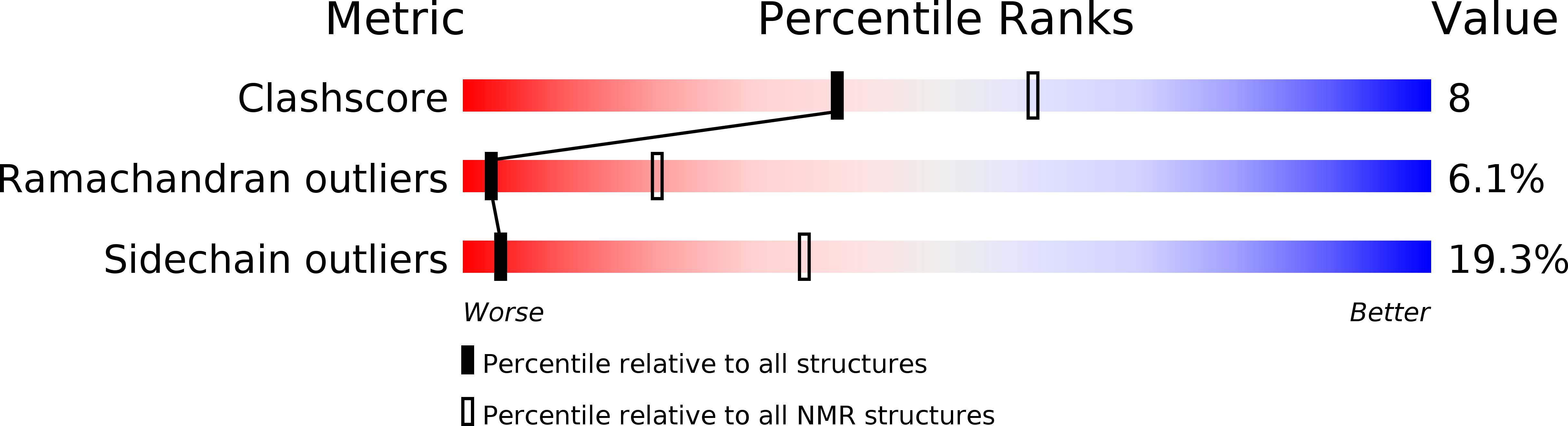Deposition Date
2019-10-10
Release Date
2020-08-12
Last Version Date
2024-06-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6T33
Keywords:
Title:
The unusual structure of Ruminococcin C1 antimicrobial peptide confers activity against clinical pathogens
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
[Ruminococcus] gnavus E1 (Taxon ID: 935582)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
100
Conformers Submitted:
20
Selection Criteria:
target function