Deposition Date
2019-10-30
Release Date
2020-08-26
Last Version Date
2023-10-11
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6UU4
Keywords:
Title:
E. coli sigma-S transcription initiation complex with a 3-nt RNA ("old" crystal soaked with GTP and dinucleotide GpA for 30 minutes)
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (Taxon ID: 562)
Escherichia coli (strain K12) (Taxon ID: 83333)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Escherichia coli (strain K12) (Taxon ID: 83333)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
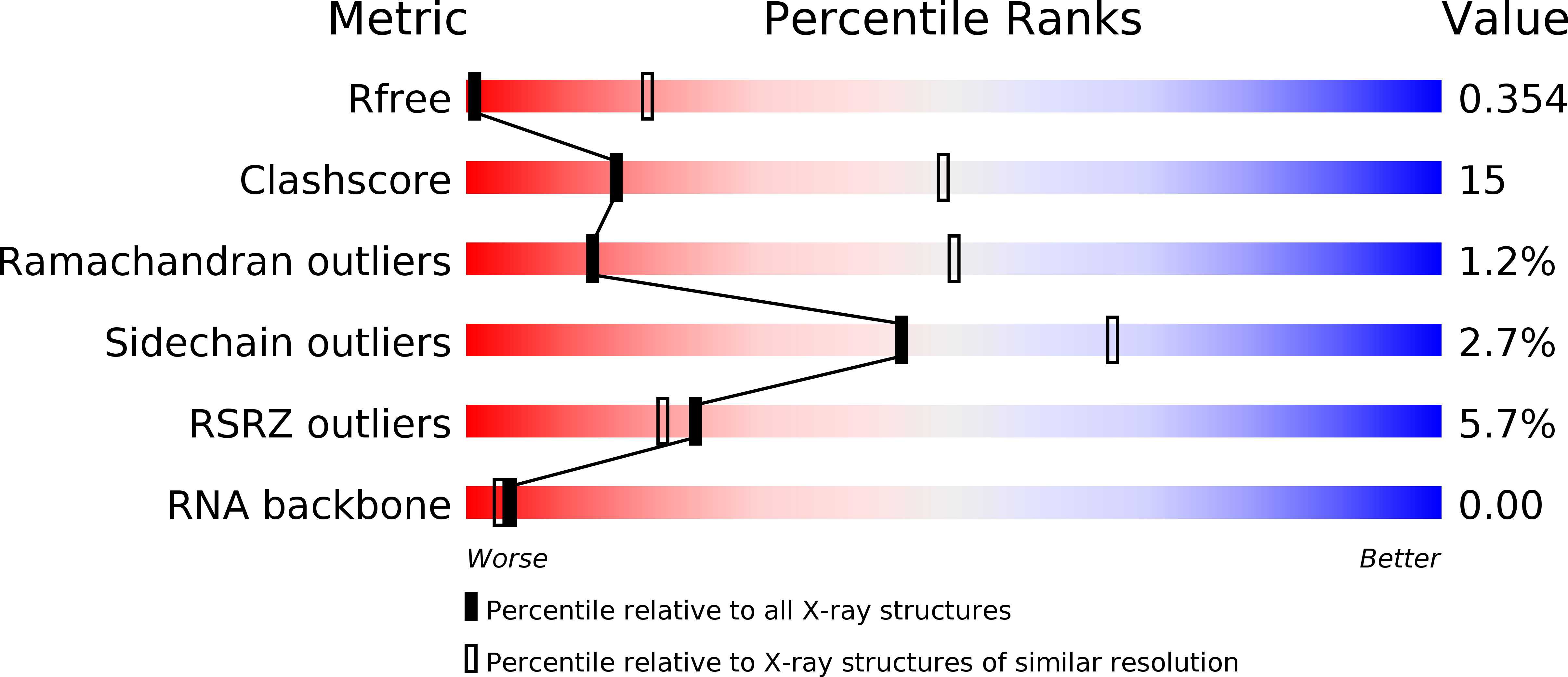
Resolution:
4.31 Å
R-Value Free:
0.36
R-Value Work:
0.30
Space Group:
P 21 21 21