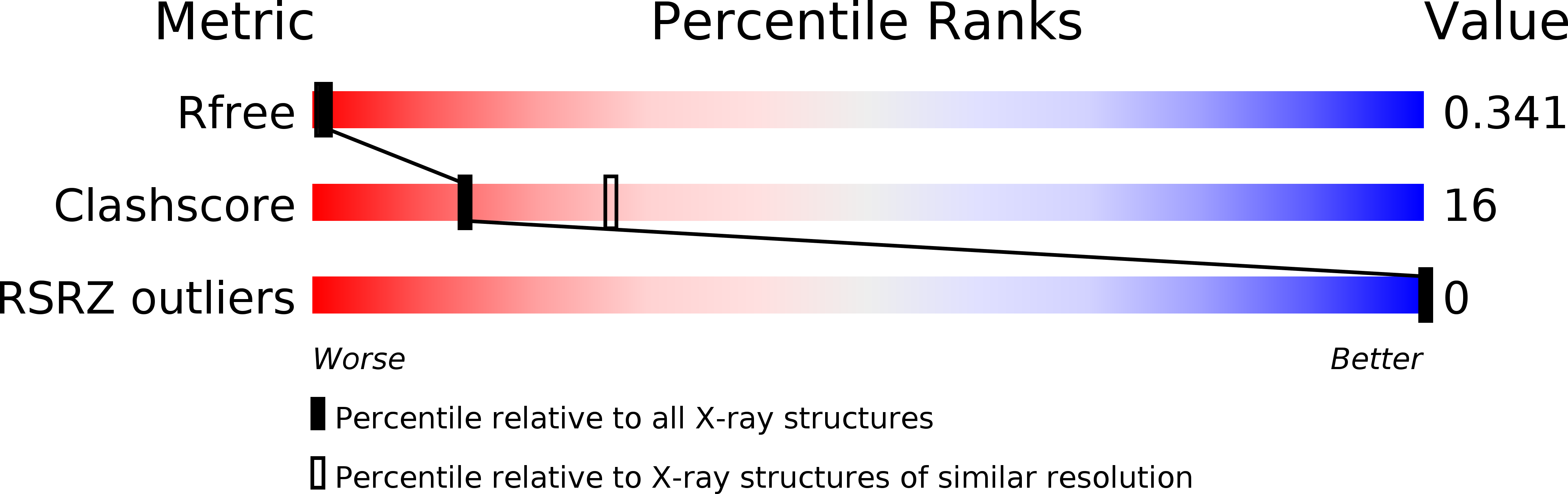Deposition Date
2019-08-13
Release Date
2019-10-16
Last Version Date
2024-03-13
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.60 Å
R-Value Free:
0.31
R-Value Work:
0.26
R-Value Observed:
0.27
Space Group:
I 41 2 2