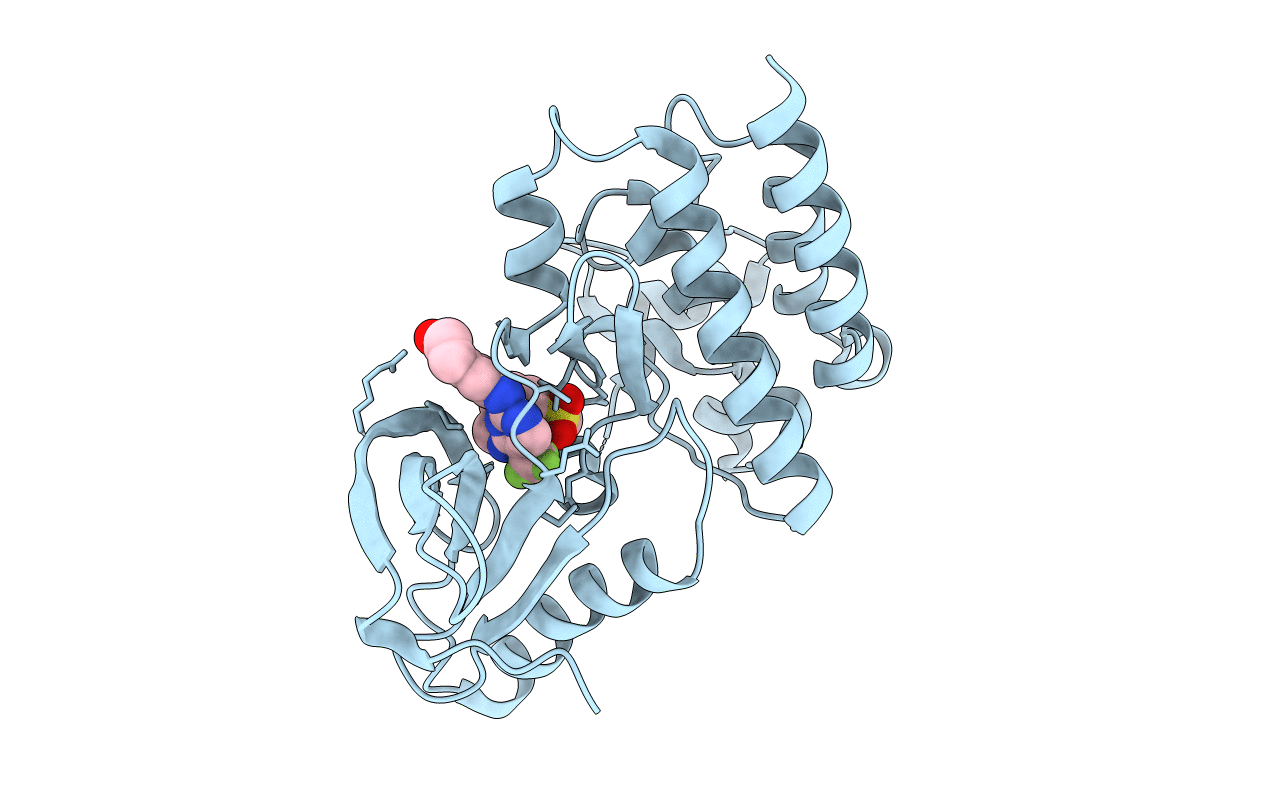
Deposition Date
2020-04-14
Release Date
2021-02-10
Last Version Date
2024-11-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6YOJ
Keywords:
Title:
FOCAL ADHESION KINASE CATALYTIC DOMAIN IN COMPLEX WITH 6-[4-(3-Methanesulfonyl-benzylamino)-5-trifluoromethyl-pyrimidin-2-ylamino]-3,4-dihydro-1H-quinolin-2-one
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
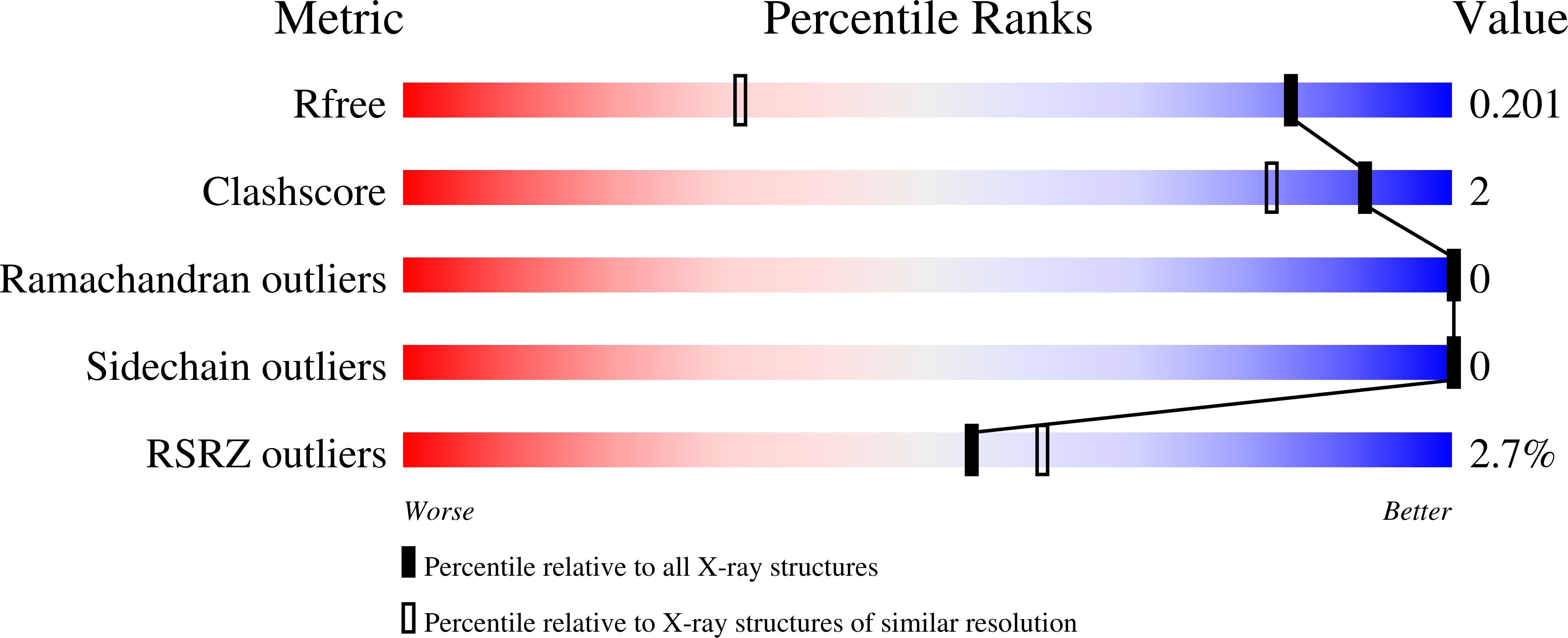
Resolution:
1.36 Å
R-Value Free:
0.19
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 21