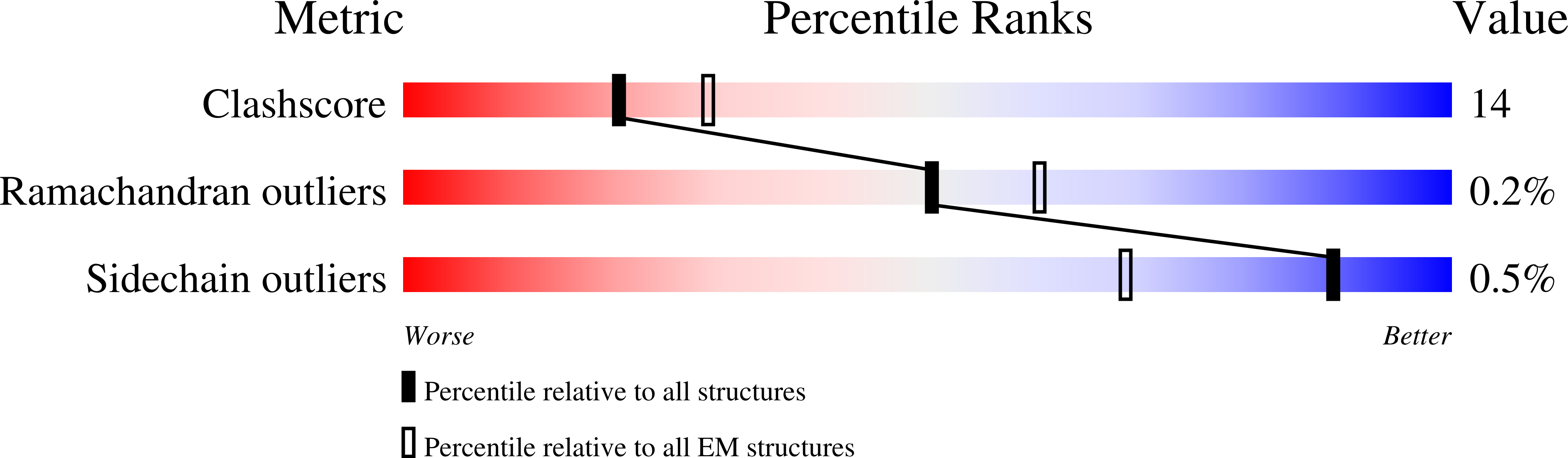Deposition Date
2020-02-10
Release Date
2020-02-26
Last Version Date
2024-10-23
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6VSB
Keywords:
Title:
Prefusion 2019-nCoV spike glycoprotein with a single receptor-binding domain up
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.46 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE