Deposition Date
2020-04-16
Release Date
2020-09-16
Last Version Date
2024-01-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6YQ6
Keywords:
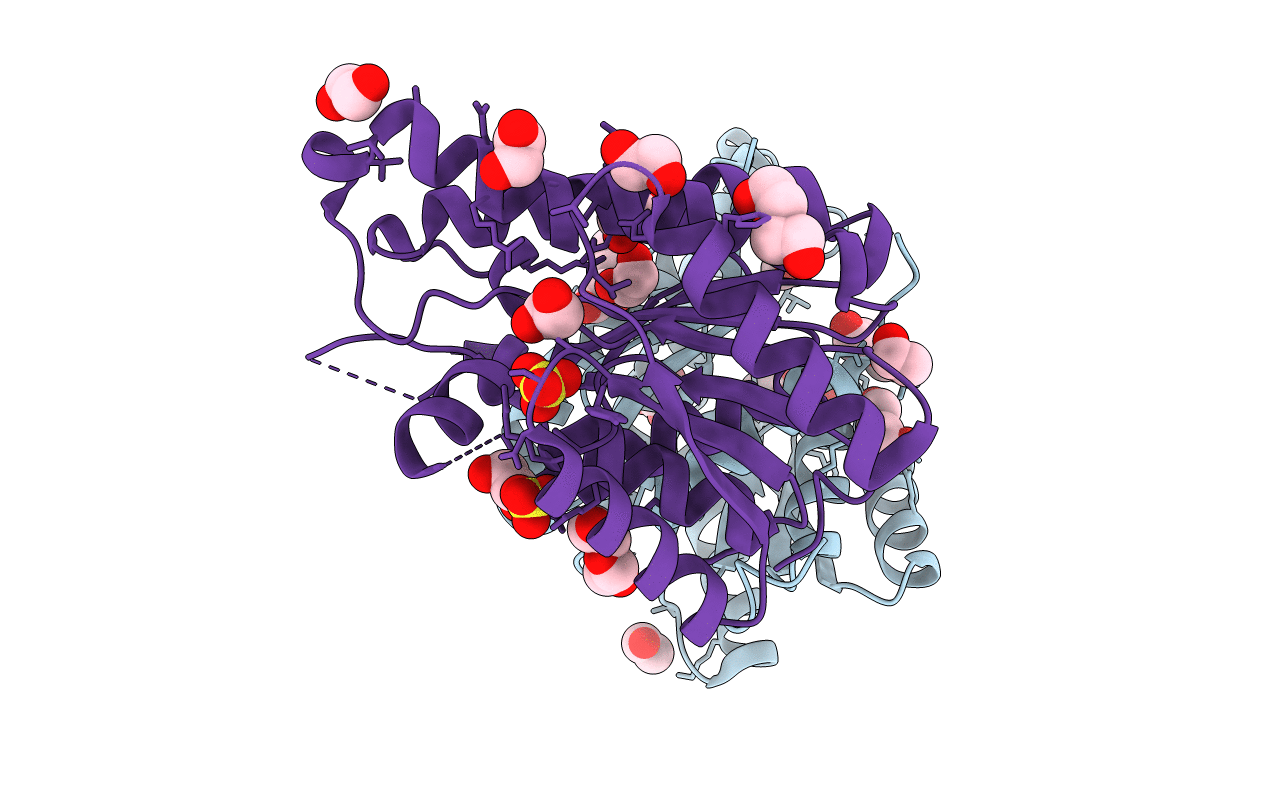
Title:
Promiscuous Reductase LugOII Catalyzes Keto-reduction at C1 during Lugdunomycin Biosynthesis
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Streptomyces sp. QL37 (Taxon ID: 2093747)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
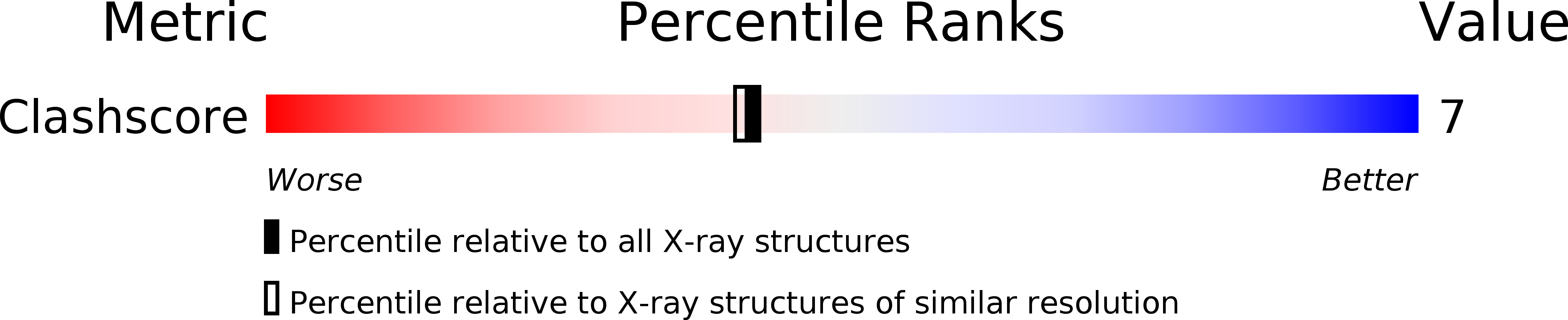
Resolution:
2.08 Å
R-Value Free:
0.20
R-Value Work:
0.16
Space Group:
P 61 2 2