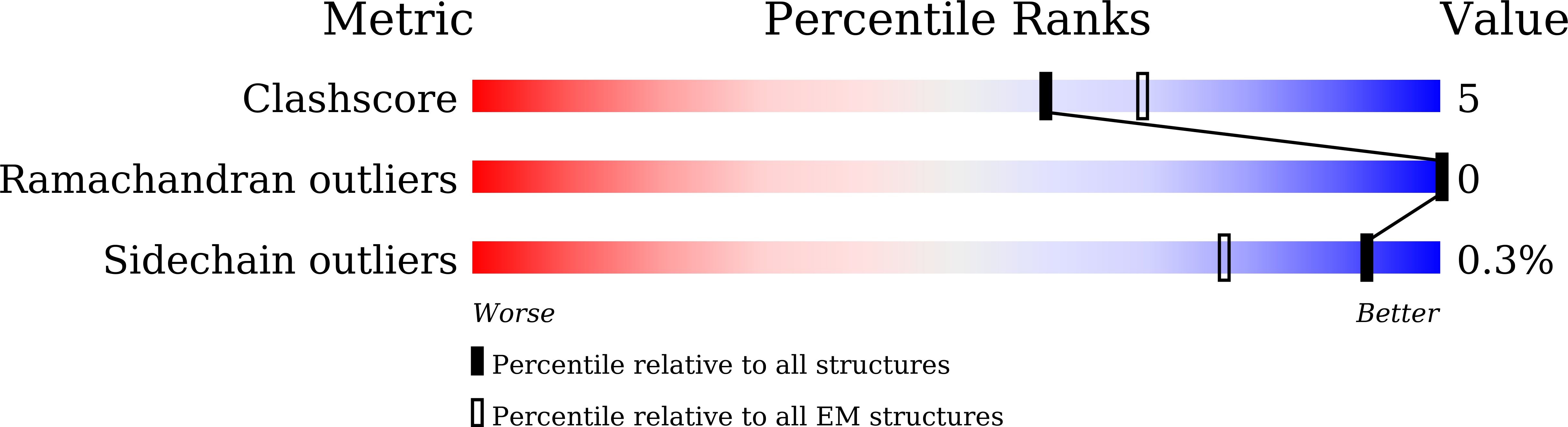
Deposition Date
2021-02-24
Release Date
2021-09-22
Last Version Date
2025-07-02
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7E6T
Keywords:
