Abstact
BACKGROUND
Isoflavones possess many biological activities, including anti-inflammatory and anticancer effects. Microtubules (composed of αβ-tubulin heterodimers) are described as one possible cellular target of some of these isoflavones. However, the binding of tubulin to isoflavones has not been extensively studied, and until now, no crystal structure of the tubulin-isoflavone complex has been solved, and details of the isoflavone-tubulin interaction remain elusive.
PURPOSE
Barbigerone is an isoflavone mainly found in the genus Milletti, such as the edible leguminous plant Millettia ferruginea, with anticancer activity. This study aims to confirm the cellular target of barbigerone and to study its anticancer mechanism.
METHOD
Surface plasmon resonance assays and X-ray crystallography were used to study the interaction of barbigerone with tubulin protein. Immunofluorescence, in-cell and in vitro tubulin polymerization assays were employed to investigate the mechanism. MTT assays, cell clonal formation assays, wound healing assays, tube formation assays and H460 xenograft models were conducted to evaluate the in vitro and in vivo anticancer activities of barbigerone and one of its derivatives, 0412.
RESULTS
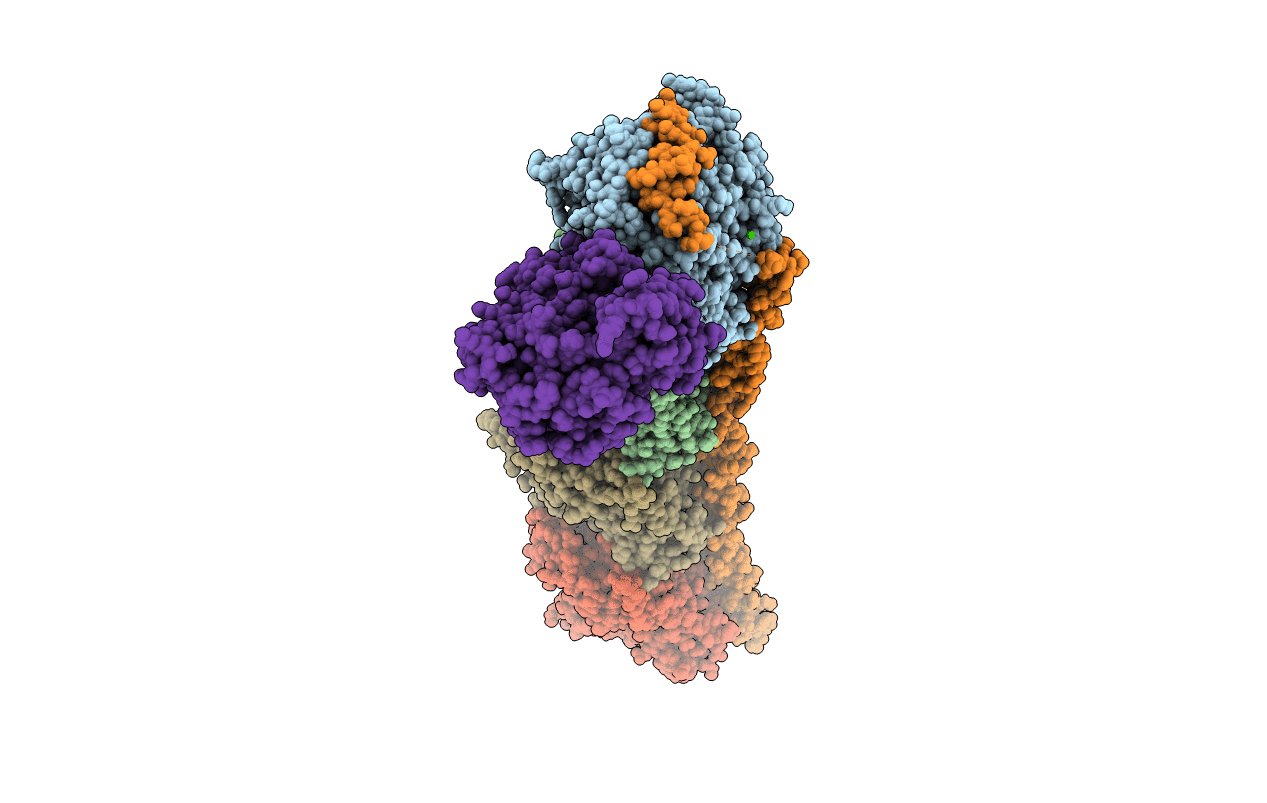
Here, we found that barbigerone binds to tubulin to inhibit tubulin polymerization. Moreover, we solved the X-ray crystal structure of the tubulin-barbigerone complex at 2.33 Å resolution, which unambiguously determined the orientation and position of barbigerone in the colchicine-binding site. Illuminated by the X-ray data, we synthetized and obtained a more active isoflavone, 0412. Both barbigerone and 0412 inhibit cancer cell proliferation, tubulin polymerization, migration of HeLa cells and capillary-like tube formation of HUVECs, induce G2/M phase cell cycle arrest and apoptosis, and exhibit anticancer activity in an H460 xenograft model.
CONCLUSION
In all, through biochemical and X-ray crystal structure results, we identified tubulin as the cellular target of one isoflavone, barbigerone, and proved that the tubulin-barbigerone complex plays a guiding role in obtaining a more active compound, 0412. These studies provide a crucial research basis for the development of isoflavones as anticancer candidate compounds.