Deposition Date
2020-08-06
Release Date
2021-06-23
Last Version Date
2024-01-17
Entry Detail
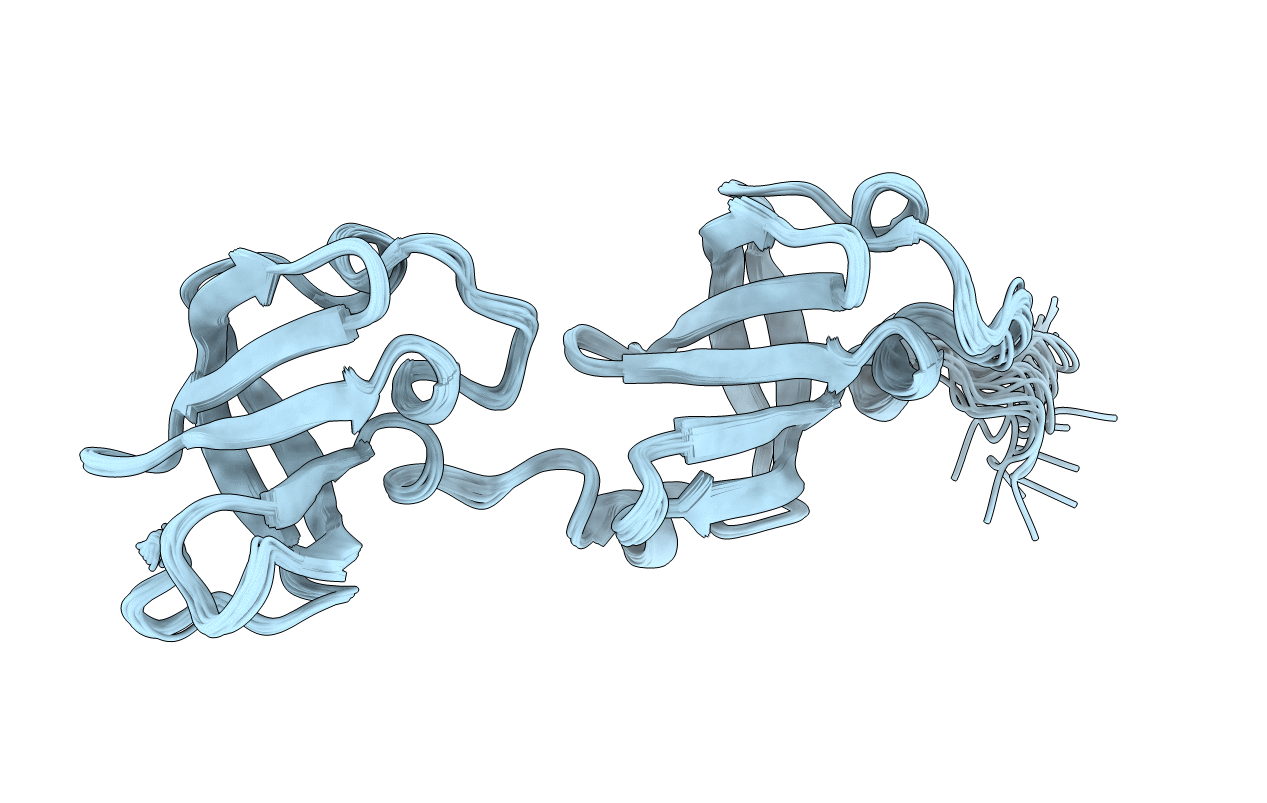
PDB ID:
7A05
Keywords:
Title:
NMR structure of D3-D4 domains of Vibrio vulnificus ribosomal protein S1
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Vibrio vulnificus (Taxon ID: 672)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
target function


