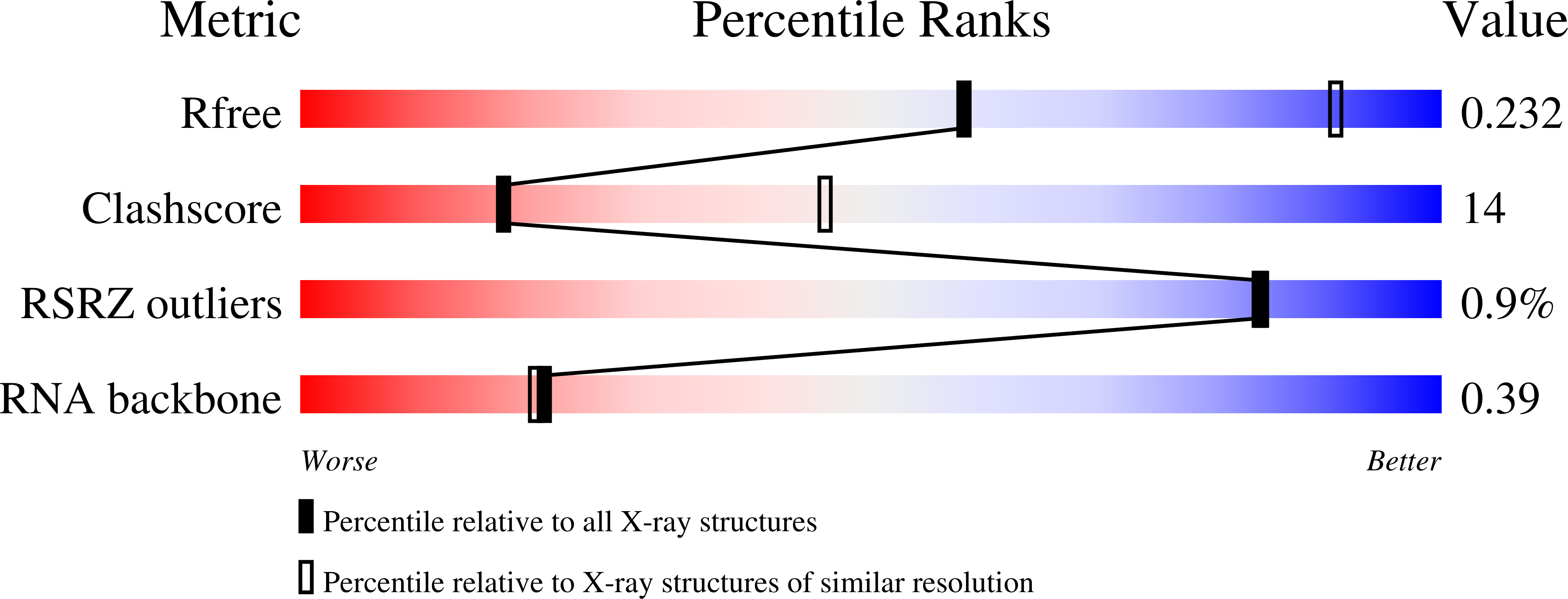
Deposition Date
2020-08-04
Release Date
2021-01-20
Last Version Date
2024-04-03
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7JNH
Keywords:
Title:
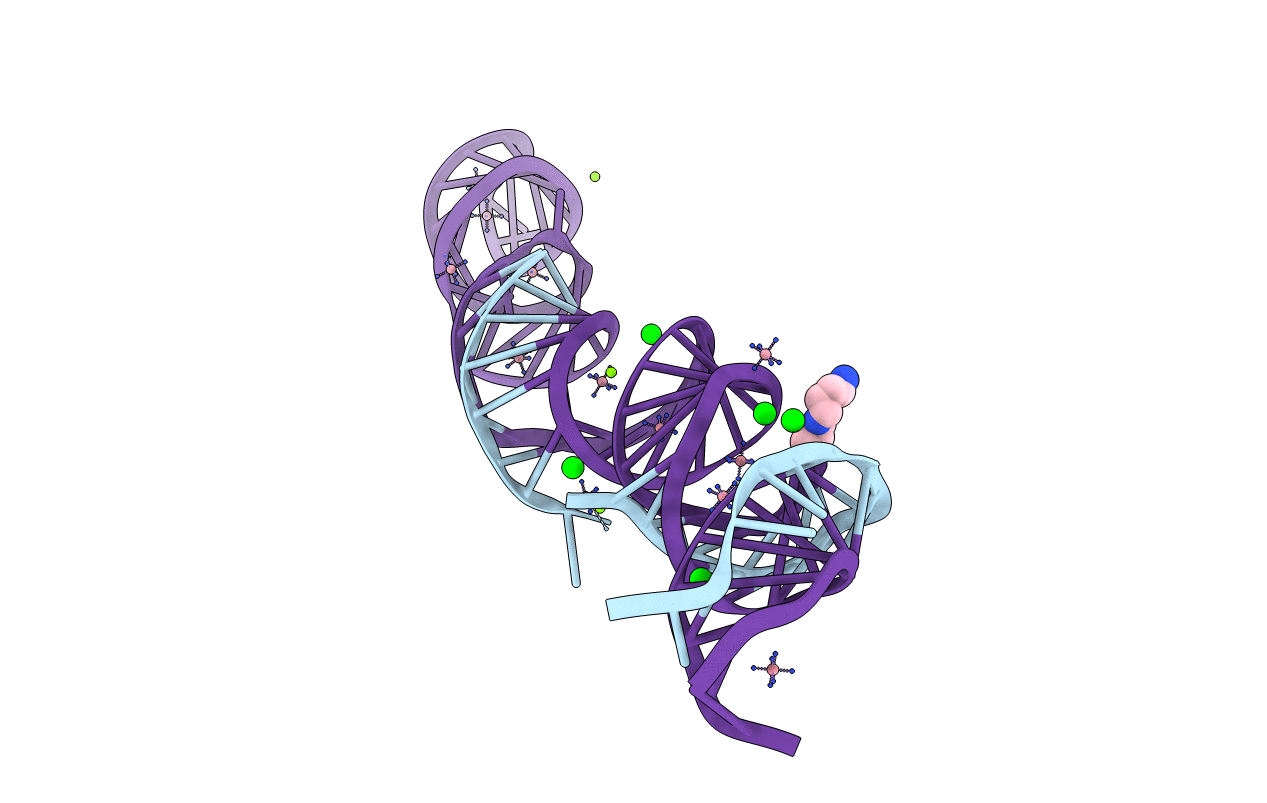
Crystal structure of a double-ENE RNA stability element in complex with a 28-mer poly(A) RNA
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Oryza sativa (Taxon ID: 4530)
Oryza sativa (Taxon ID: 4530)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.89 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 64 2 2