Title:
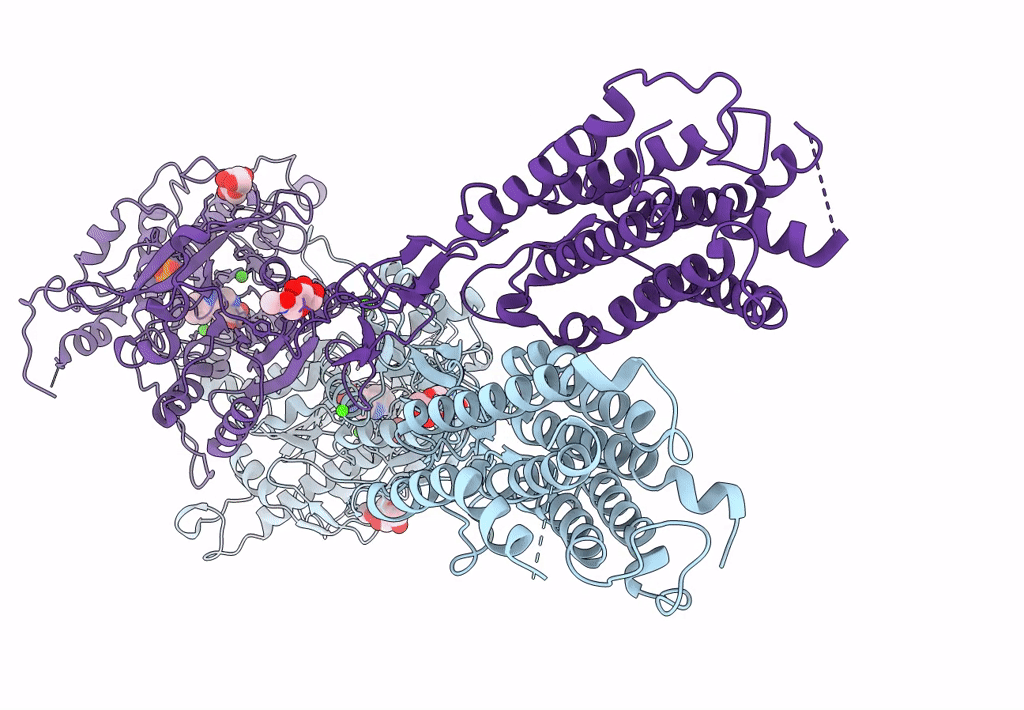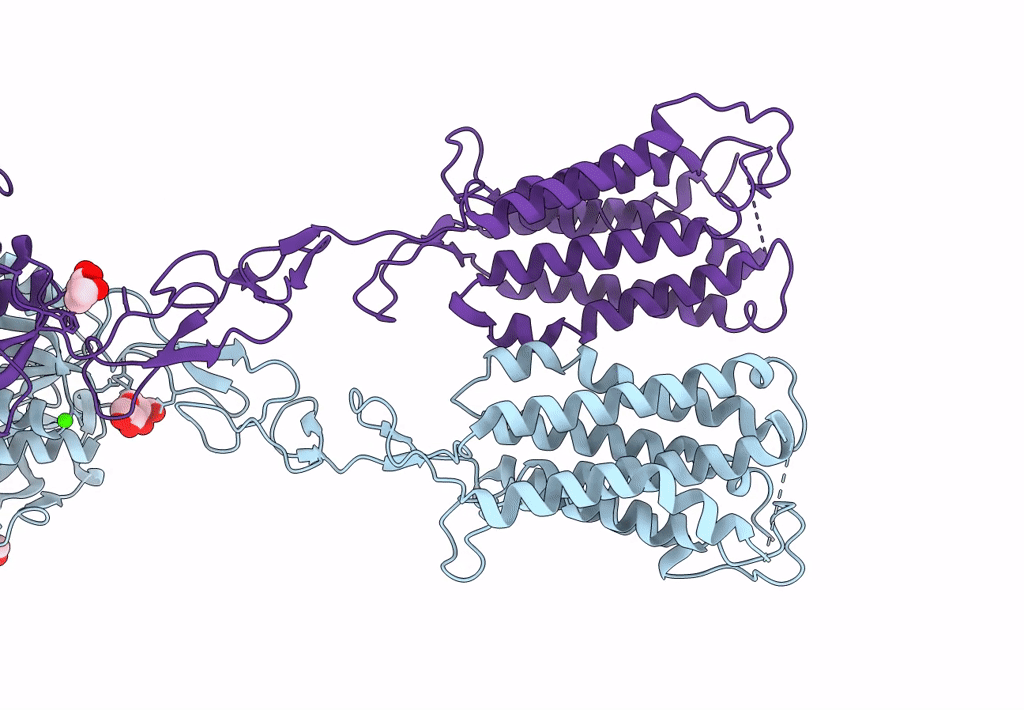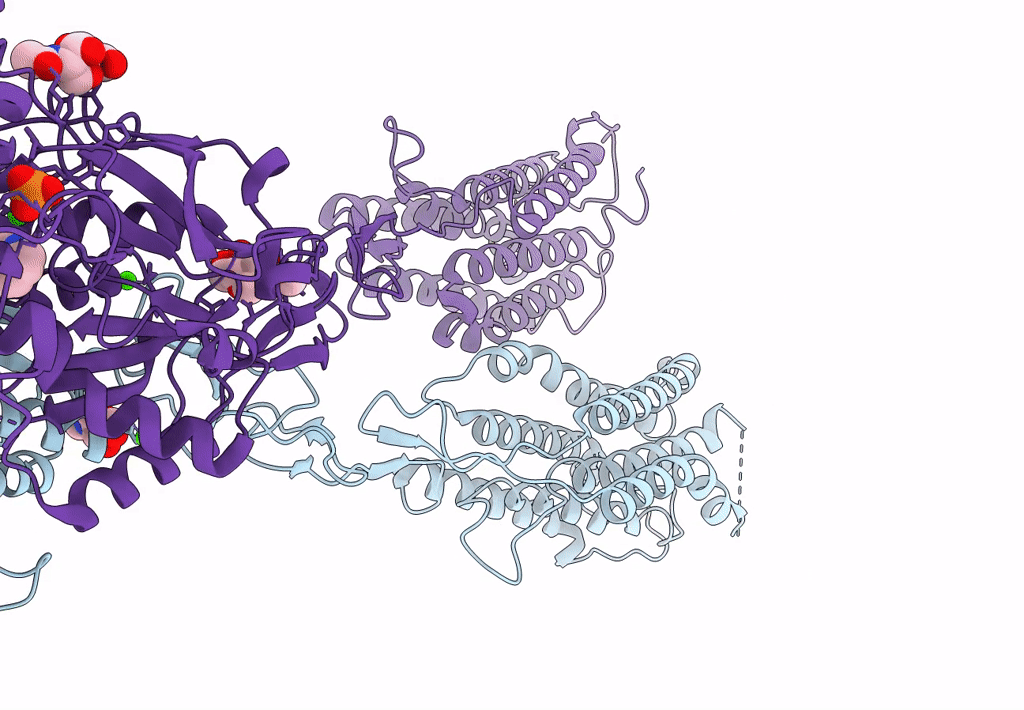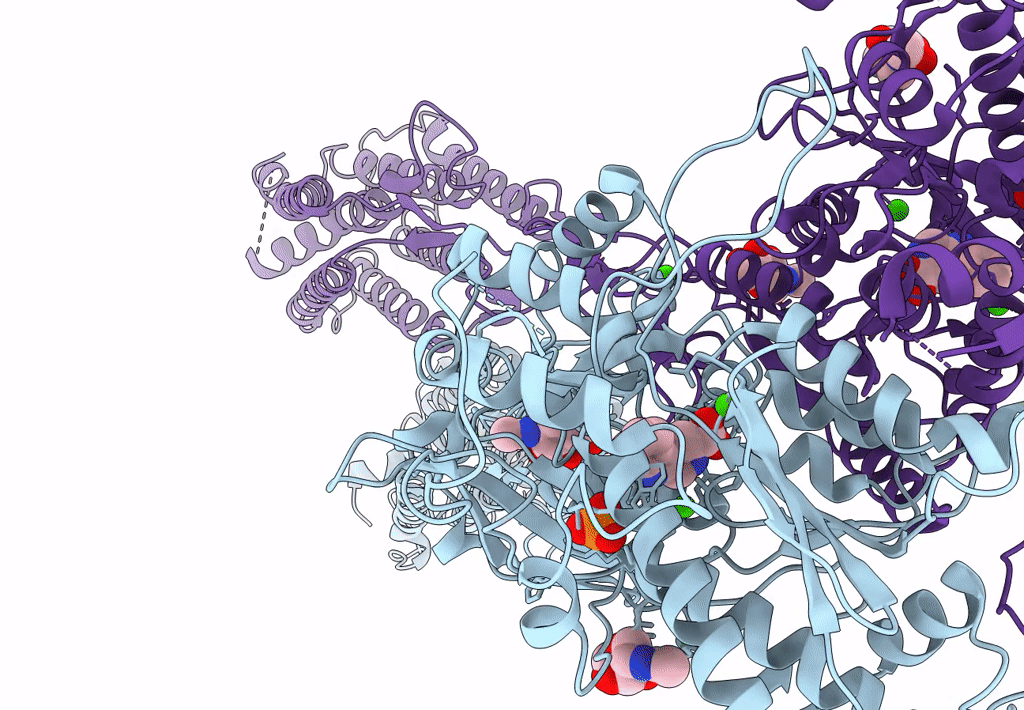
Structural insights into the activation of human calcium-sensing receptor
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.00 Å
Aggregation State:
2D ARRAY
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE