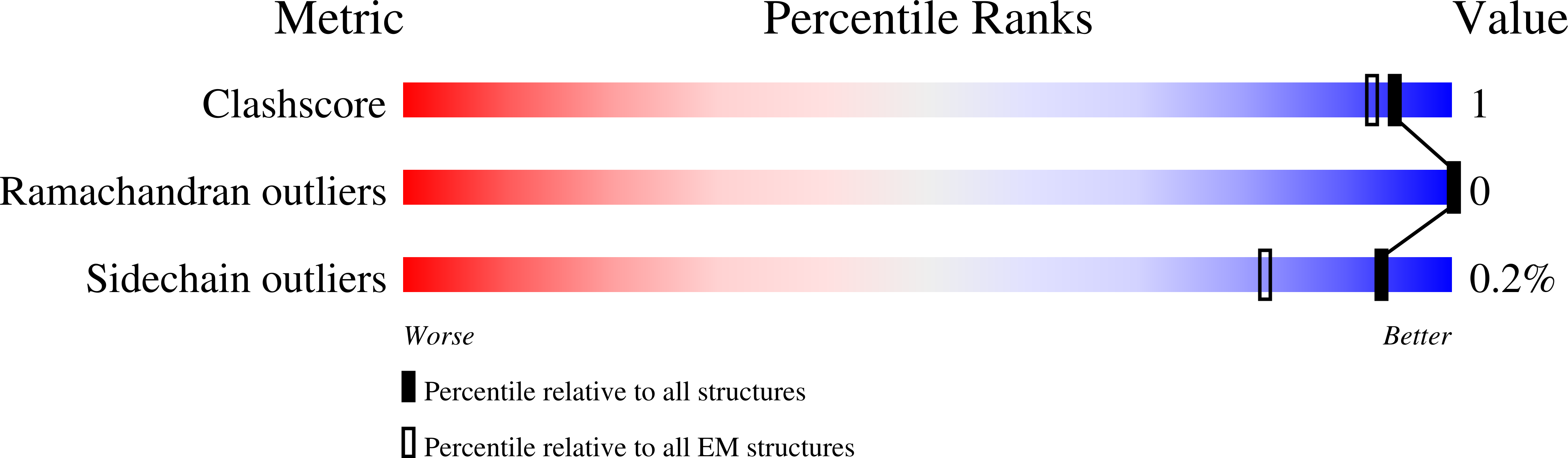
Deposition Date
2019-11-09
Release Date
2020-06-10
Last Version Date
2024-03-06
Entry Detail
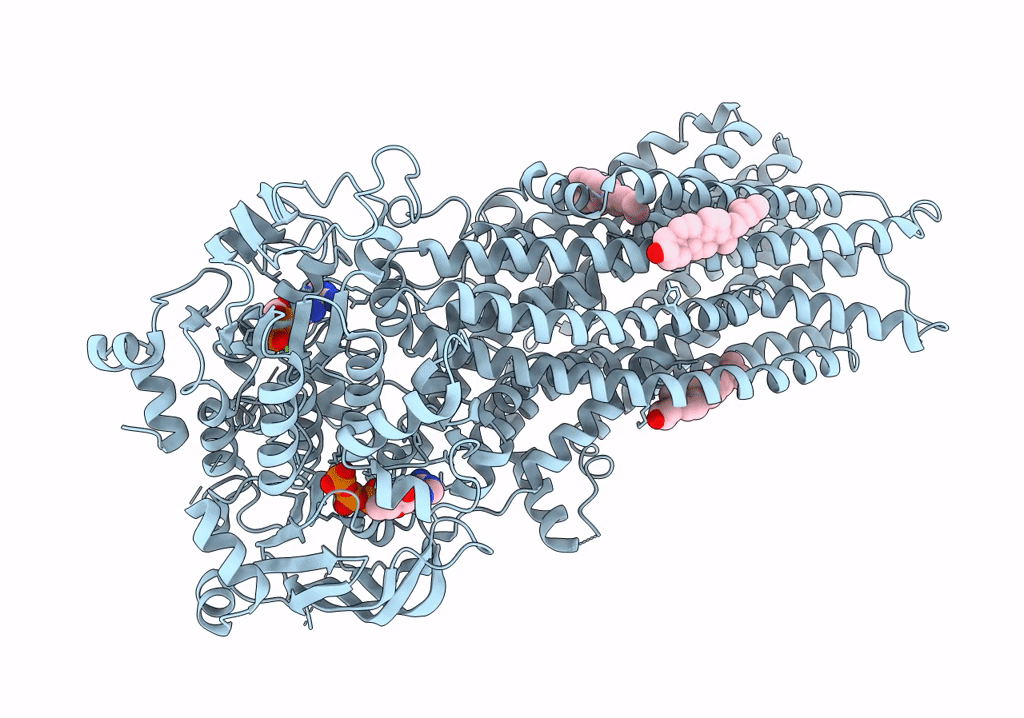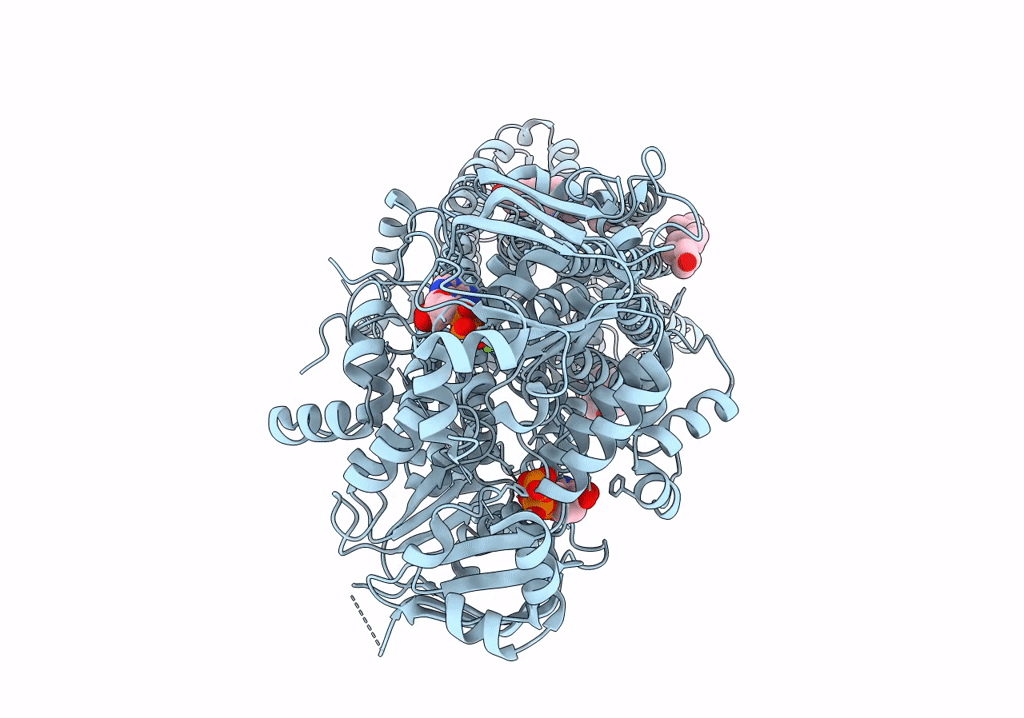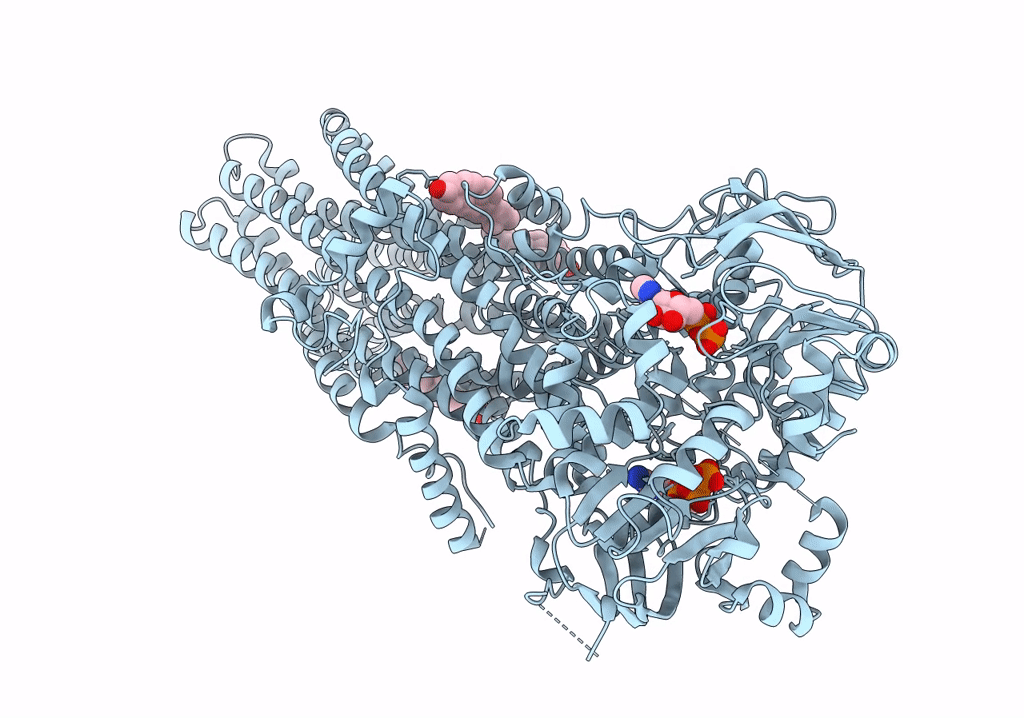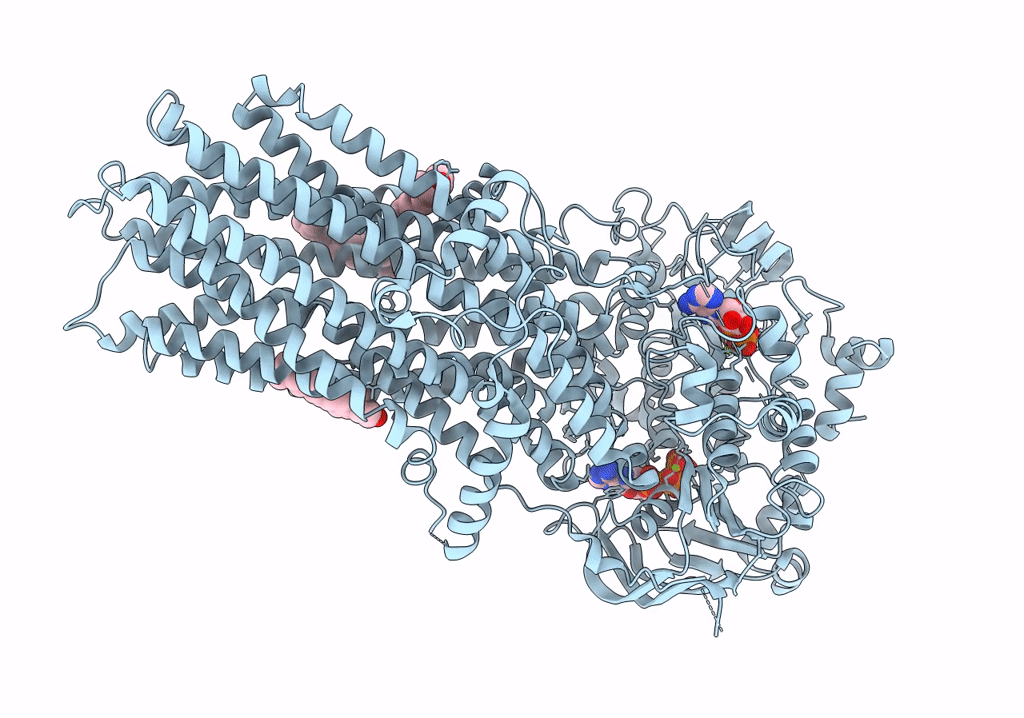
PDB ID:
6UY0
Keywords:
Title:
Cryo-EM structure of wild-type bovine multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) under active turnover conditions
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Bos taurus (Taxon ID: 9913)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.23 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE