Deposition Date
2019-10-06
Release Date
2020-08-19
Last Version Date
2023-10-11
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6UKU
Keywords:
Title:
STING C-terminal Domain Complexed with Non-cyclic Dinucleotide Compound 3
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Taxon ID: 559292)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
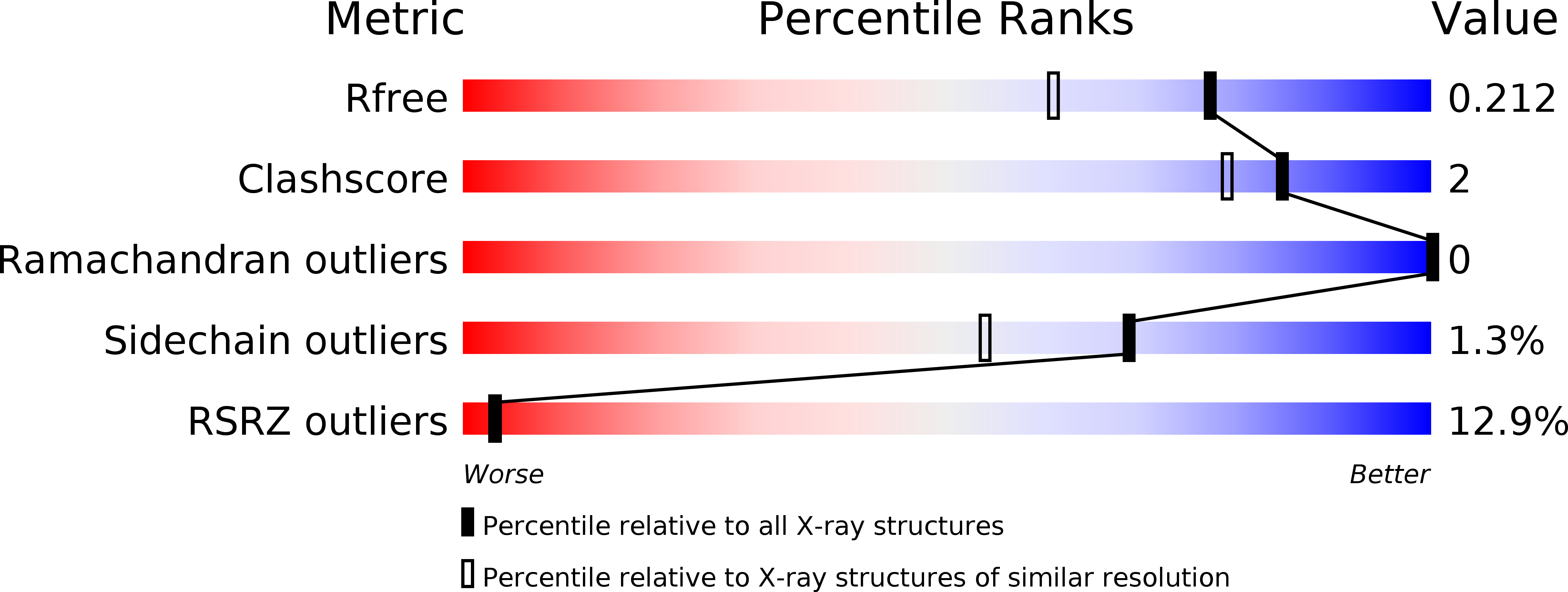
Resolution:
1.68 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.20
R-Value Observed:
0.20
Space Group:
C 1 2 1