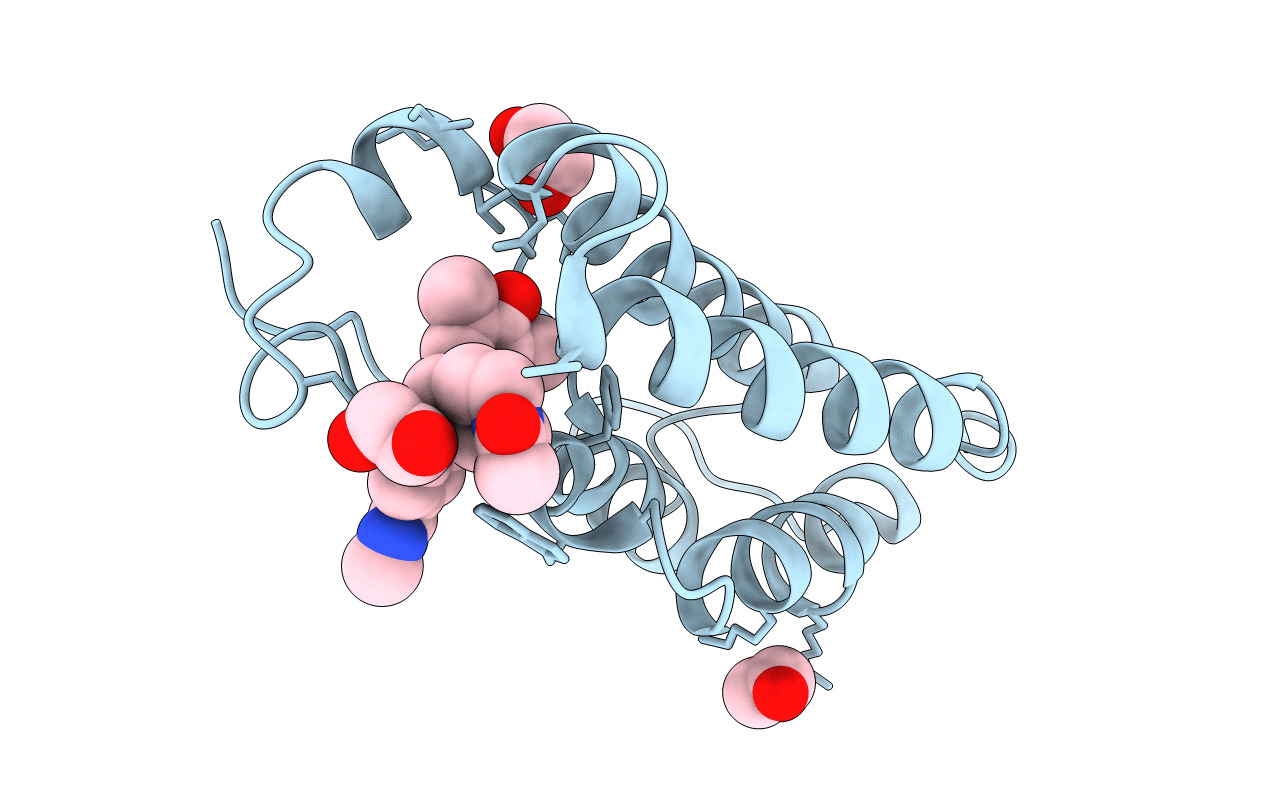
Deposition Date
2019-12-15
Release Date
2020-01-15
Last Version Date
2024-05-01
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6TPX
Keywords:
Title:
N-TERMINAL BROMODOMAIN OF HUMAN BRD4 WITH 1-((1-acetylpiperidin-4-yl)methyl)-2-(4-hydroxy-3,5-dimethylphenyl)-N-methyl-1H-benzo[d]imidazole-5-carboxamide
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
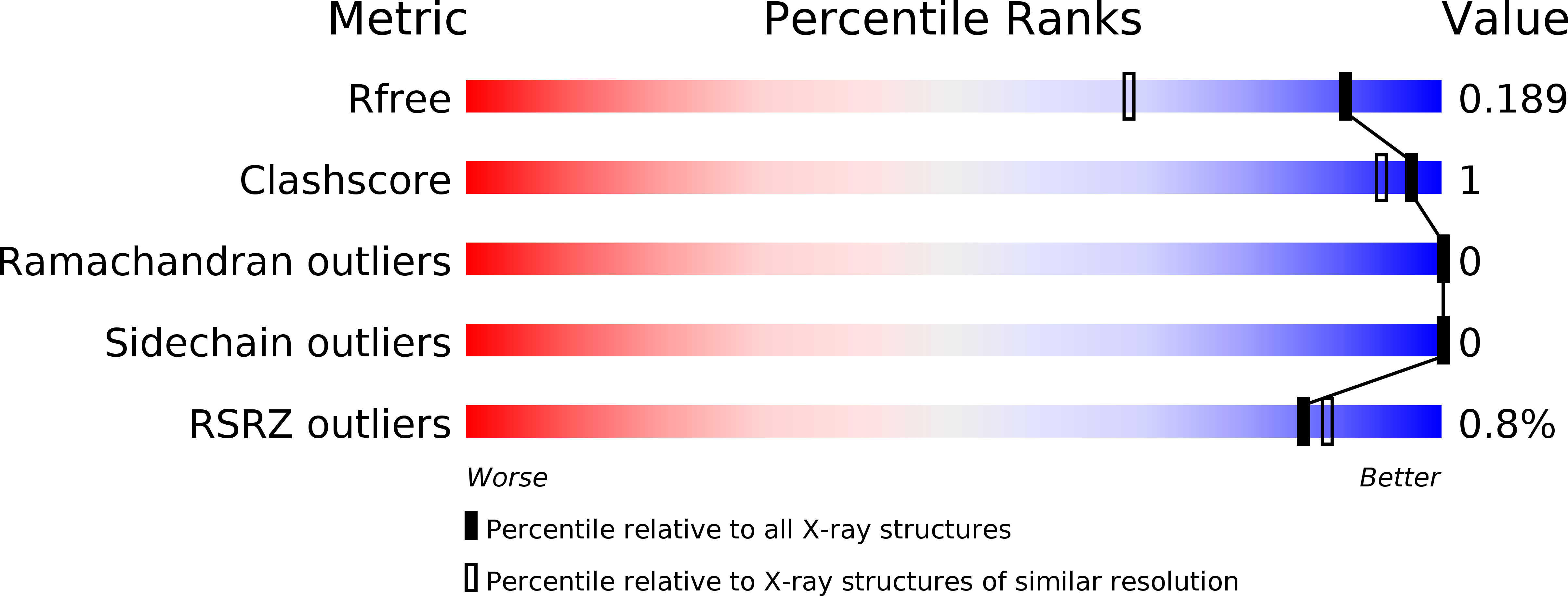
Resolution:
1.48 Å
R-Value Free:
0.18
R-Value Work:
0.15
Space Group:
P 21 21 21