Deposition Date
2020-03-26
Release Date
2020-06-10
Last Version Date
2024-08-07
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6YFY
Keywords:
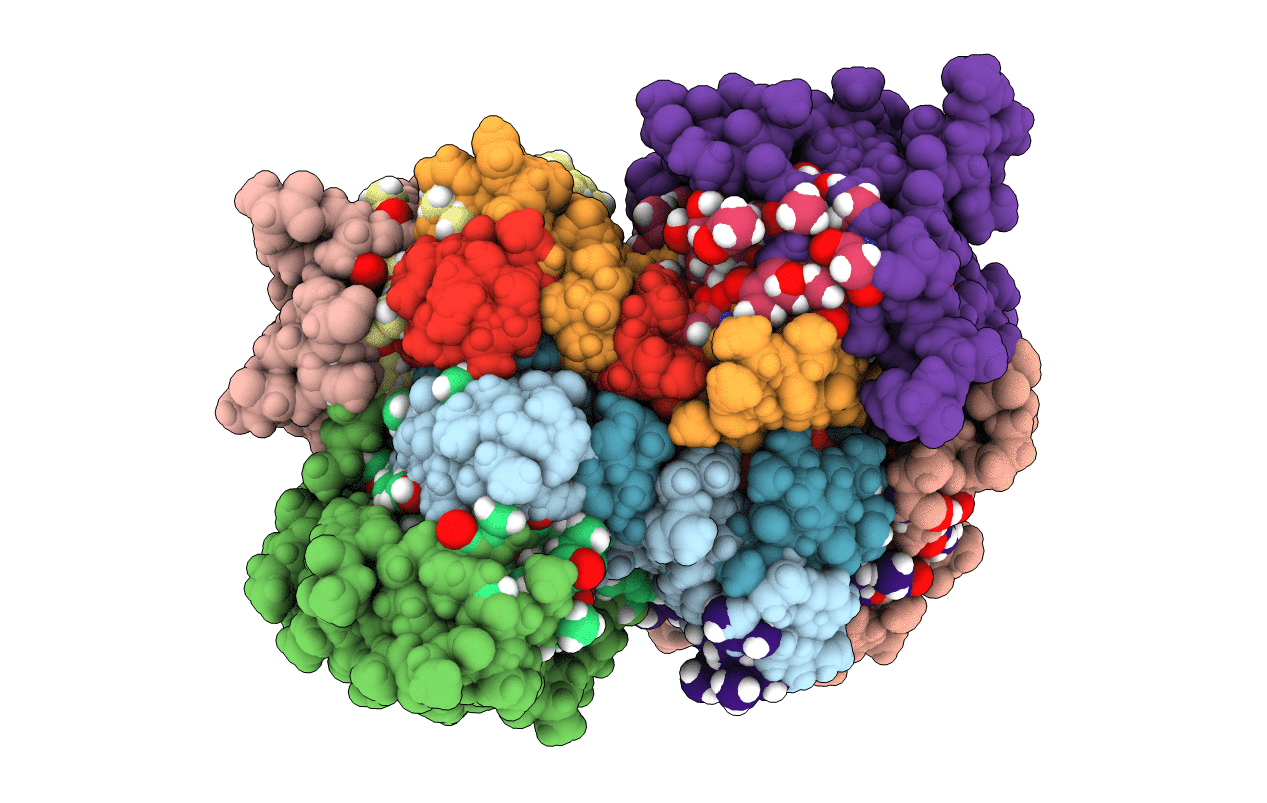
Title:
Solid-state NMR structure of the D-Arg4,L10-teixobactin - Lipid II complex in lipid bilayers.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Eleftheria terrae (Taxon ID: 1597781)
Staphylococcus simulans (Taxon ID: 1286)
Staphylococcus simulans (Taxon ID: 1286)
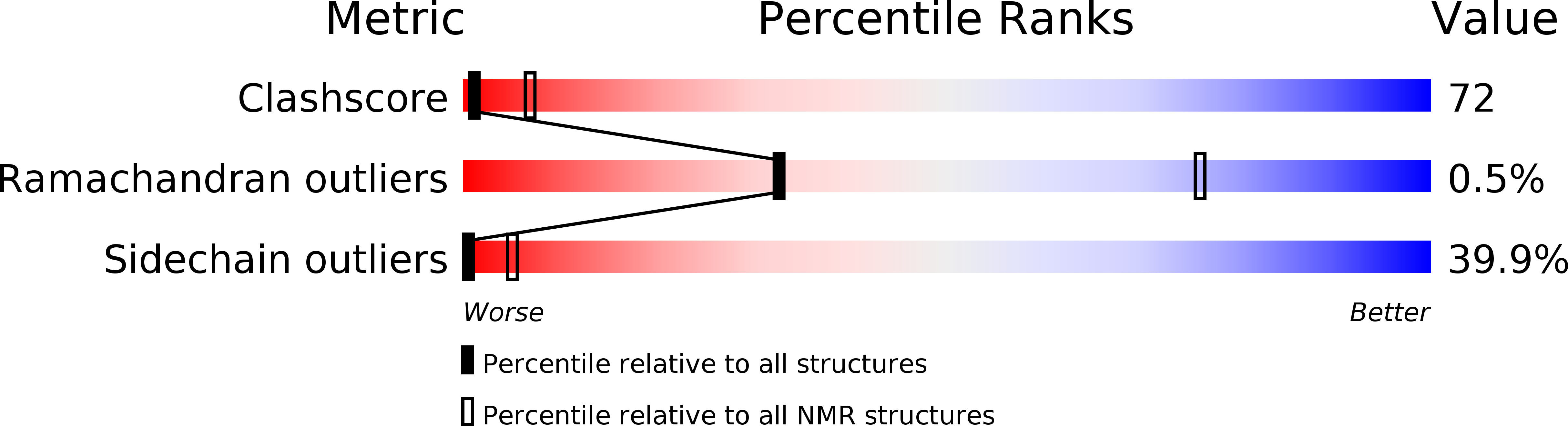
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
26
Conformers Submitted:
26
Selection Criteria:
all calculated structures submitted