Deposition Date
2020-11-26
Release Date
2021-03-03
Last Version Date
2024-01-31
Entry Detail
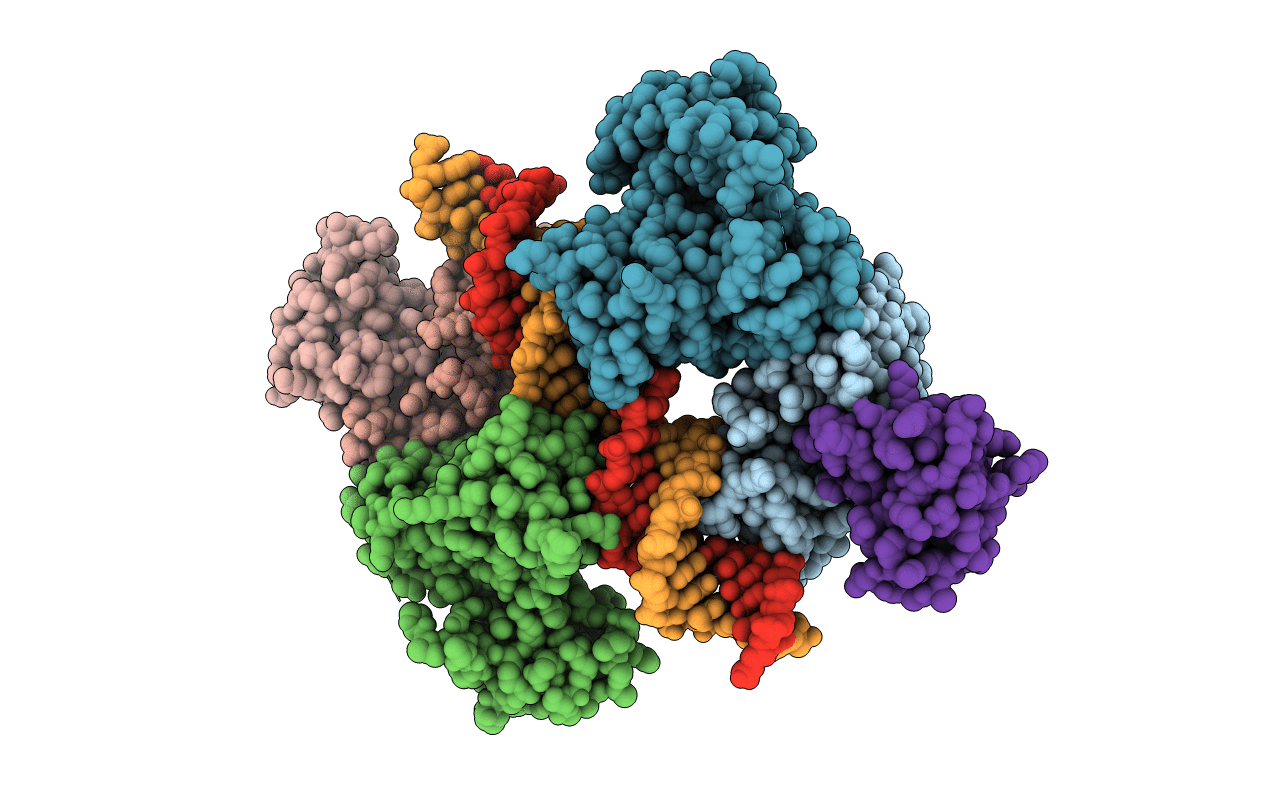
PDB ID:
7B24
Keywords:
Title:
DtxR-like iron-dependent regulator IdeR (P39G variant) complexed with cobalt and its consensus DNA-binding sequence
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.05 Å
R-Value Free:
0.25
R-Value Work:
0.22
R-Value Observed:
0.22
Space Group:
C 1 2 1


