Deposition Date
2021-07-19
Release Date
2021-09-01
Last Version Date
2023-11-29
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7FE6
Keywords:
Title:
AvmM Catalyzes Macrocyclization in Alchivemycin A Biosynthesis
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Streptomyces sp. NBRC 109436 (Taxon ID: 1559982)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
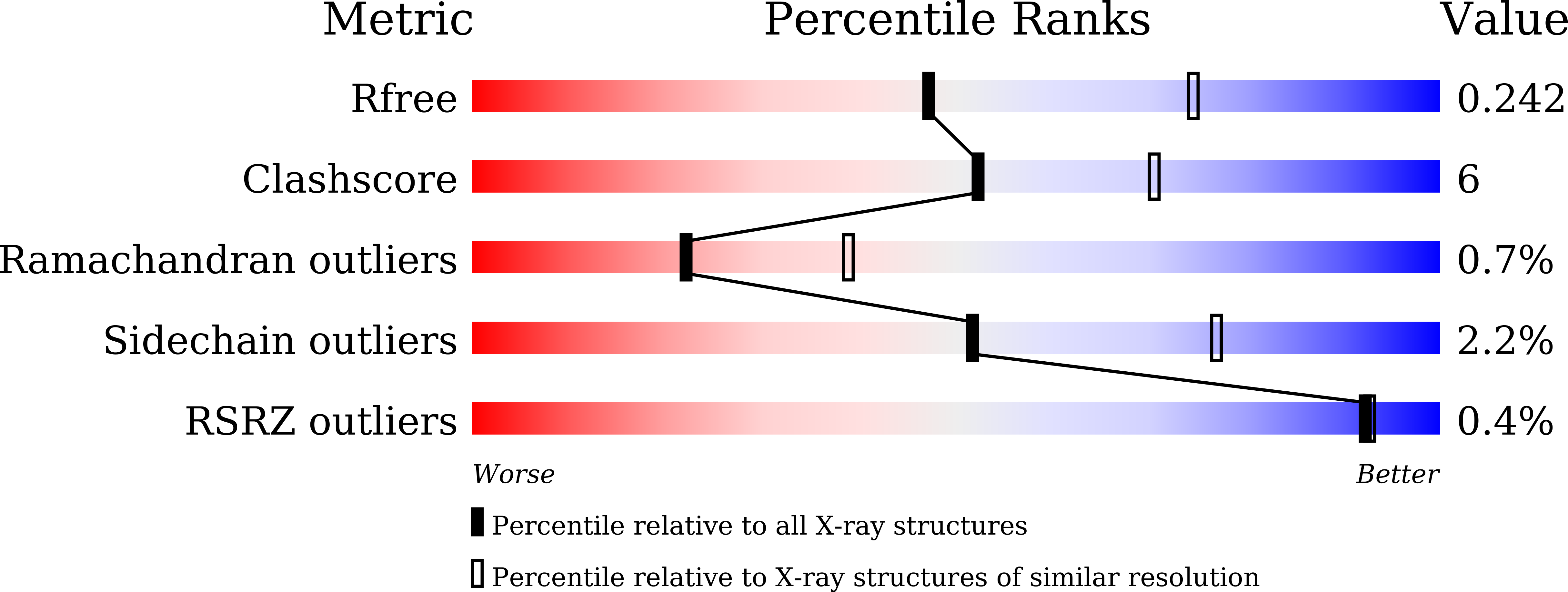
Resolution:
2.50 Å
R-Value Free:
0.24
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 41 21 2