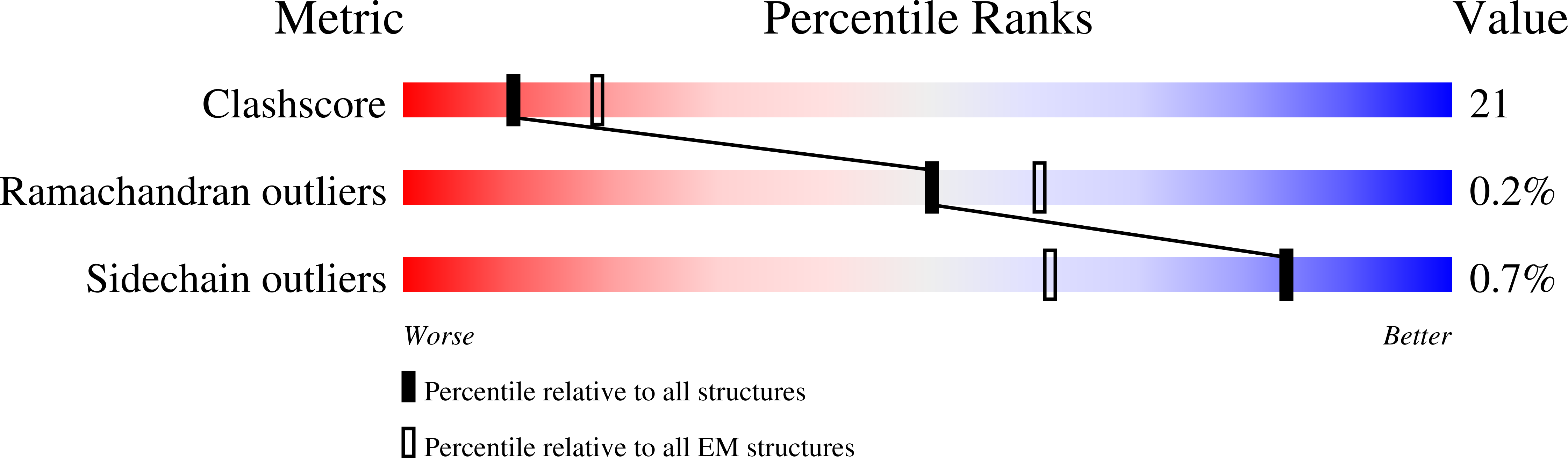
Deposition Date
2020-04-28
Release Date
2021-06-09
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6WQH
Keywords:
Title:
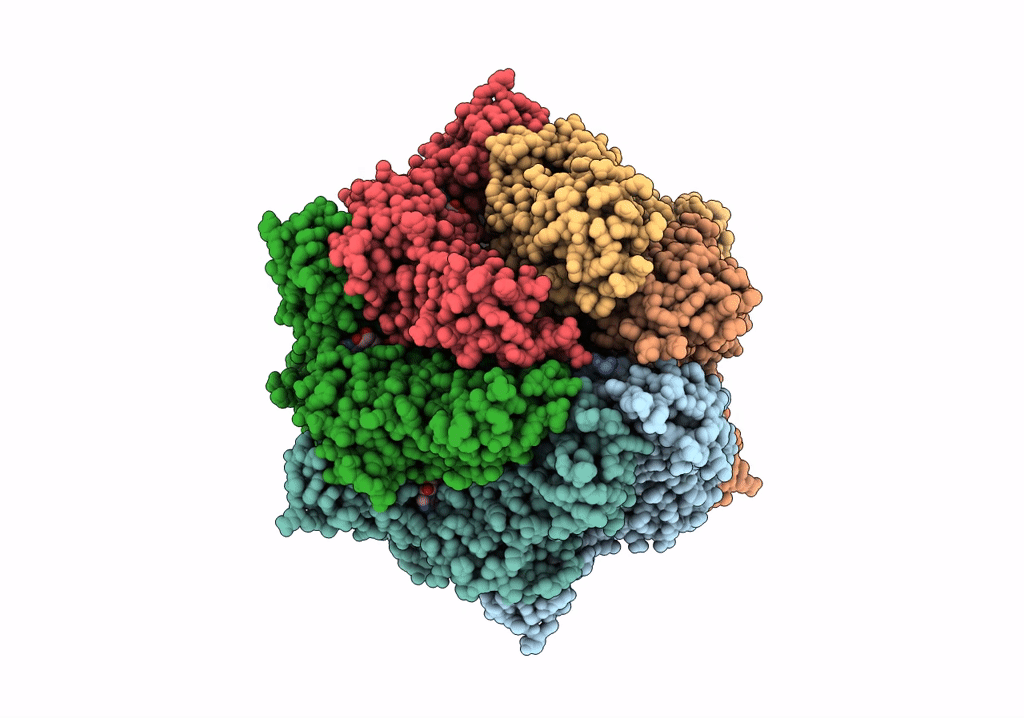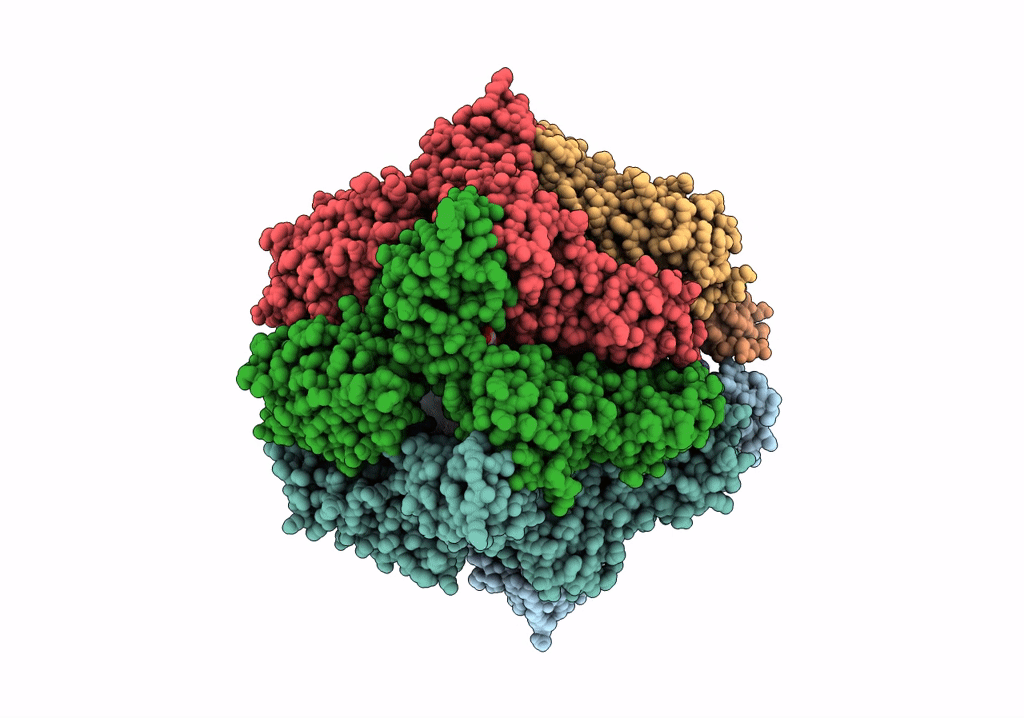