Deposition Date
2020-11-16
Release Date
2021-07-28
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
7AZ4
Keywords:
Title:
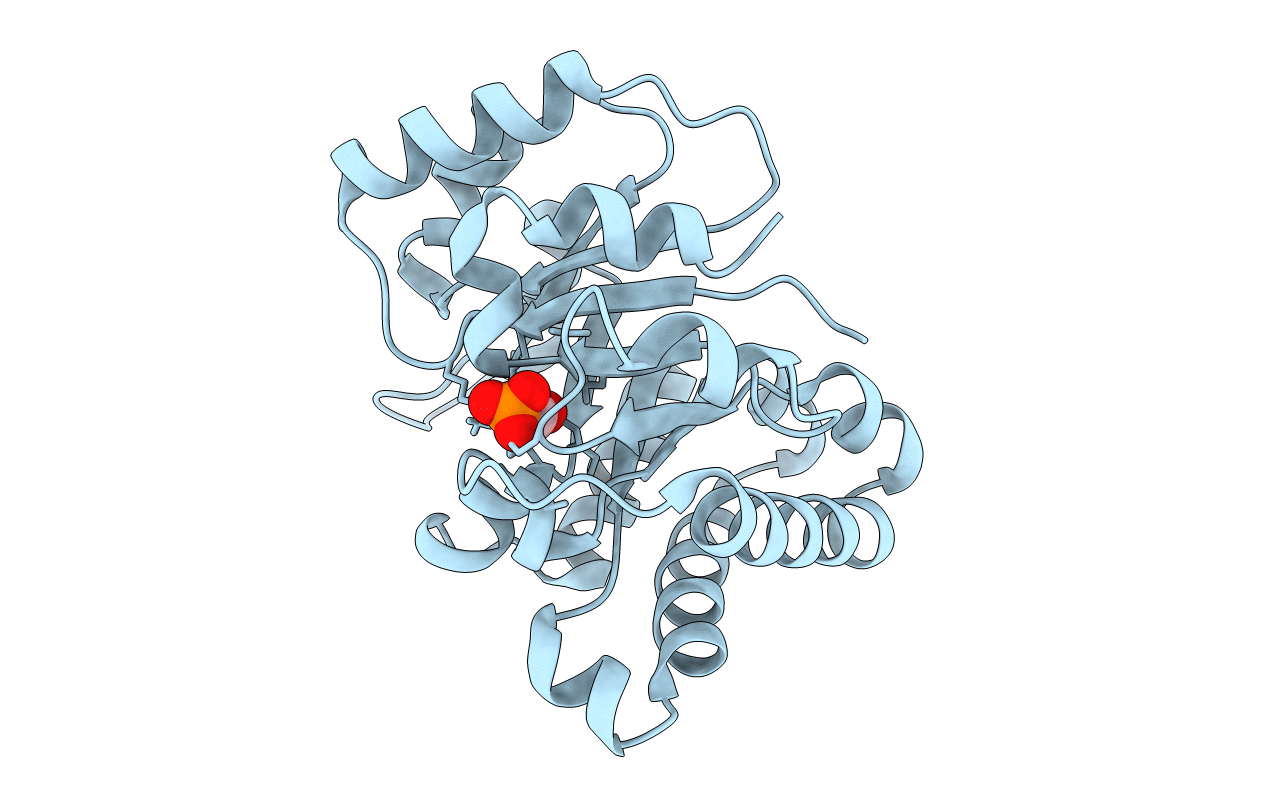
Perdeuterated E65Q-TIM complexed with 2-PHOSPHOGLYCOLIC ACID
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Leishmania mexicana (Taxon ID: 5665)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
R-Value Free:
['0.15
R-Value Work:
['0.14
R-Value Observed:
['0.14
Space Group:
C 1 2 1