Deposition Date
2020-09-28
Release Date
2021-07-21
Last Version Date
2023-11-29
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7D5X
Keywords:
Title:
Bovine heart cytochrome c oxidase in a catalytic intermediate, IO10, at 1.74 angstrom resolution
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
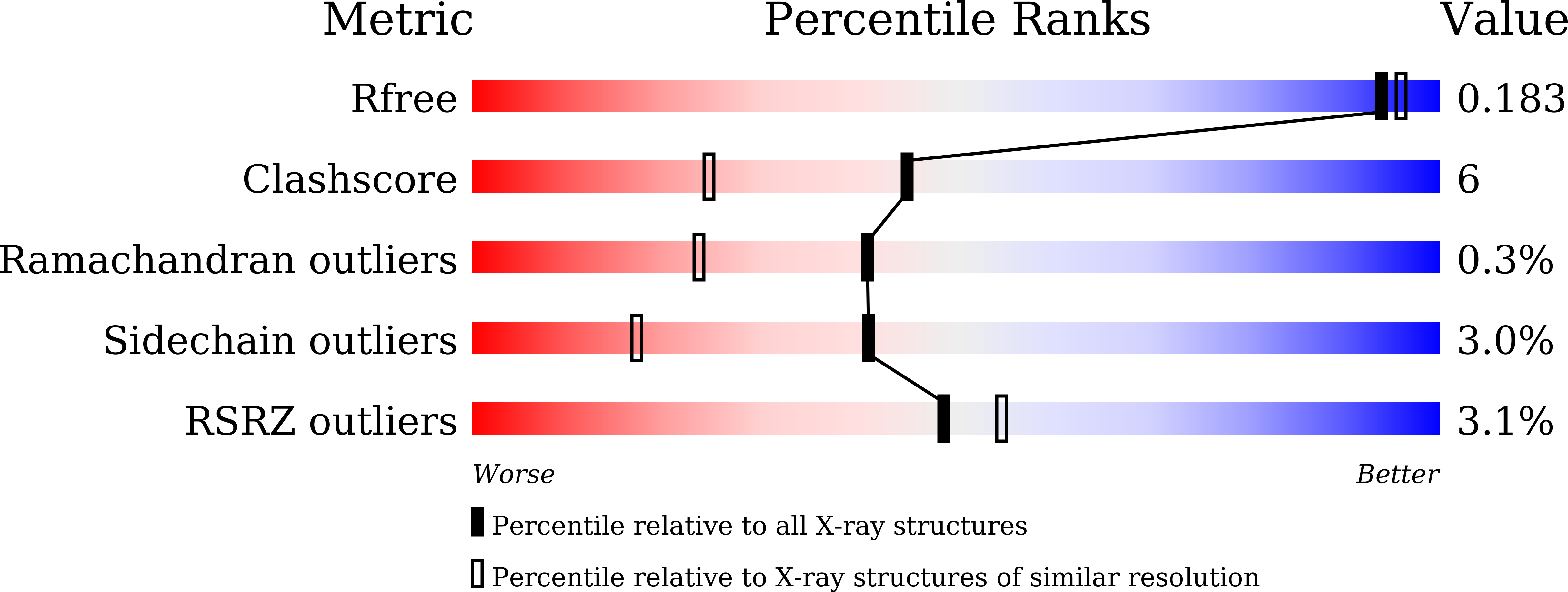
Resolution:
1.74 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.15
R-Value Observed:
0.15
Space Group:
P 21 21 21