Deposition Date
2020-05-13
Release Date
2020-09-23
Last Version Date
2025-04-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6Z1F
Keywords:
Title:
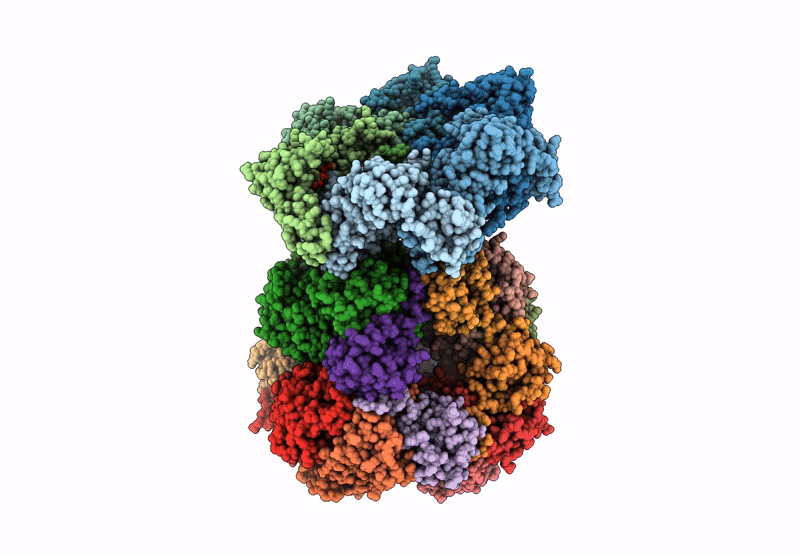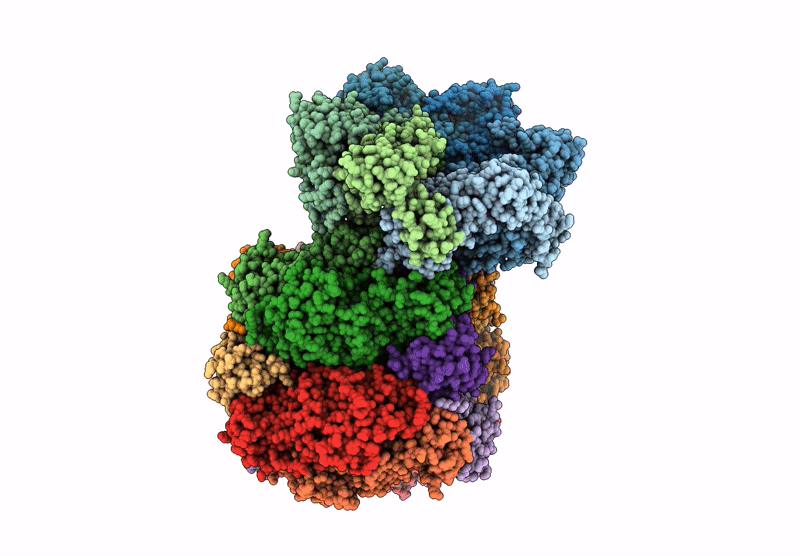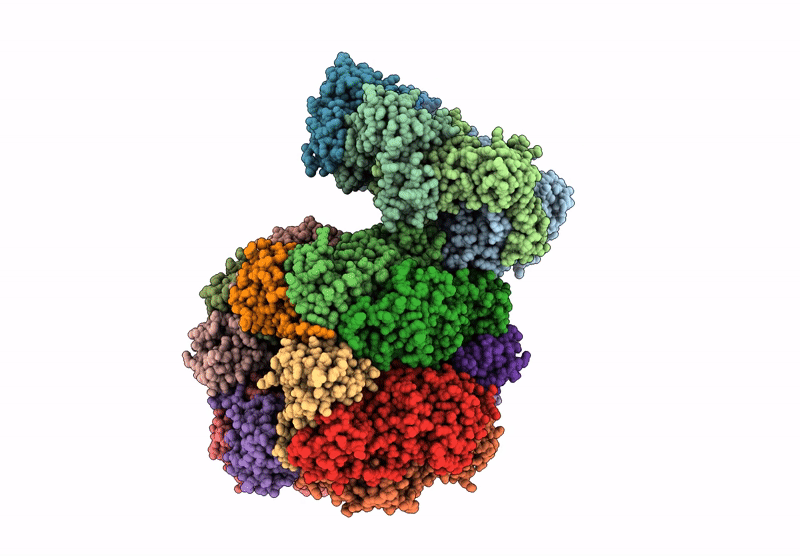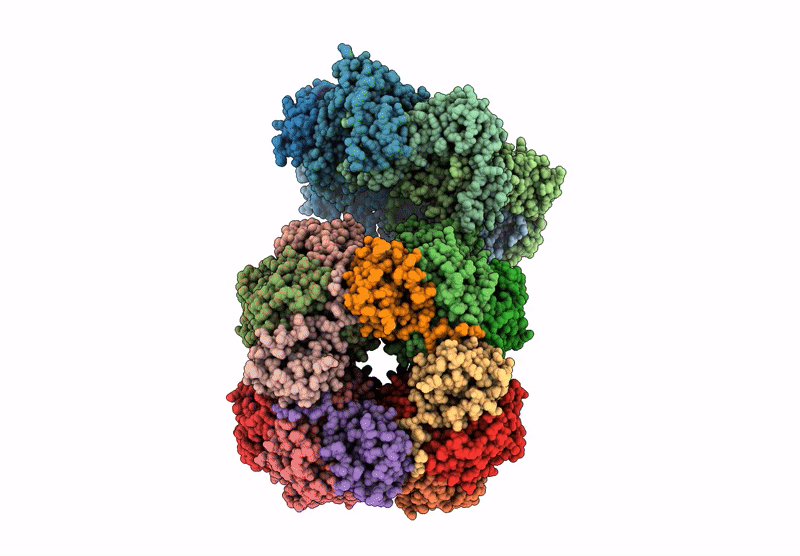
CryoEM structure of Rubisco Activase with its substrate Rubisco from Nostoc sp. (strain PCC7120)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.86 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


