Deposition Date
2020-06-04
Release Date
2020-07-15
Last Version Date
2024-01-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6ZA5
Keywords:
Title:
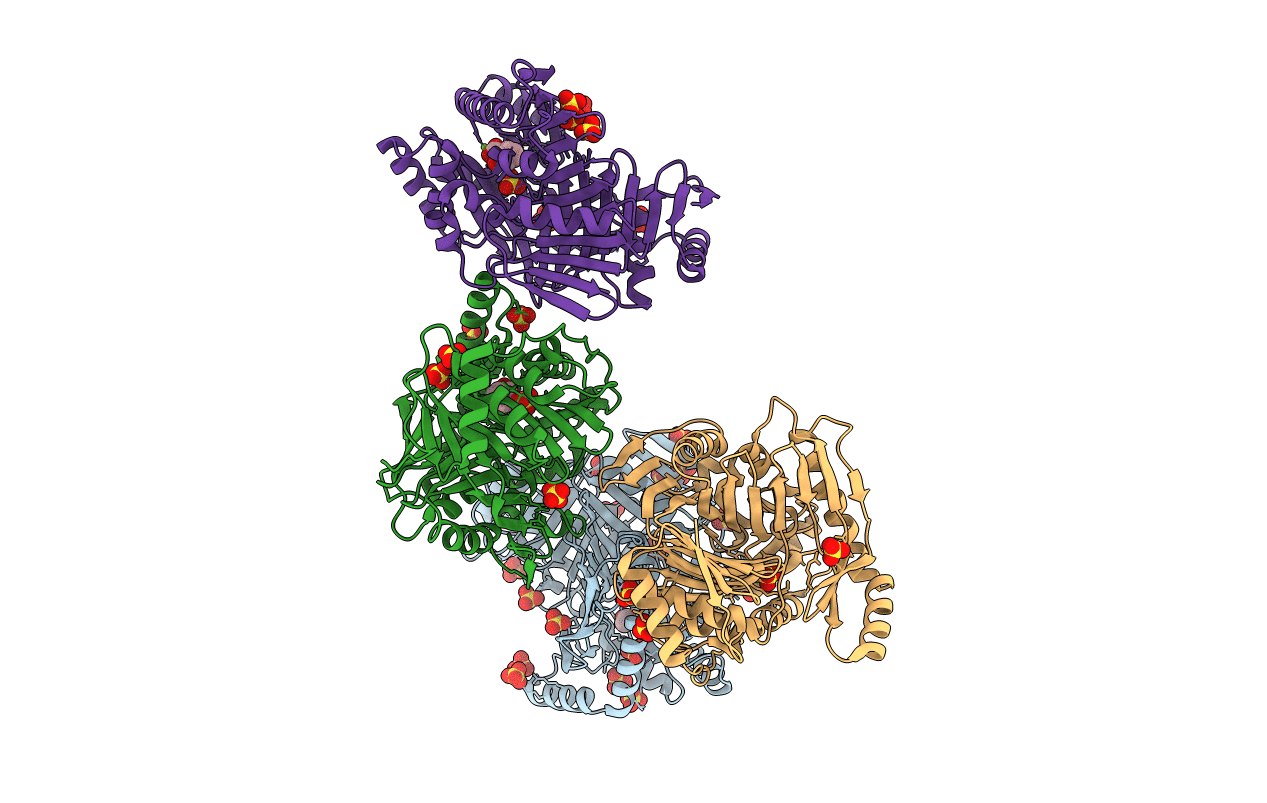
M. tuberculosis salicylate synthase MbtI in complex with salicylate and Mg2+
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
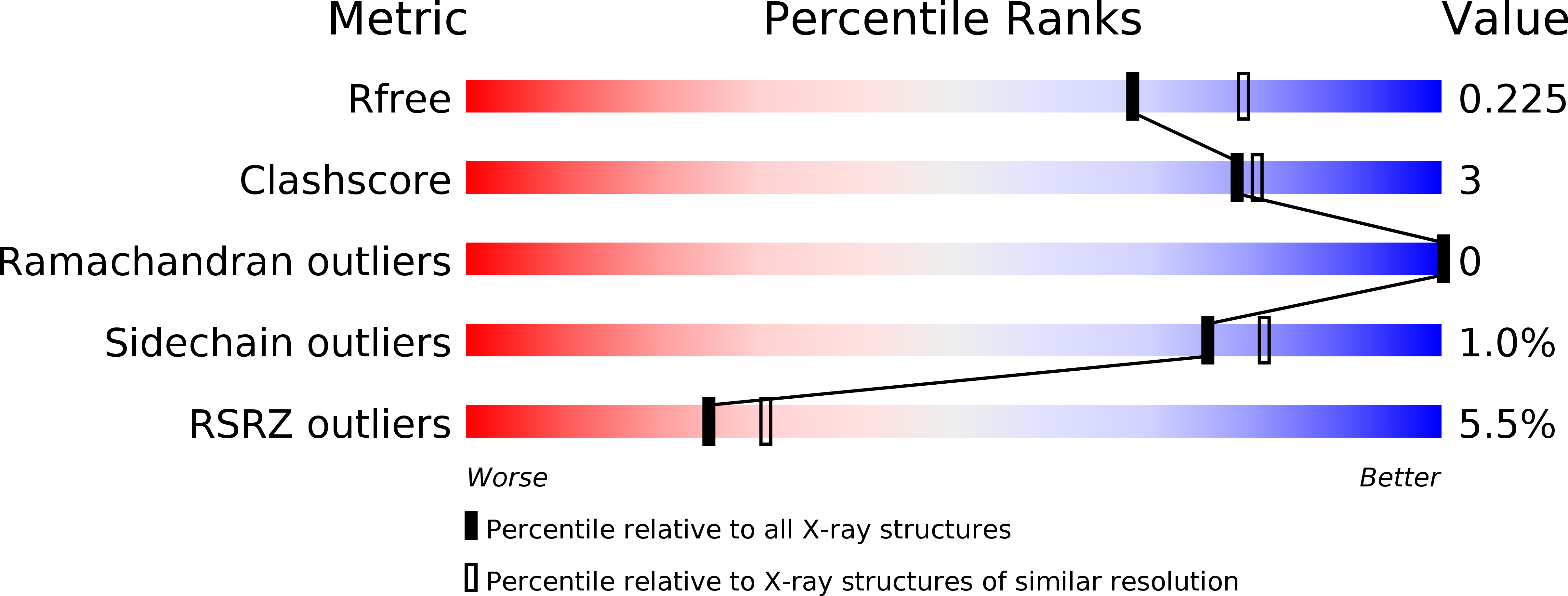
Resolution:
2.11 Å
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
I 4 2 2