Deposition Date
2019-10-04
Release Date
2019-12-18
Last Version Date
2023-10-11
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6UKI
Keywords:
Title:
HhaI endonuclease in Complex with DNA in space group P212121 (pH 6.0)
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Haemophilus parahaemolyticus (Taxon ID: 735)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
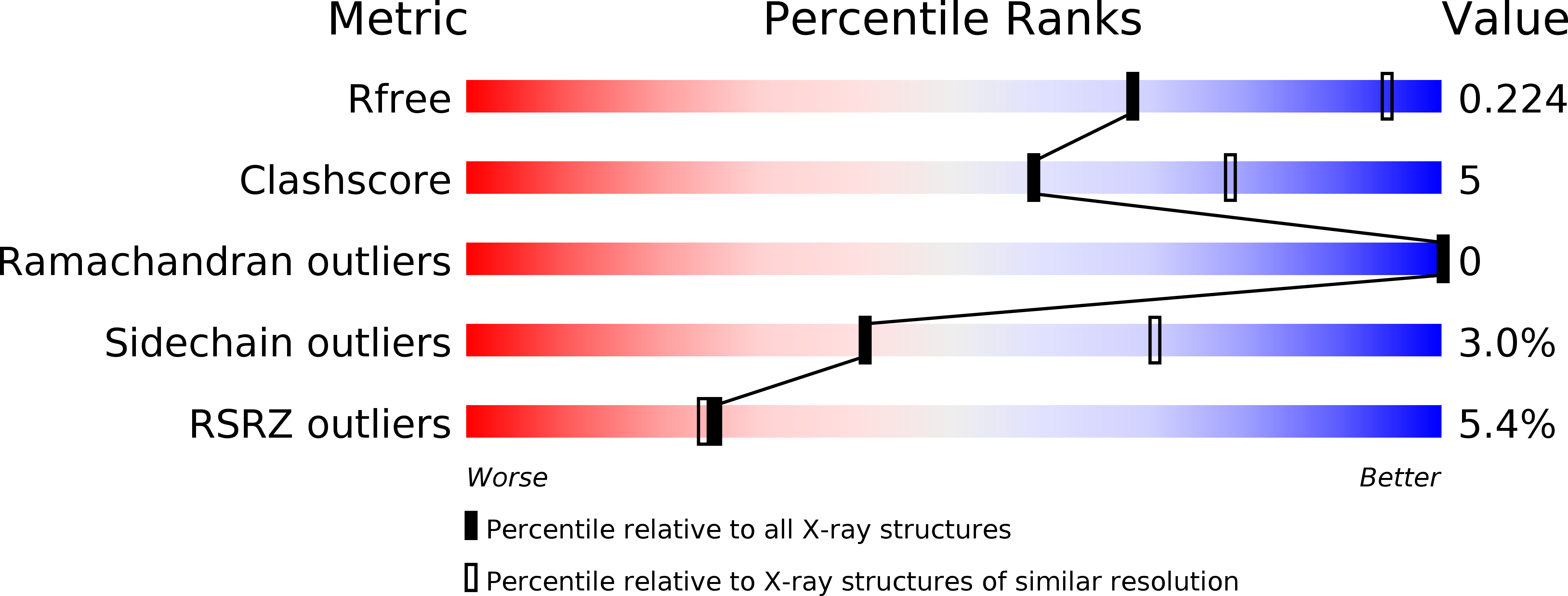
Resolution:
2.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.22
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
P 21 21 21