Deposition Date
2020-06-28
Release Date
2021-04-07
Last Version Date
2024-03-06
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6XLJ
Keywords:
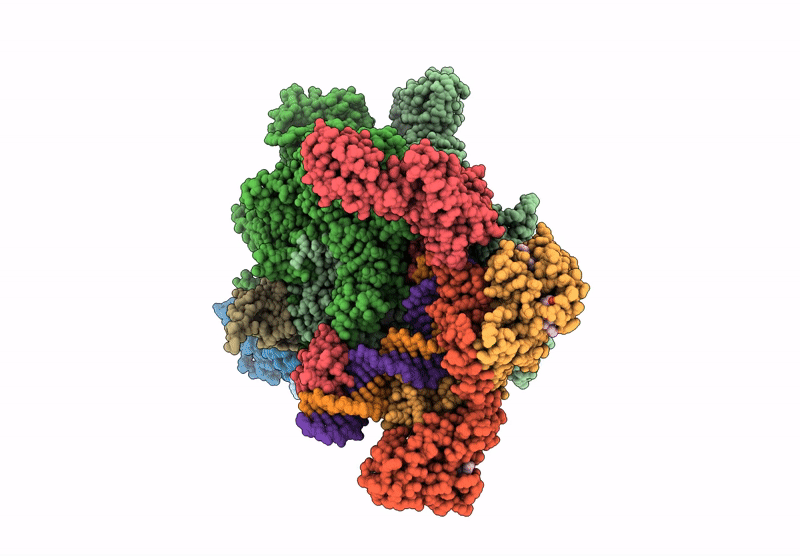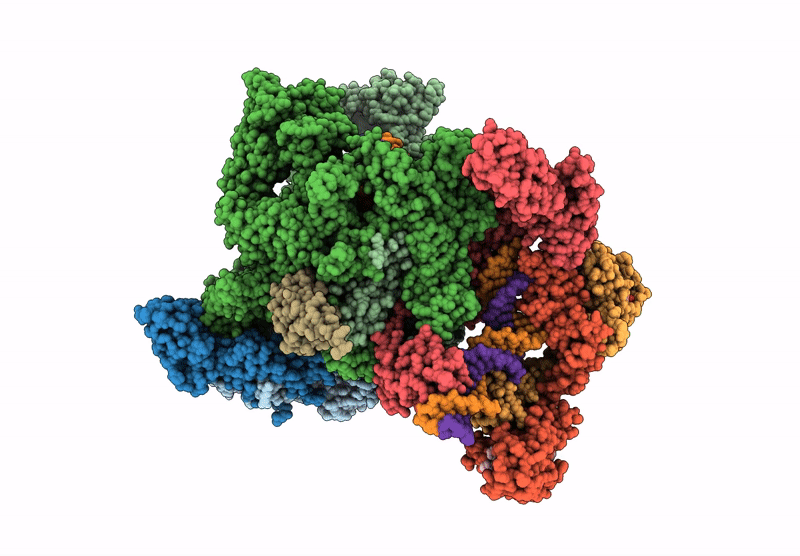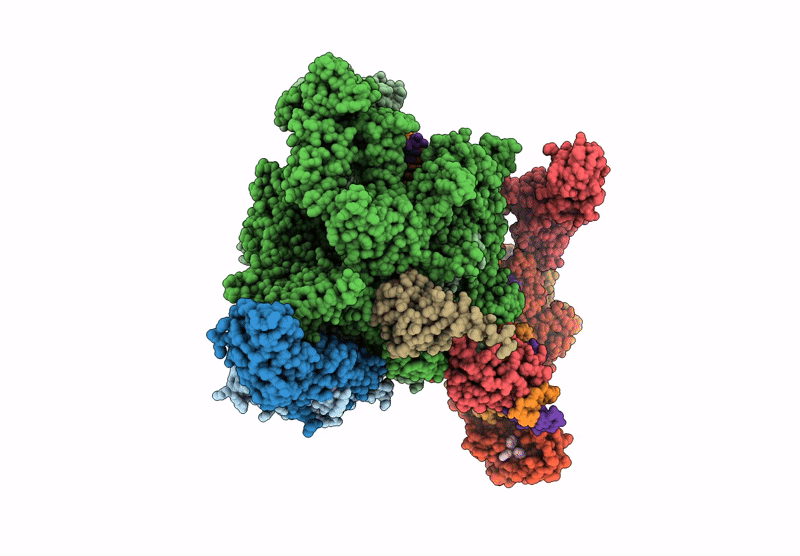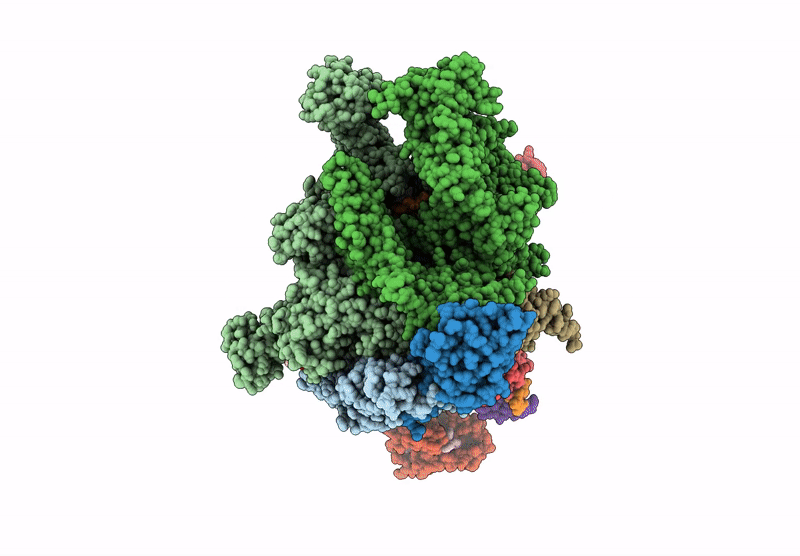
Title:
Cryo-EM structure of EcmrR-RNAP-promoter initial transcribing complex with 4-nt RNA transcript (EcmrR-RPitc-4nt)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Escherichia coli O157:H7 (Taxon ID: 83334)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.70 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


