Deposition Date
2020-06-03
Release Date
2021-06-09
Last Version Date
2023-10-18
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6XA0
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of C-As lyase with mutation K105R with Ni(II)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
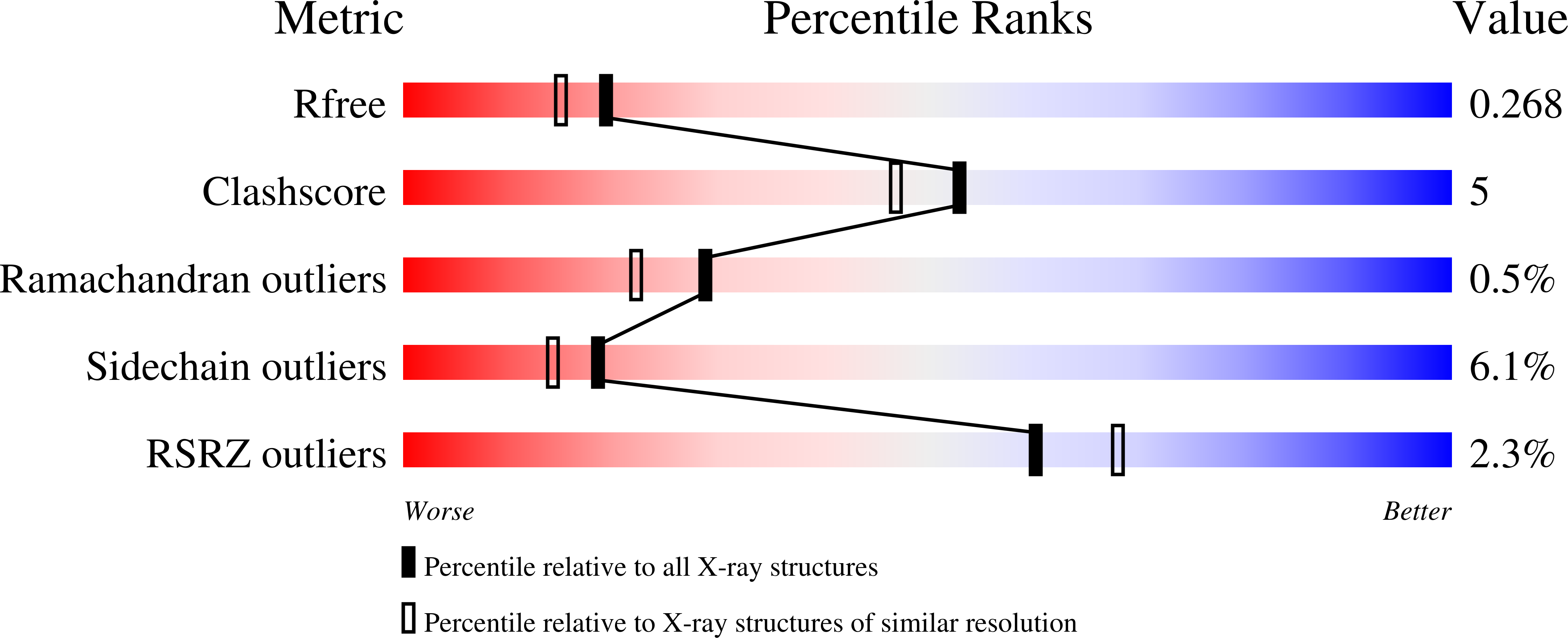
Resolution:
2.15 Å
R-Value Free:
0.26
R-Value Work:
0.19
R-Value Observed:
0.19
Space Group:
P 21 21 21