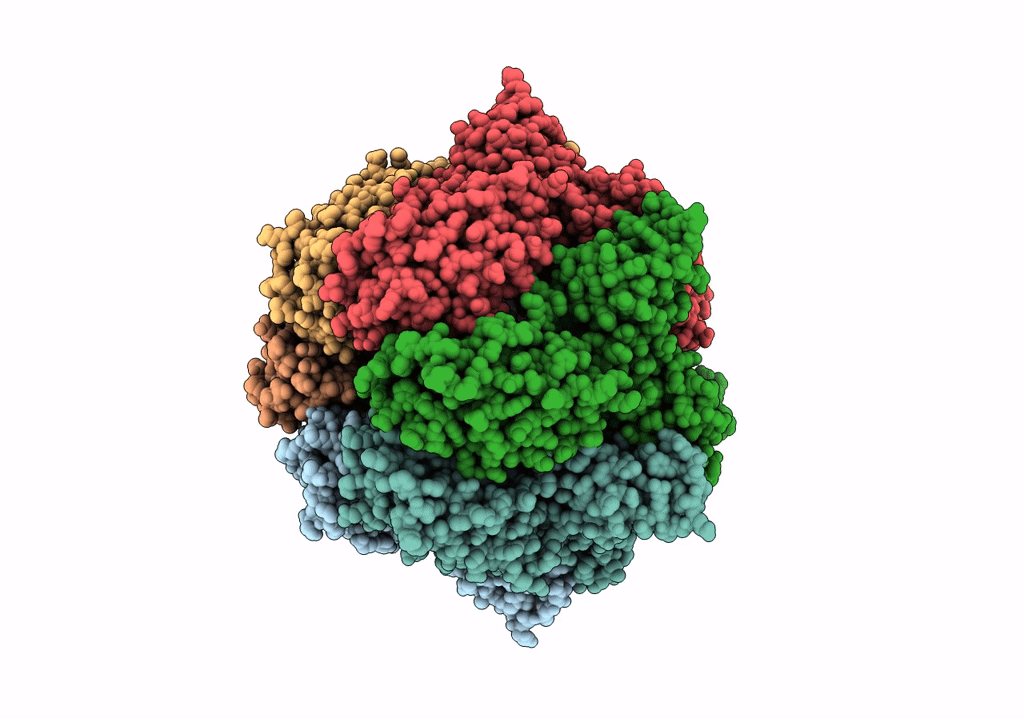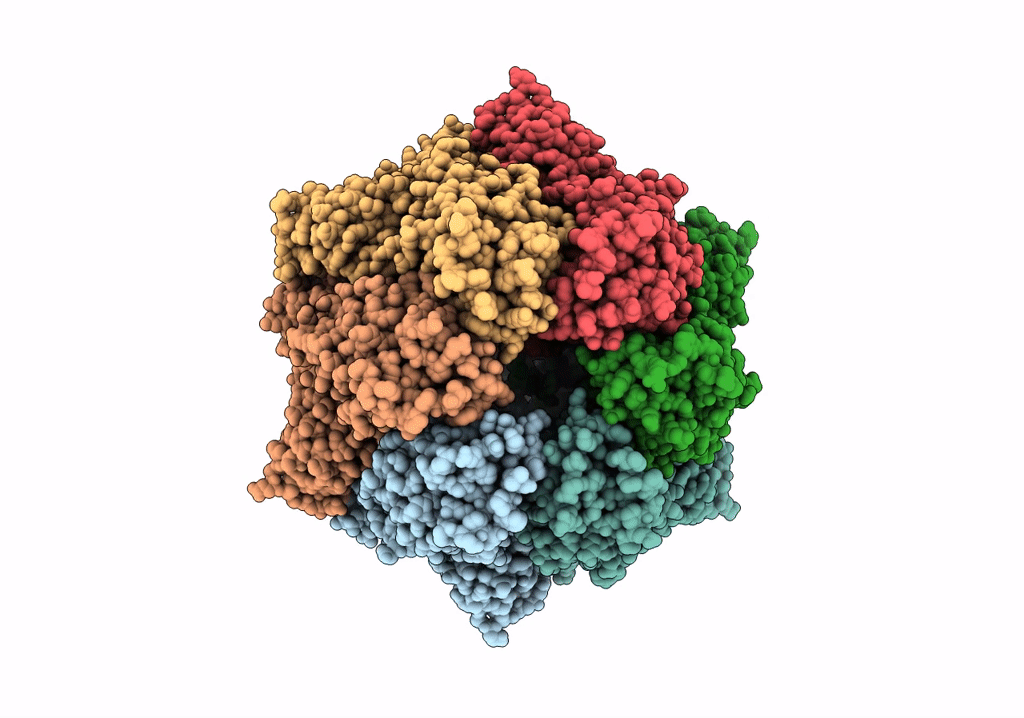
Molecular basis for the ATPase-powered substrate translocation by the Lon AAA+ protease
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Meiothermus taiwanensis (Taxon ID: 172827)
Dictyostelium discoideum (Taxon ID: 44689)
Dictyostelium discoideum (Taxon ID: 44689)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.60 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE