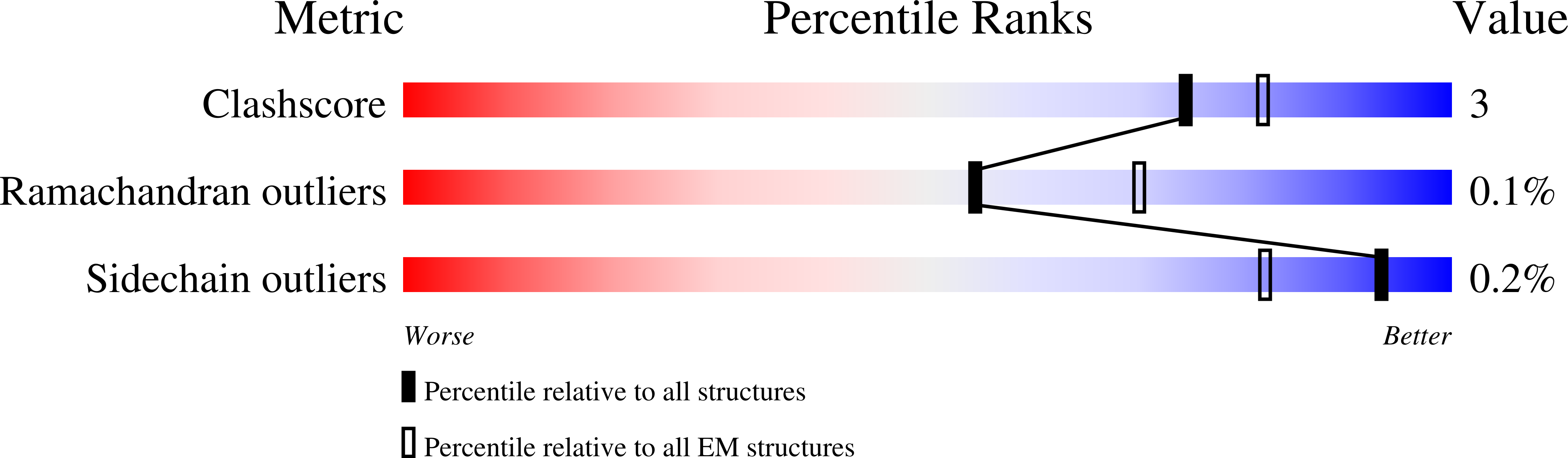
Deposition Date
2020-03-27
Release Date
2020-05-13
Last Version Date
2024-11-20
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6WBY
Keywords:
Title:
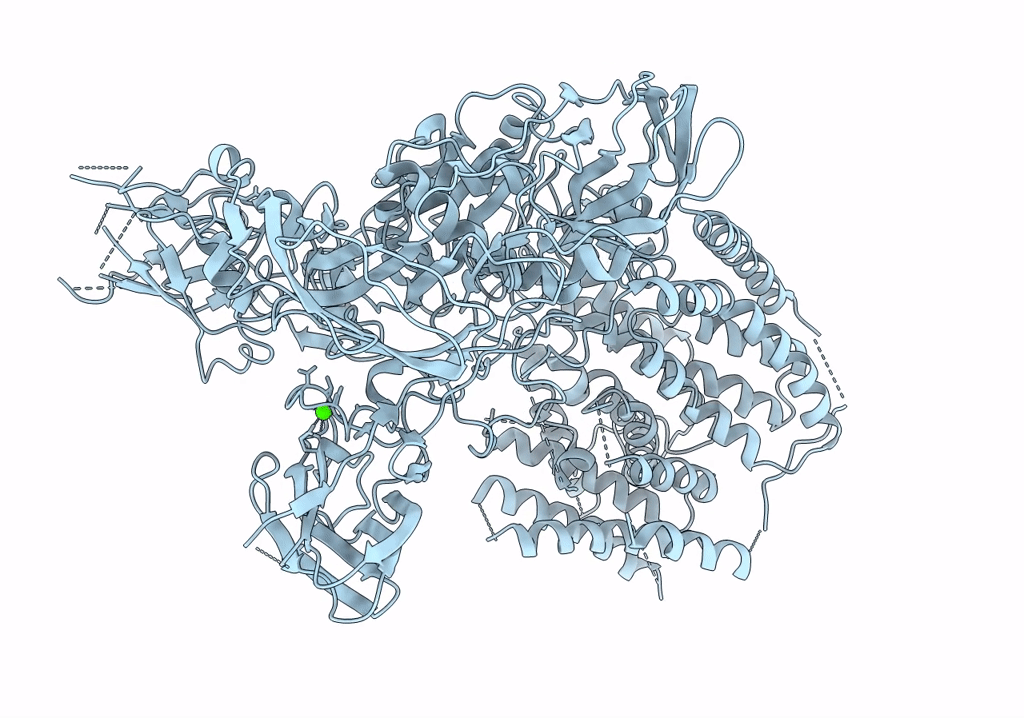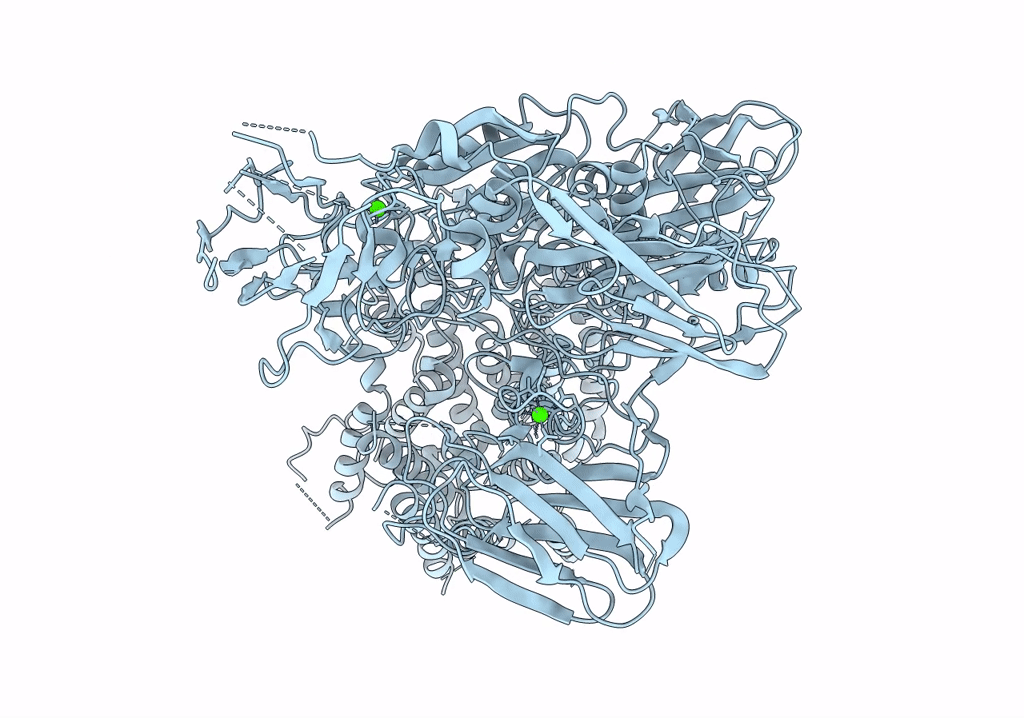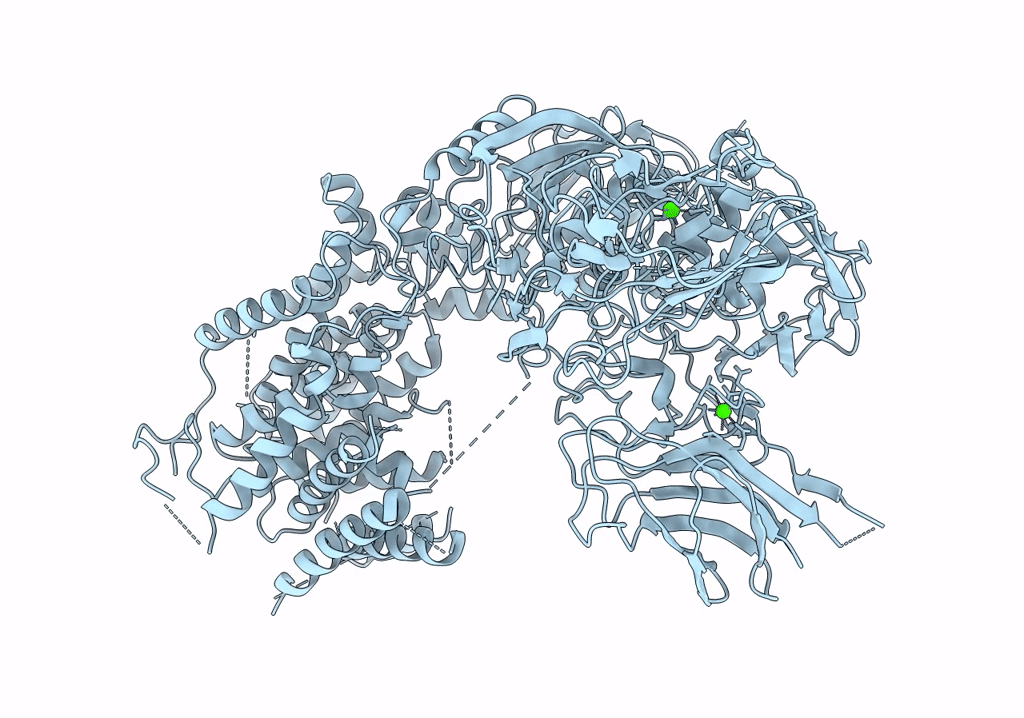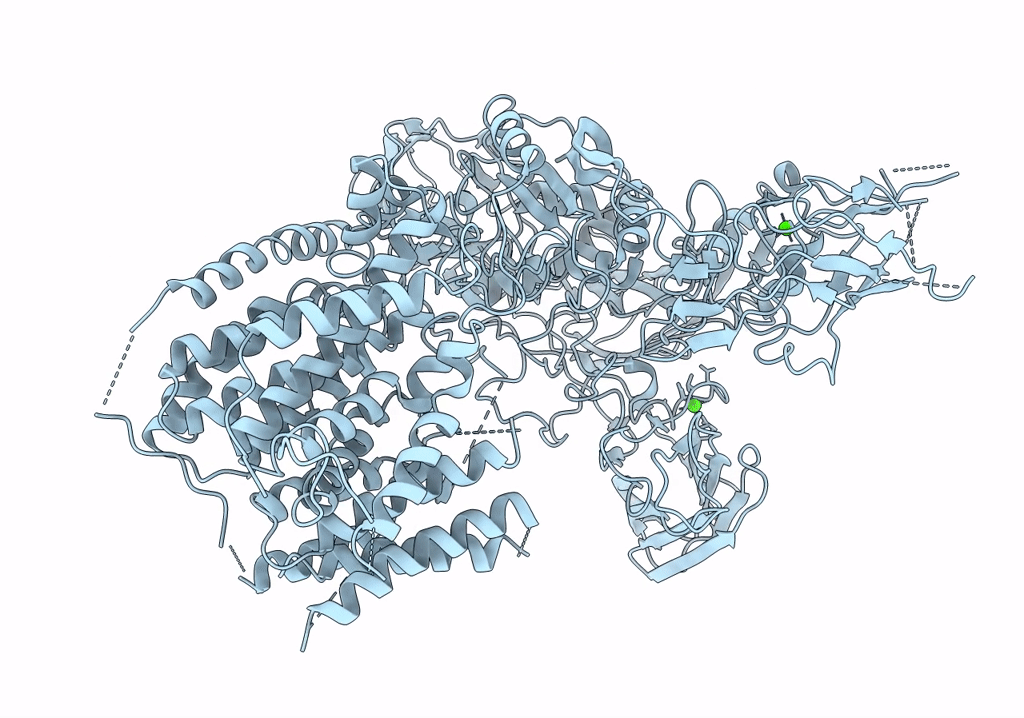
Single-Particle Cryo-EM Structure of Arabinofuranosyltransferase AftD from Mycobacteria, Mutant R1389S Class 2
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mycobacteroides abscessus (Taxon ID: 36809)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.40 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE