Deposition Date
2020-06-18
Release Date
2021-03-03
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6ZG3
Keywords:
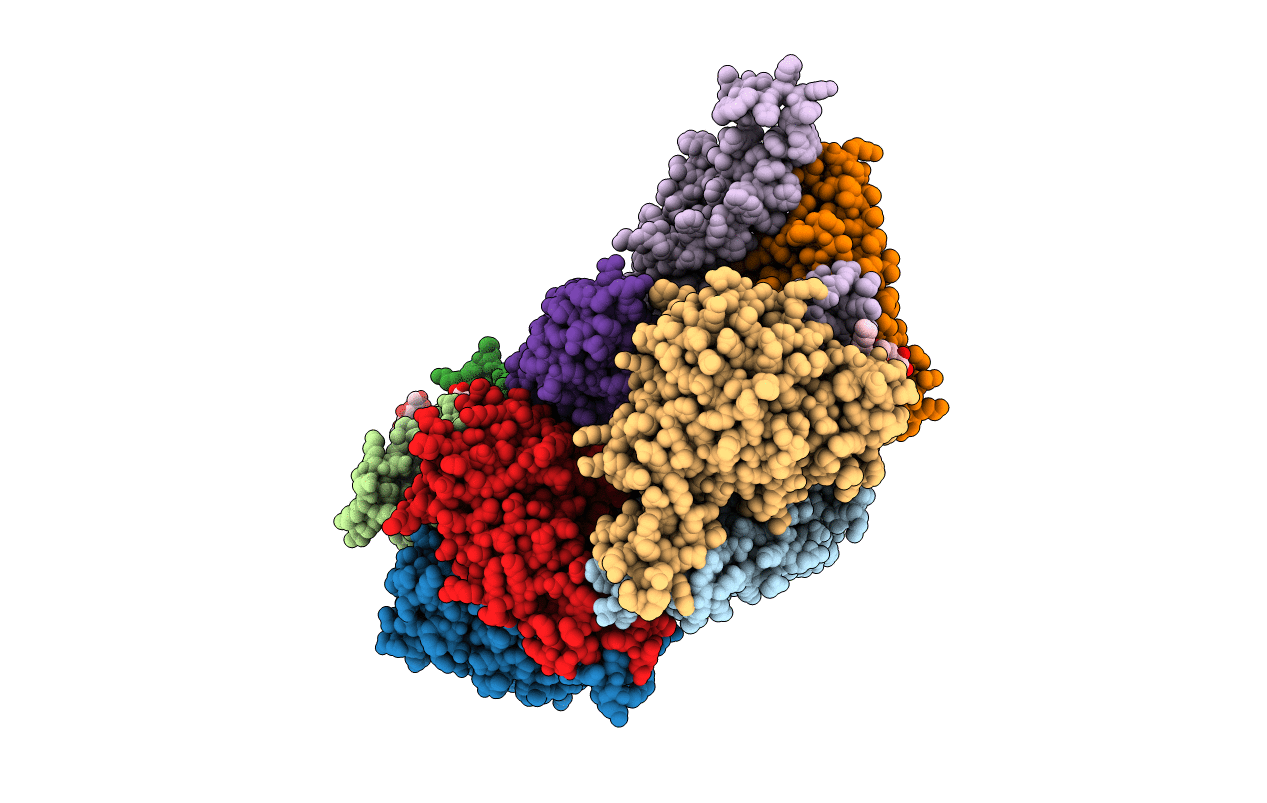
Title:
the structure of ECF PanT transporter in a complex with a nanobody
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus ATCC 11842 = JCM 1002 (Taxon ID: 390333)
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Lama glama (Taxon ID: 9844)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
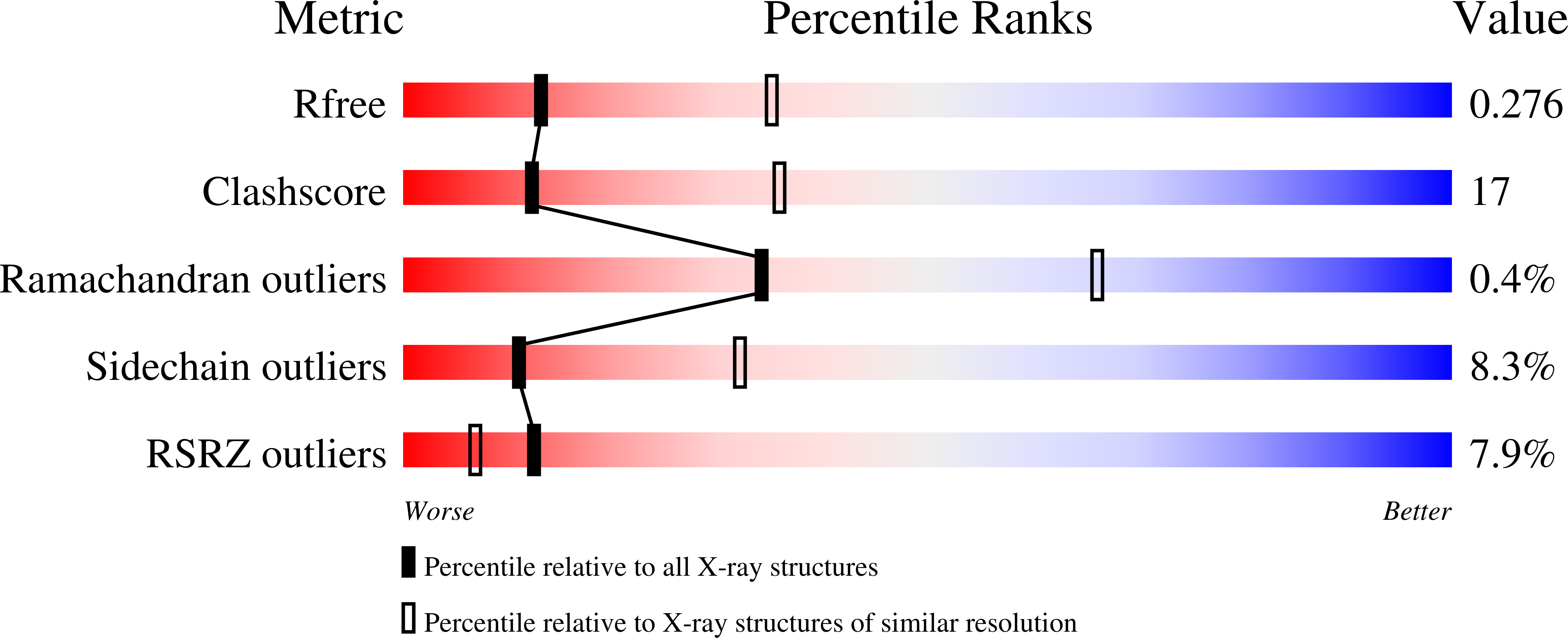
Resolution:
2.80 Å
R-Value Free:
0.27
R-Value Work:
0.24
R-Value Observed:
0.24
Space Group:
P 1