Deposition Date
2025-05-27
Release Date
2025-10-22
Last Version Date
2025-12-10
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7IBD
Keywords:
Title:
PanDDA analysis group deposition -- SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 in complex with fragment X2317 (well E01) from the KIT library
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
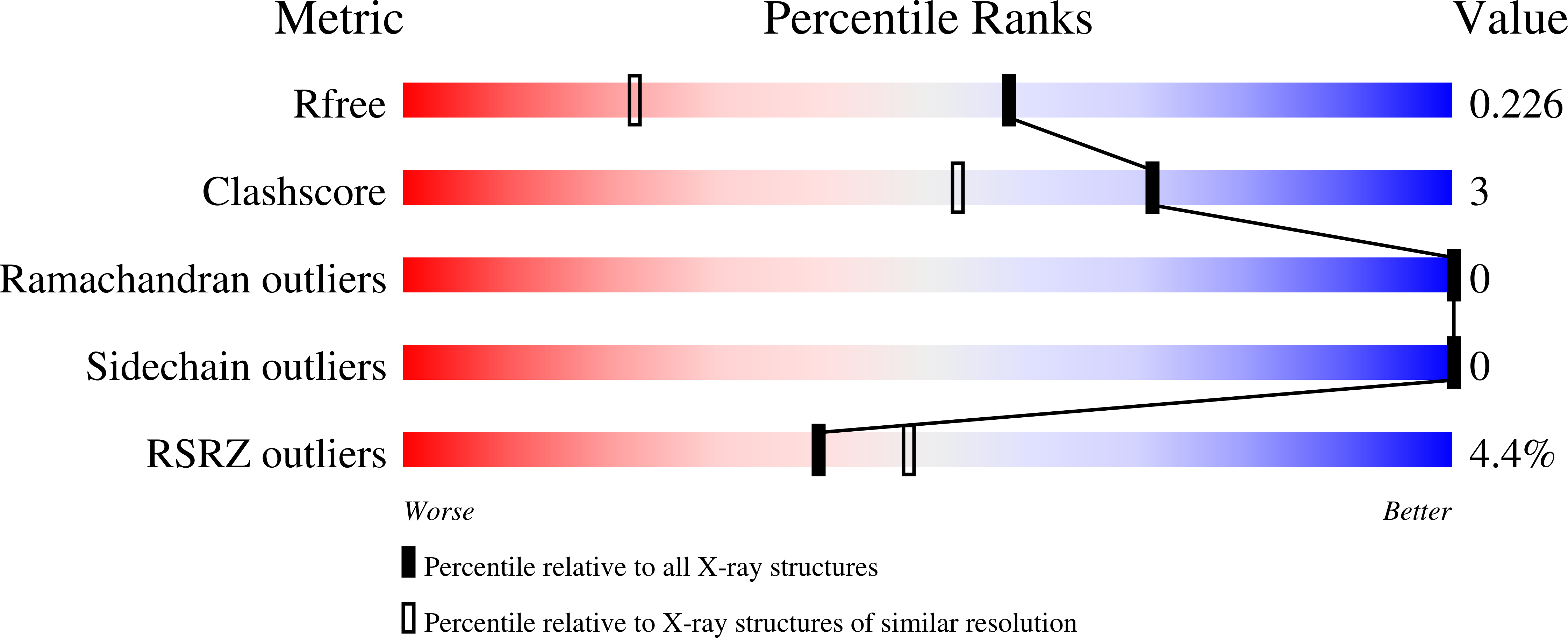
Resolution:
1.54 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
P 43 21 2