Deposition Date
2020-11-25
Release Date
2021-09-29
Last Version Date
2024-05-29
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7DL0
Keywords:
Title:
The mutant E310G/A314Y of 3,5-DAHDHcca complex with NADPH
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Cloacimonas acidaminovorans (strain Evry) (Taxon ID: 459349)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
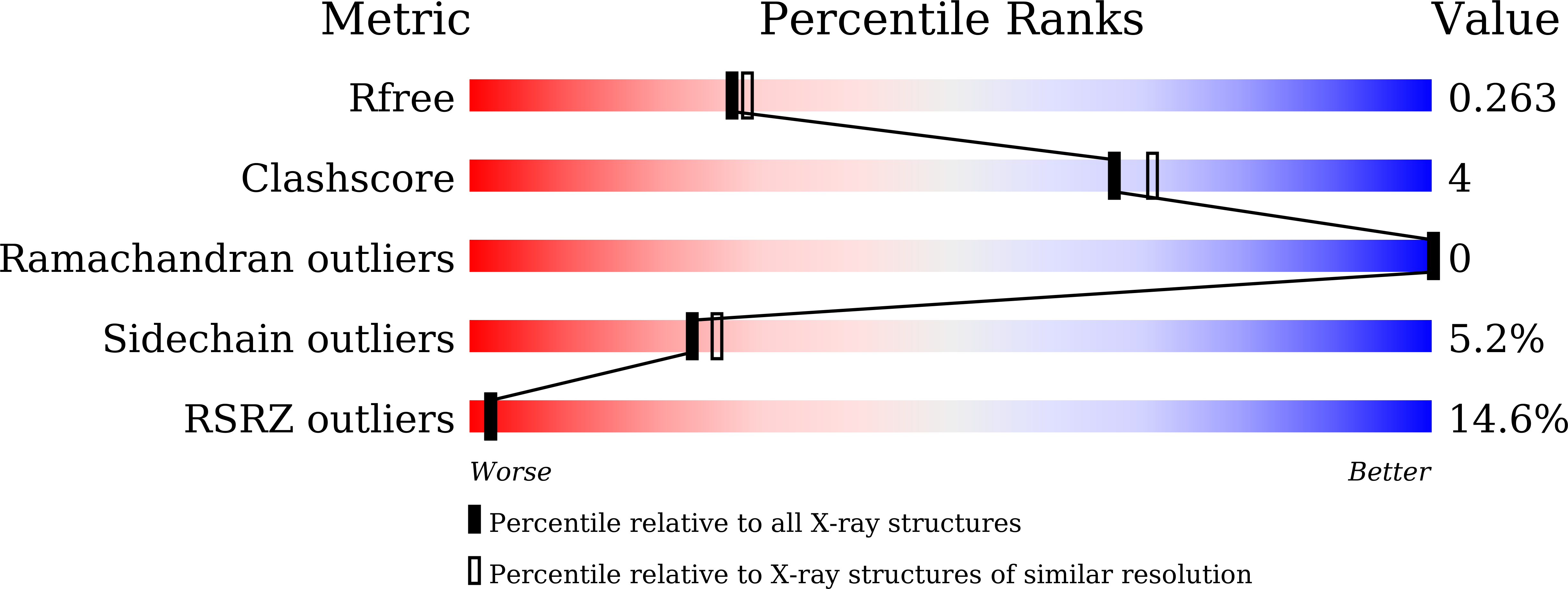
Resolution:
2.17 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.21
R-Value Observed:
0.21
Space Group:
I 41 2 2