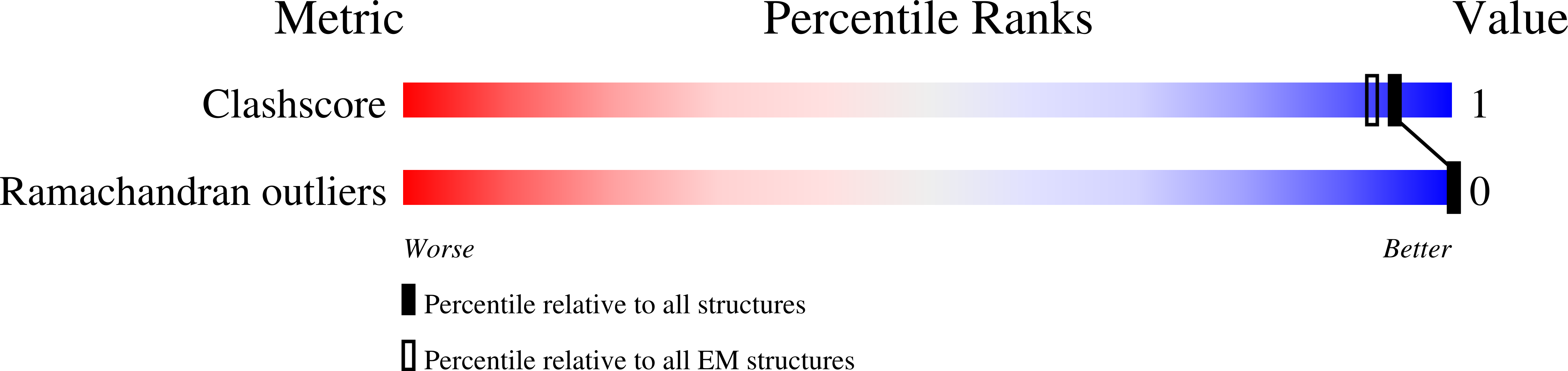
Deposition Date
2020-07-27
Release Date
2021-08-04
Last Version Date
2024-07-10
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6ZW4
Keywords:
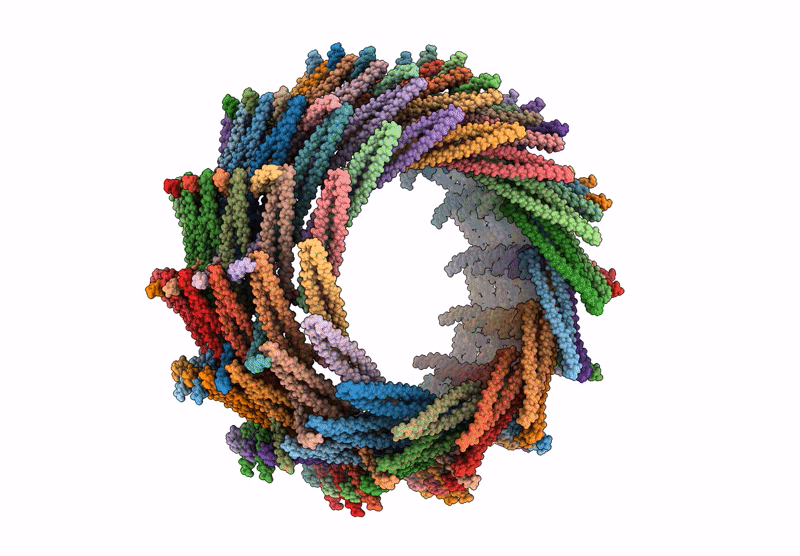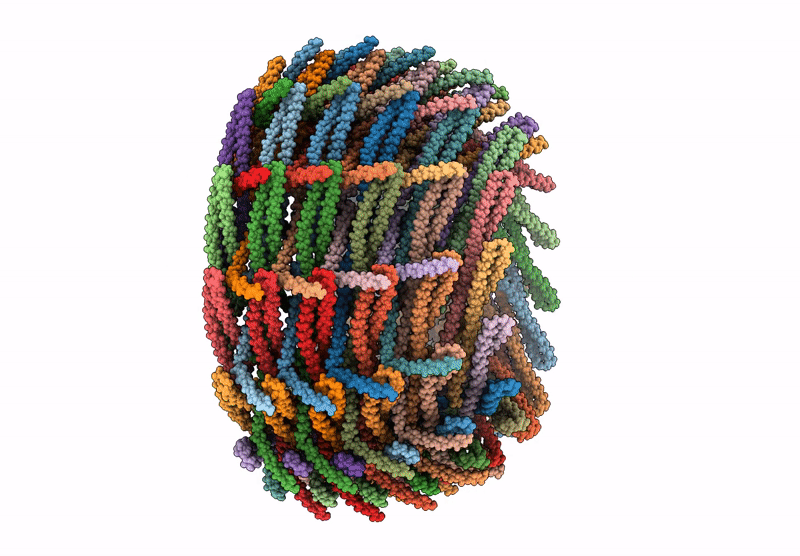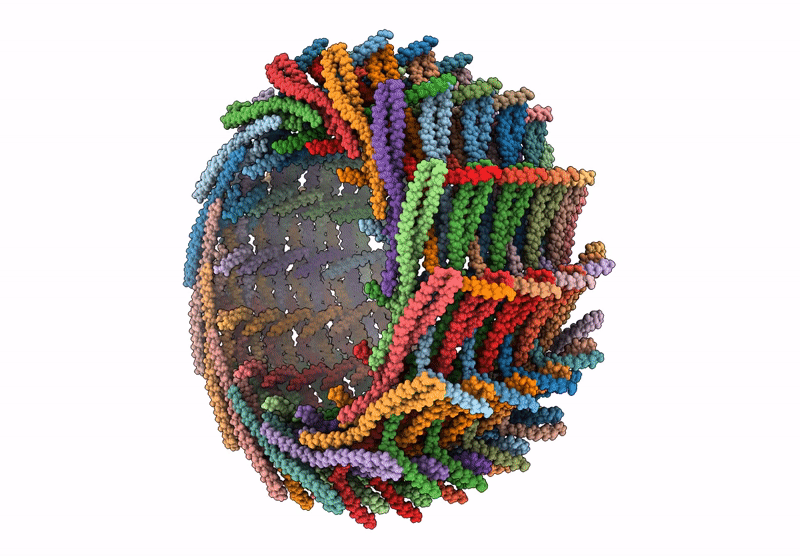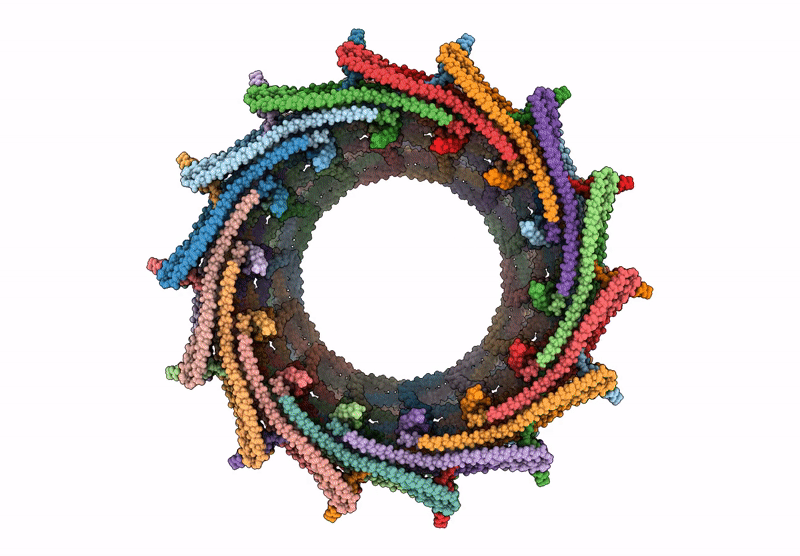
Title:
C14 symmetry: Bacterial Vipp1 and PspA are members of the ancient ESCRT-III membrane-remodeling superfamily.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Nostoc punctiforme (Taxon ID: 272131)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
6.50 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE