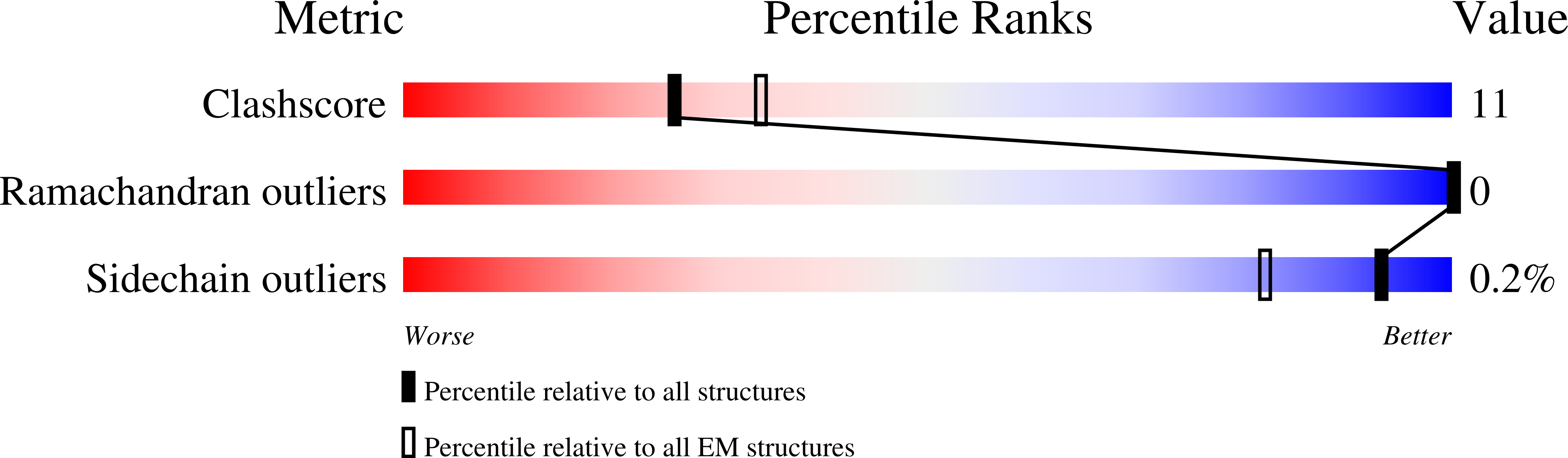
Deposition Date
2020-02-21
Release Date
2021-02-24
Last Version Date
2024-11-13
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6VX4
Keywords:
Title:
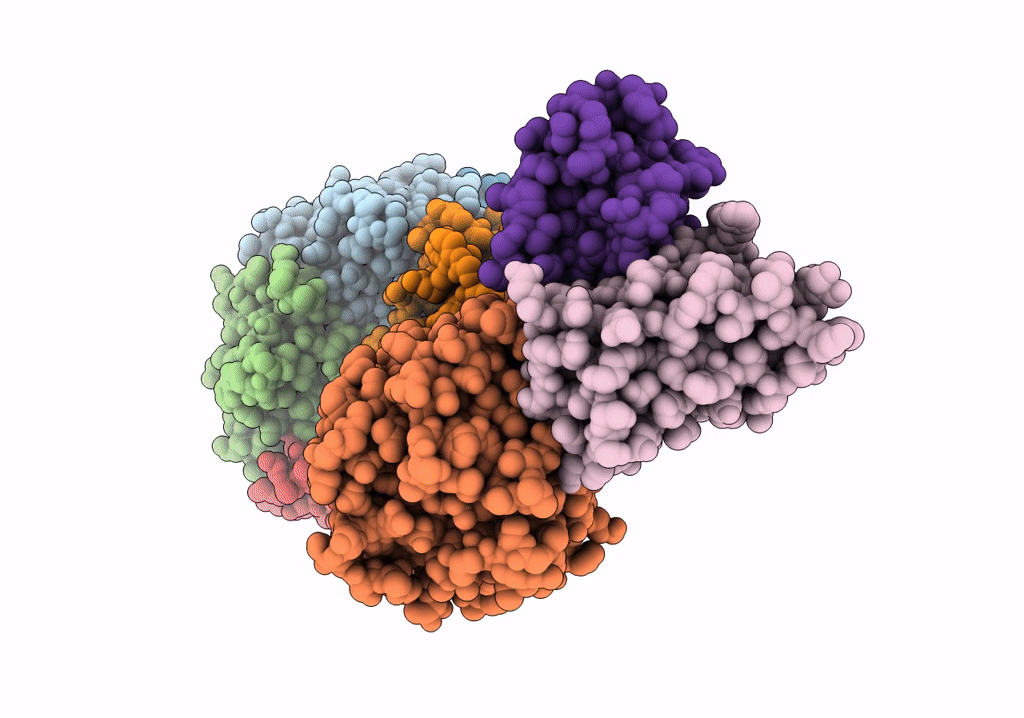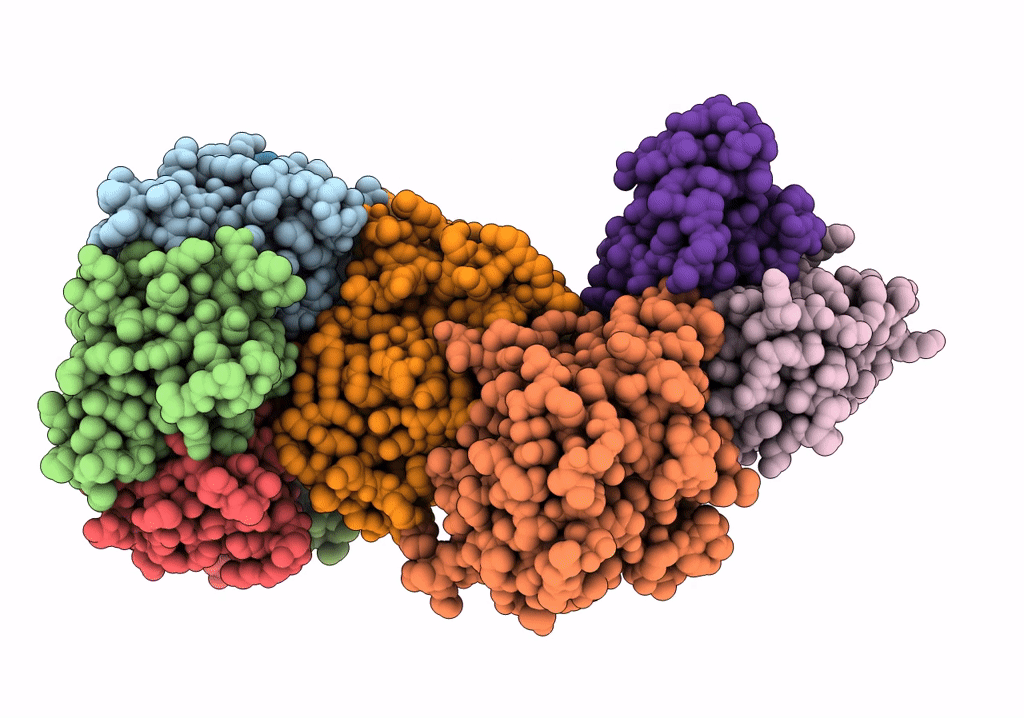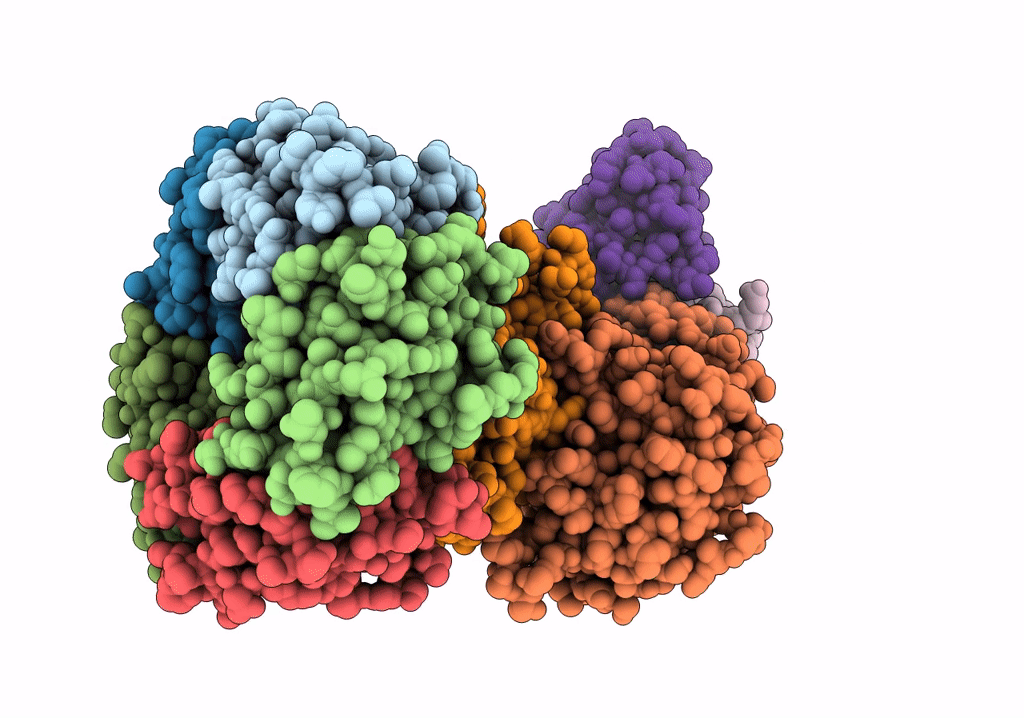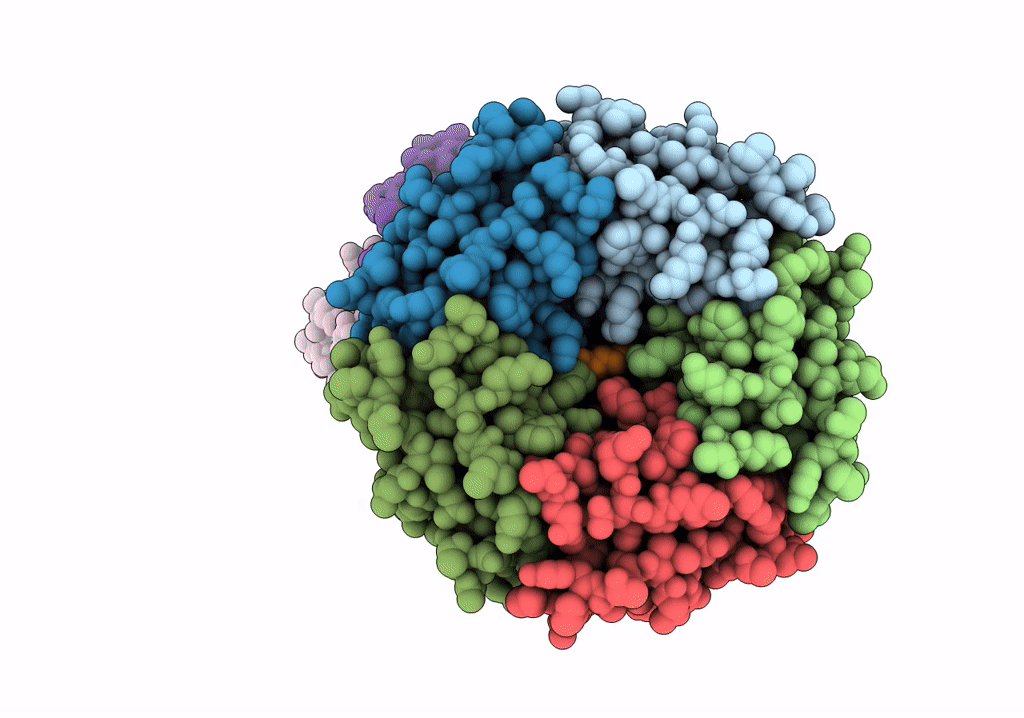
Density-fitted Model Structure of Antibody Variable Domains of TyTx11 in Complex with Typhoid Toxin
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Mus musculus (Taxon ID: 10090)
Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi str. CT18 (Taxon ID: 220341)
Salmonella enterica subsp. enterica serovar Typhi str. CT18 (Taxon ID: 220341)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.12 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE