Deposition Date
2019-11-26
Release Date
2020-12-16
Last Version Date
2024-01-24
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6TJN
Keywords:
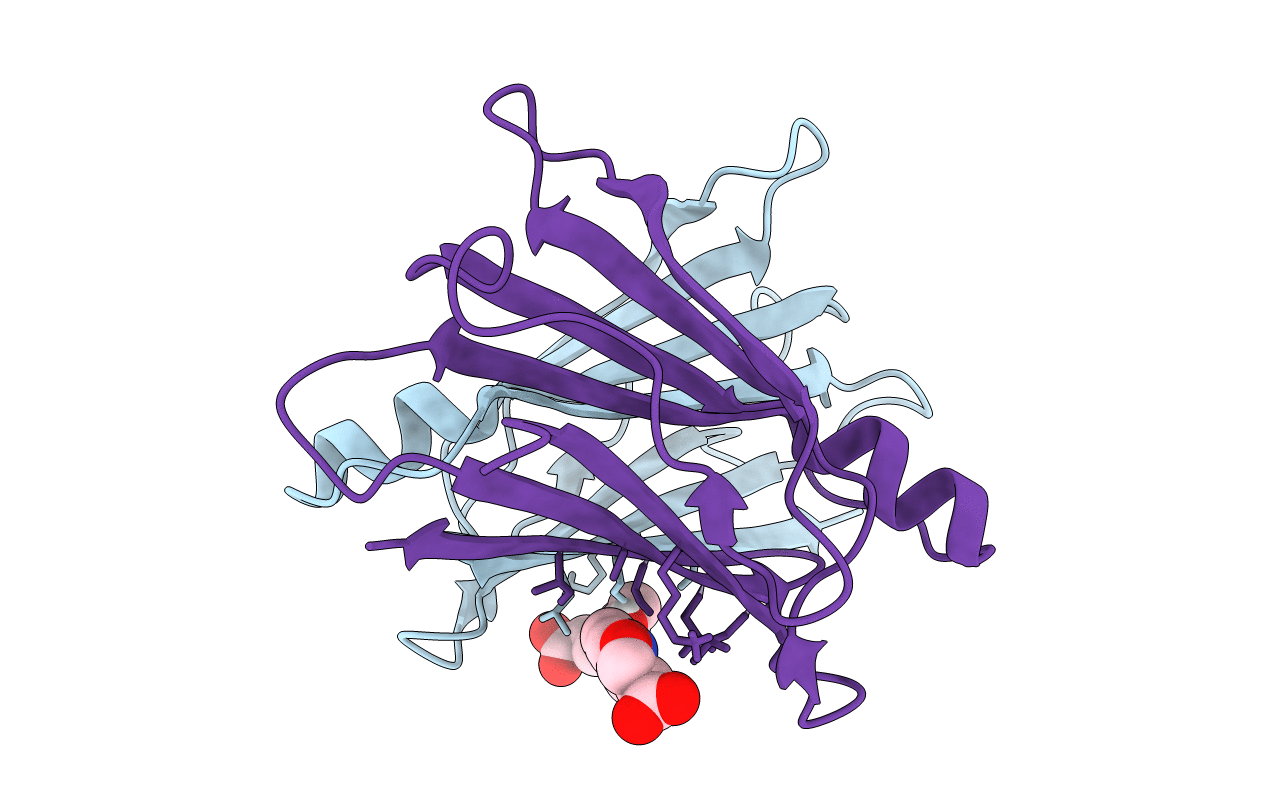
Title:
Human transthyretin (TTR) complexed with (E)-3-(((4-hydroxybenzylidene)amino)oxy)propanoic acid
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Homo sapiens (Taxon ID: 9606)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
1.70 Å
R-Value Free:
0.19
R-Value Work:
0.17
R-Value Observed:
0.17
Space Group:
P 21 21 2


