Deposition Date
2020-07-02
Release Date
2022-01-12
Last Version Date
2025-05-14
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6XN3
Keywords:
Title:
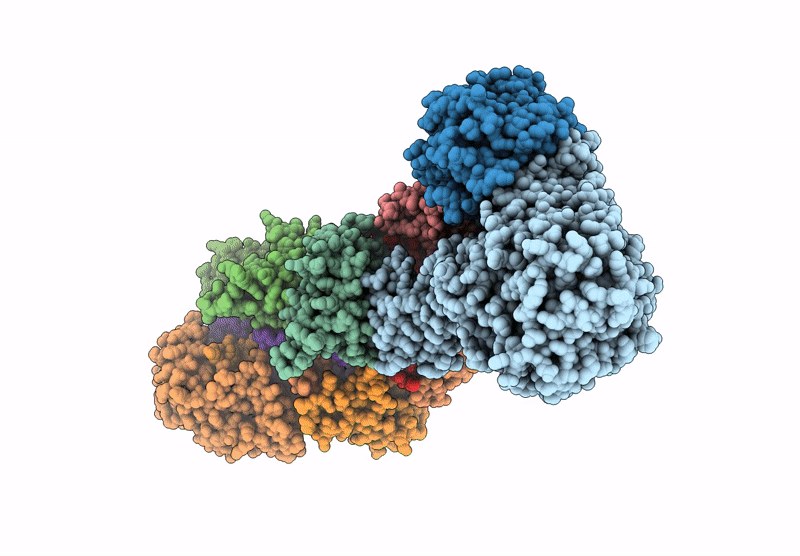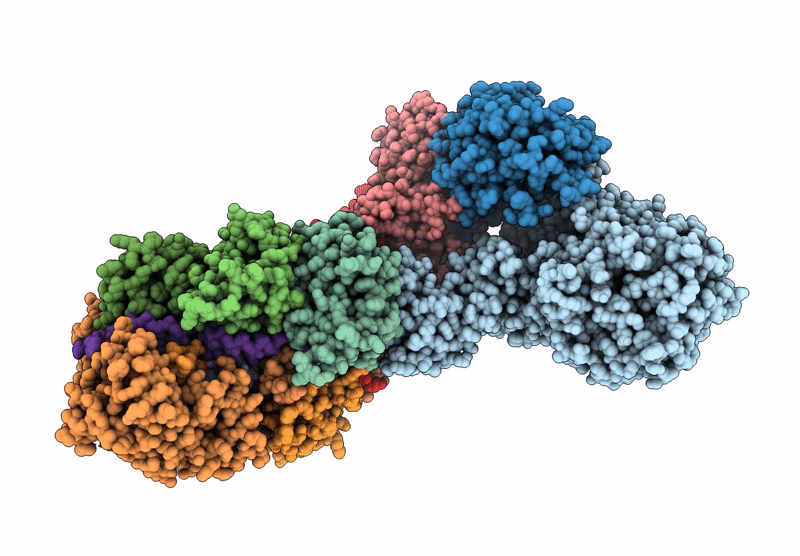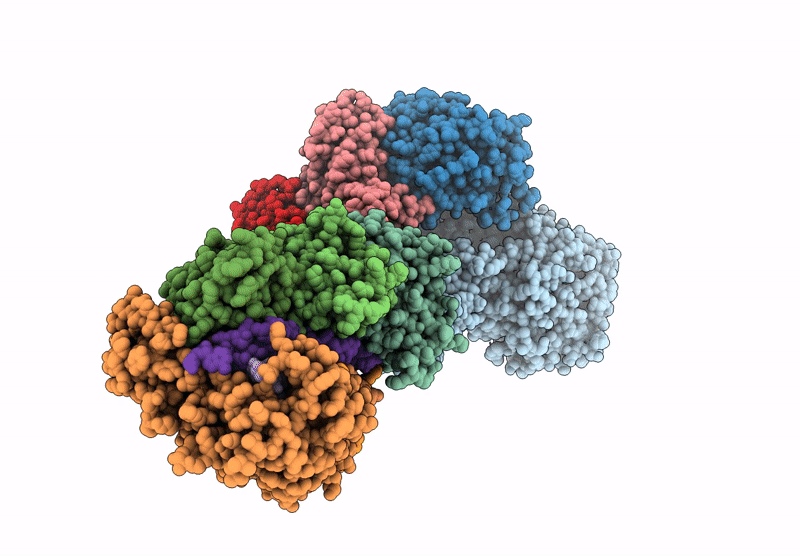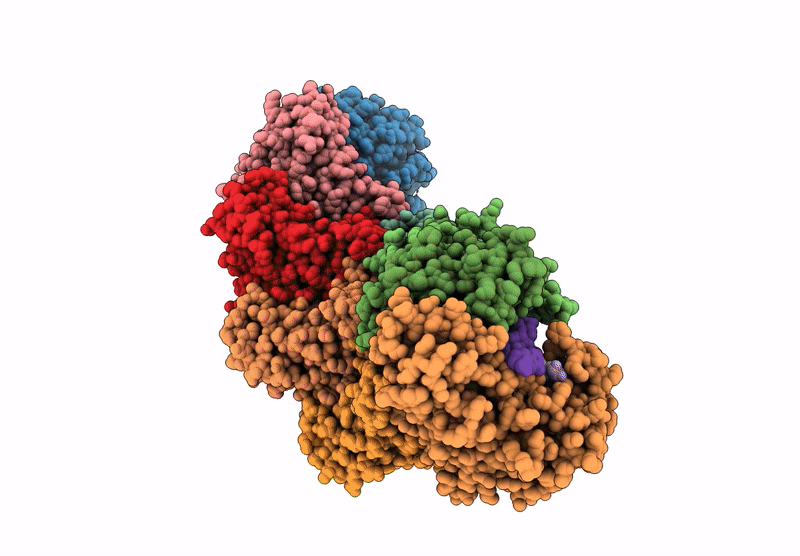
Structure of the Lactococcus lactis Csm CTR_4:3 CRISPR-Cas Complex
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis (Taxon ID: 1360)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.00 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


