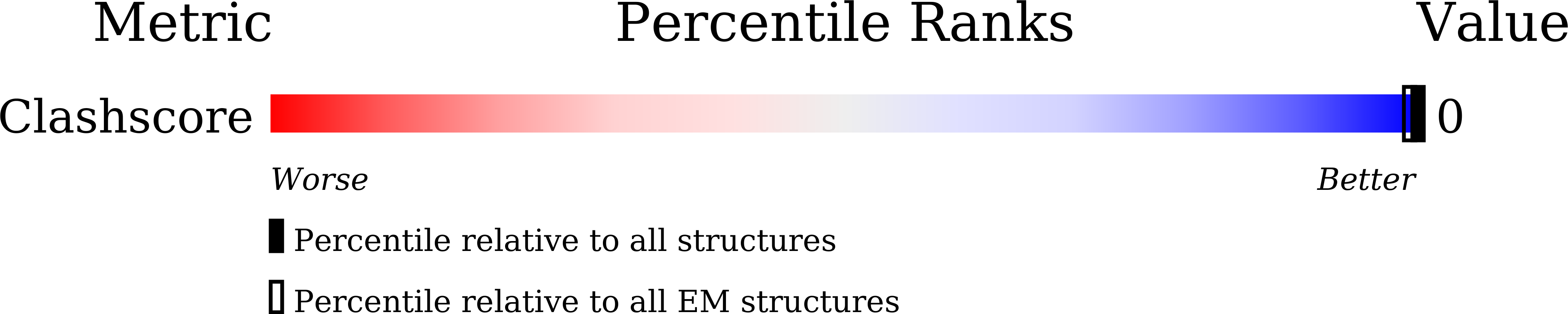Deposition Date
2020-08-27
Release Date
2020-11-04
Last Version Date
2024-03-27
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7CVZ
Keywords:
Title:
Cryo-EM structure of Chikungunya virus in complex with Fab fragments of mAb CHK-263
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Chikungunya virus (Taxon ID: 37124)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.70 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE