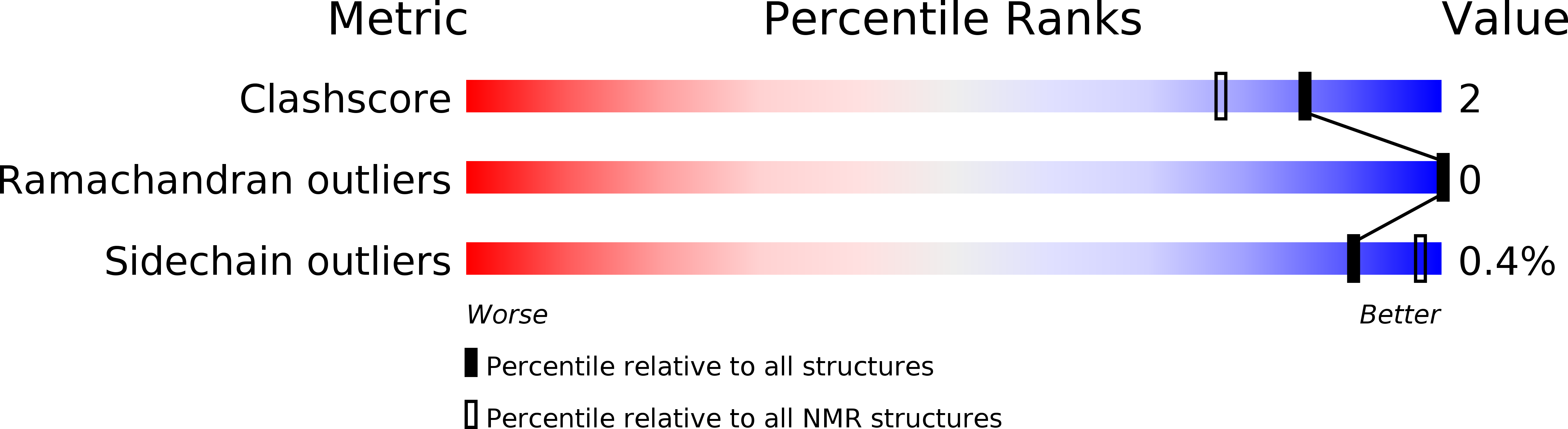Deposition Date
2019-11-15
Release Date
2020-02-19
Last Version Date
2024-06-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6TG5
Keywords:
Title:
Solution structure of MacpD, a acyl carrier protein, from Pseudomonas fluorescens involved in Mupirocin biosynthesis.
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Pseudomonas fluorescens (Taxon ID: 294)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
250
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
structures with the least restraint violations