Deposition Date
2020-05-13
Release Date
2021-08-25
Last Version Date
2024-01-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6Z1K
Keywords:
Title:
A de novo Enzyme for the Morita-Baylis-Hillman Reaction BH32.6
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
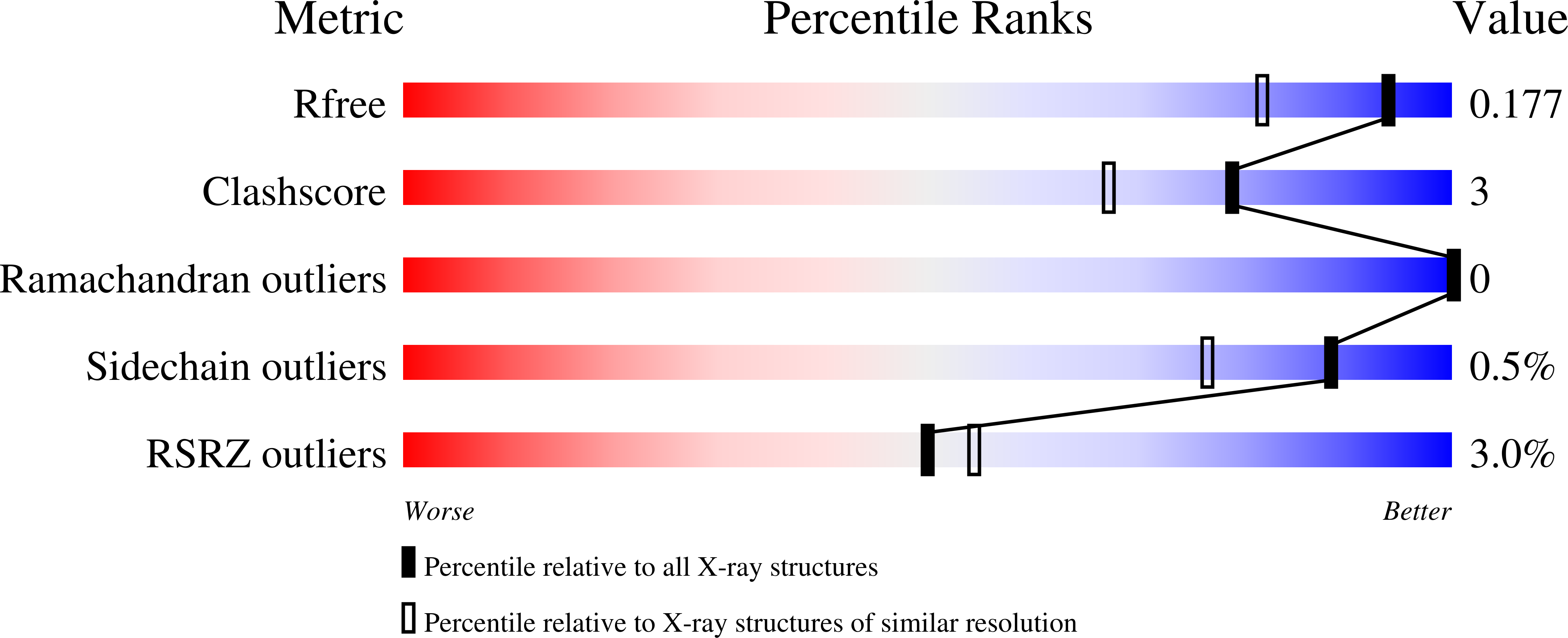
Resolution:
1.48 Å
R-Value Free:
0.17
R-Value Work:
0.15
R-Value Observed:
0.15
Space Group:
P 31 2 1