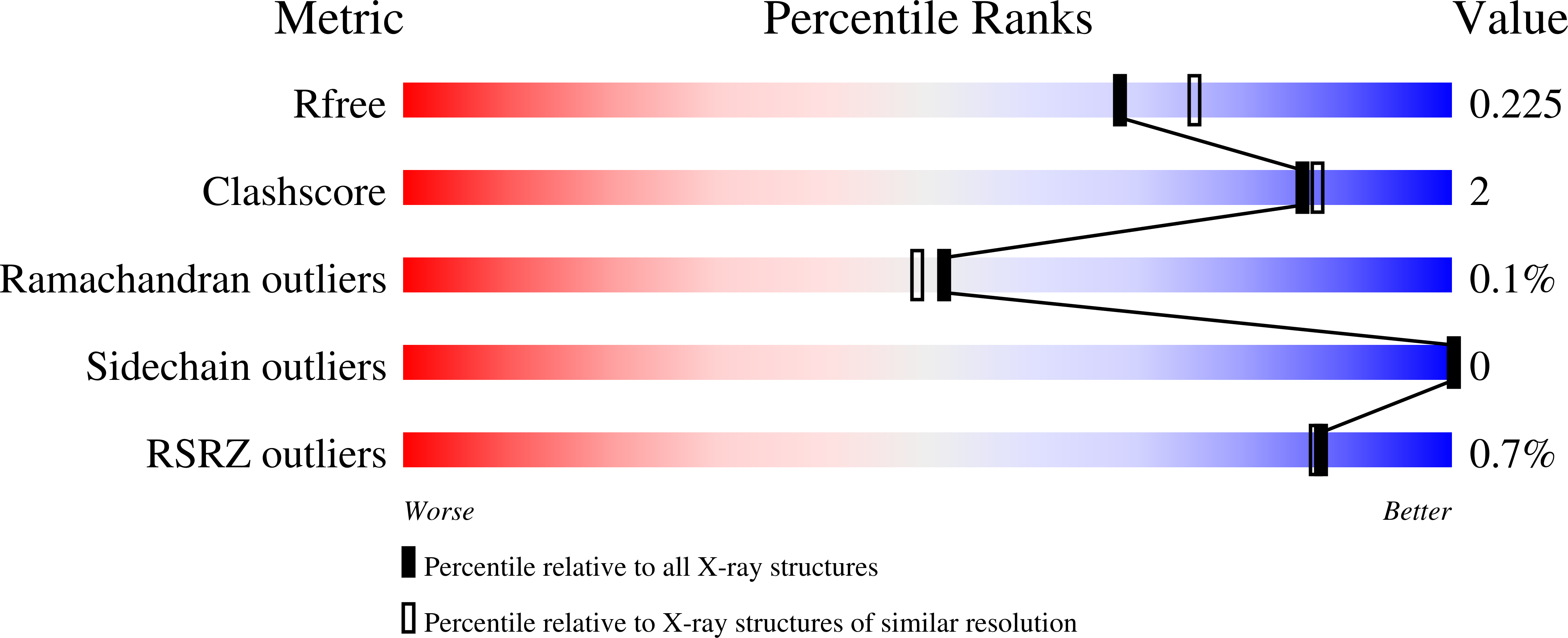
Resolution:
2.00 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 21 21 21