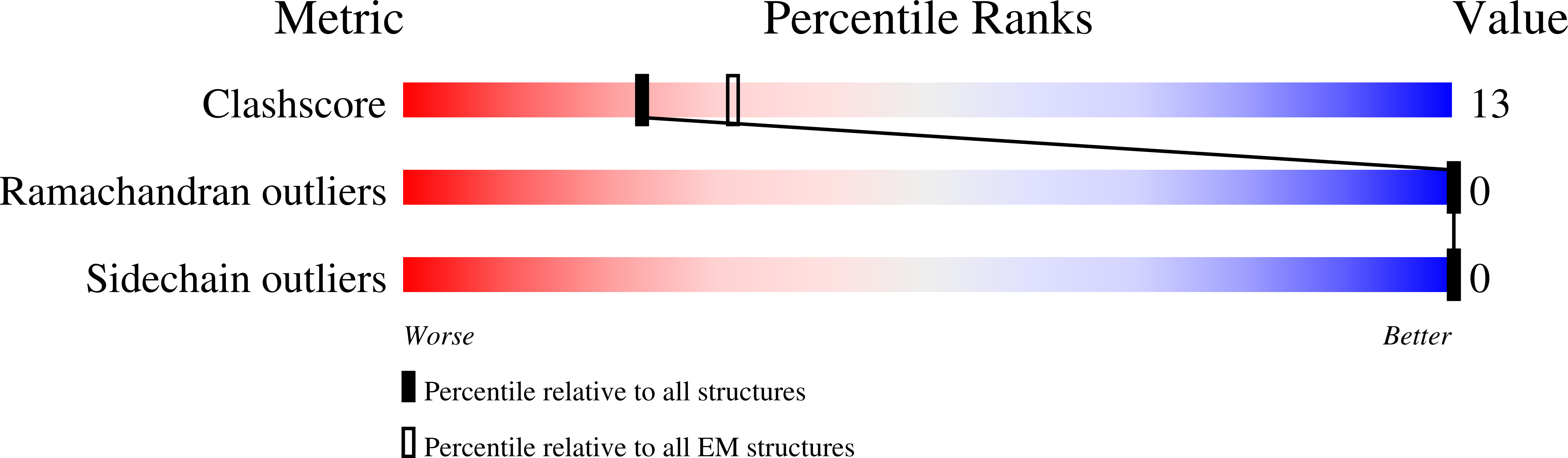
Deposition Date
2020-09-29
Release Date
2021-10-06
Last Version Date
2024-07-10
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
4.00 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE