Deposition Date
2020-06-02
Release Date
2020-09-09
Last Version Date
2025-12-17
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6Z8M
Keywords:
Title:
Structure of [NiFeSe] hydrogenase G491S variant from Desulfovibrio vulgaris Hildenborough pressurized with Oxygen gas - structure G491S-O2
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
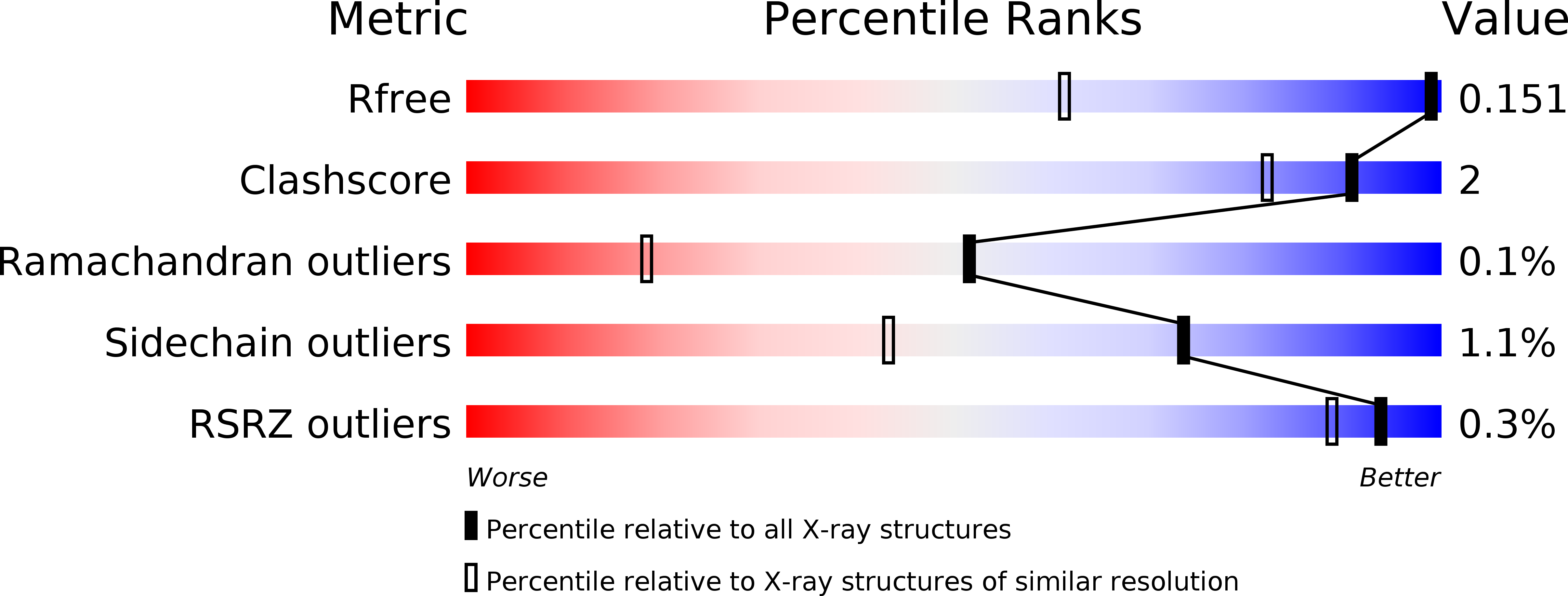
Resolution:
1.02 Å
R-Value Free:
0.15
R-Value Work:
0.13
R-Value Observed:
0.13
Space Group:
C 1 2 1