Deposition Date
2020-03-17
Release Date
2020-08-12
Last Version Date
2024-01-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6YBR
Keywords:
Title:
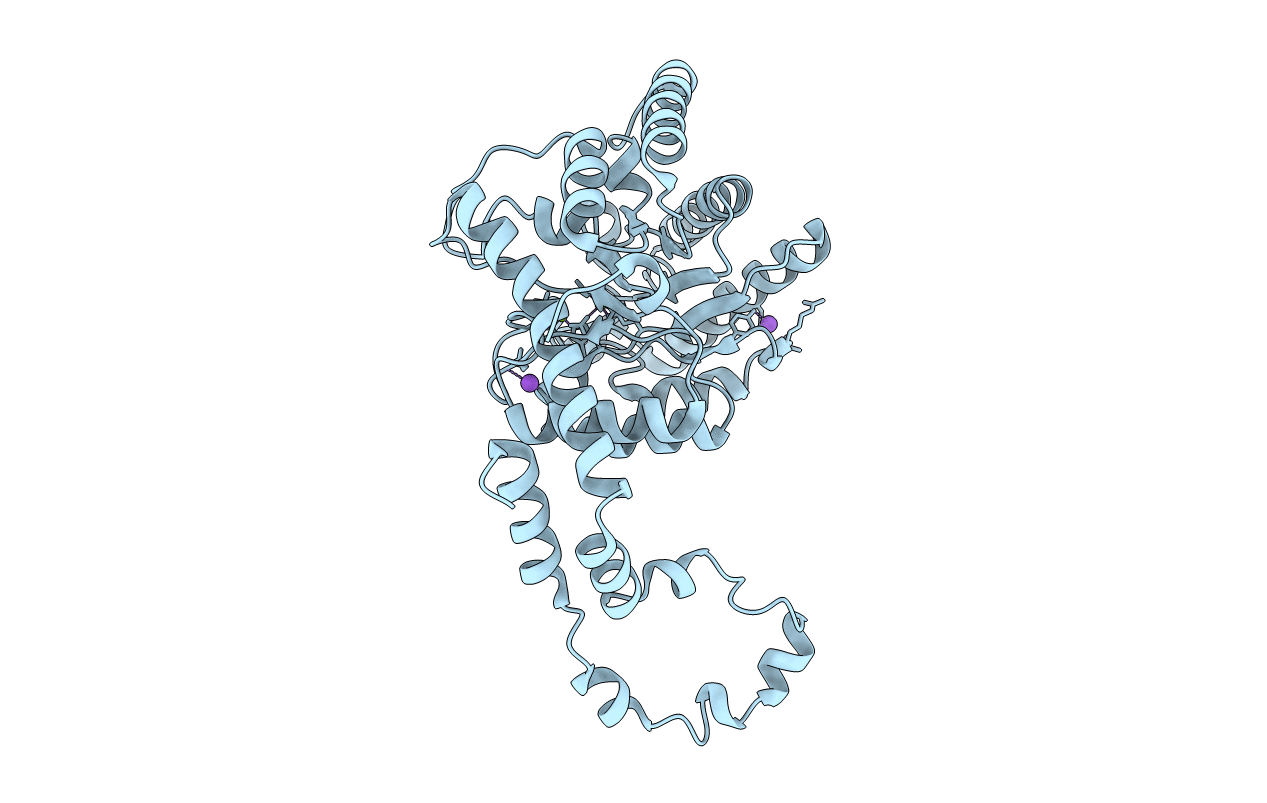
RT structure of Glucose Isomerase obtained at 1.20 A resolution from crystal grown in a Mylar microchip.
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Streptomyces rubiginosus (Taxon ID: 1929)
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.20 Å
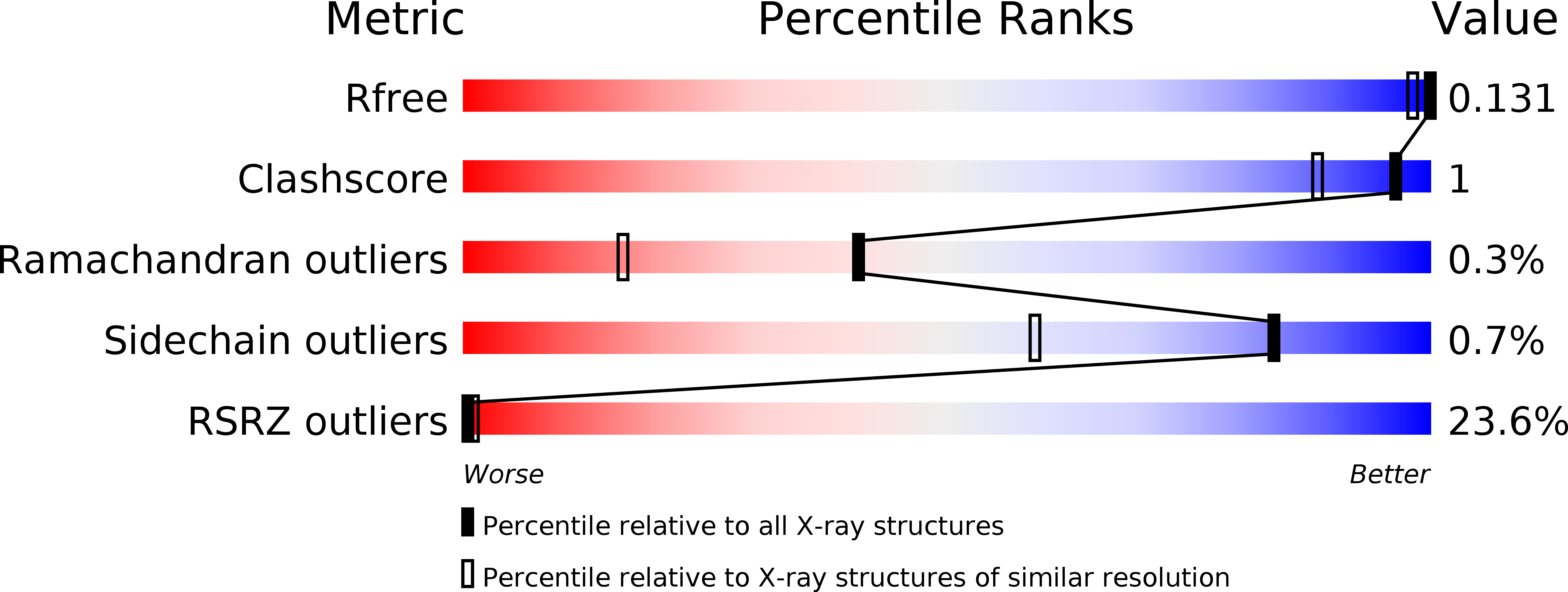
R-Value Free:
0.13
R-Value Work:
0.12
R-Value Observed:
0.12
Space Group:
I 2 2 2