Deposition Date
2019-08-05
Release Date
2020-05-13
Last Version Date
2025-07-09
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6SGT
Keywords:
Title:
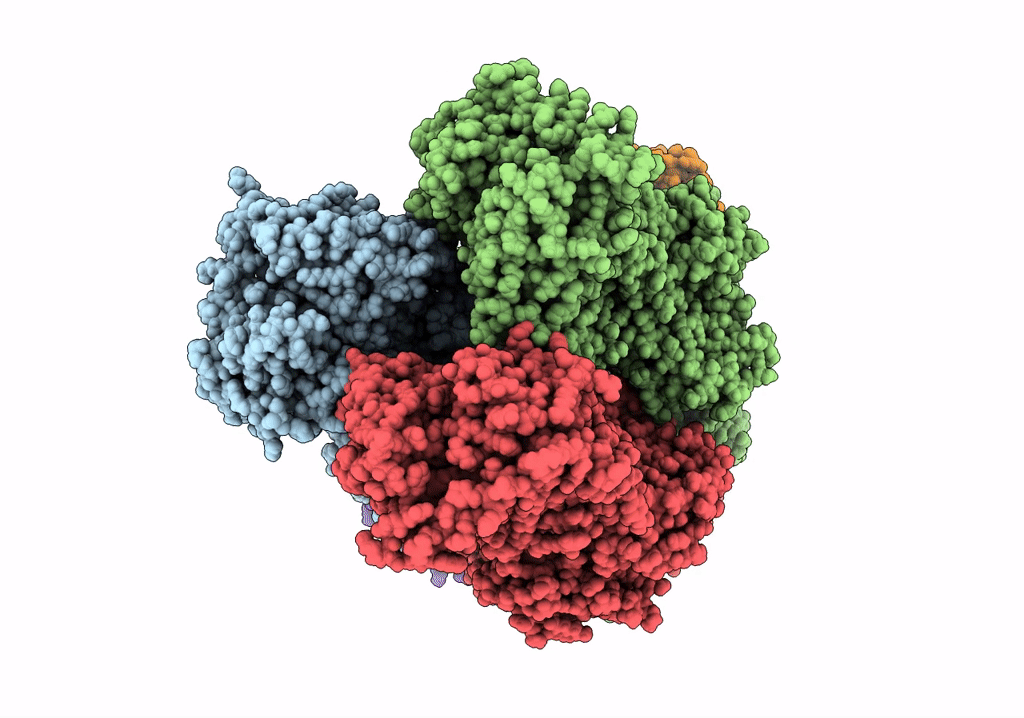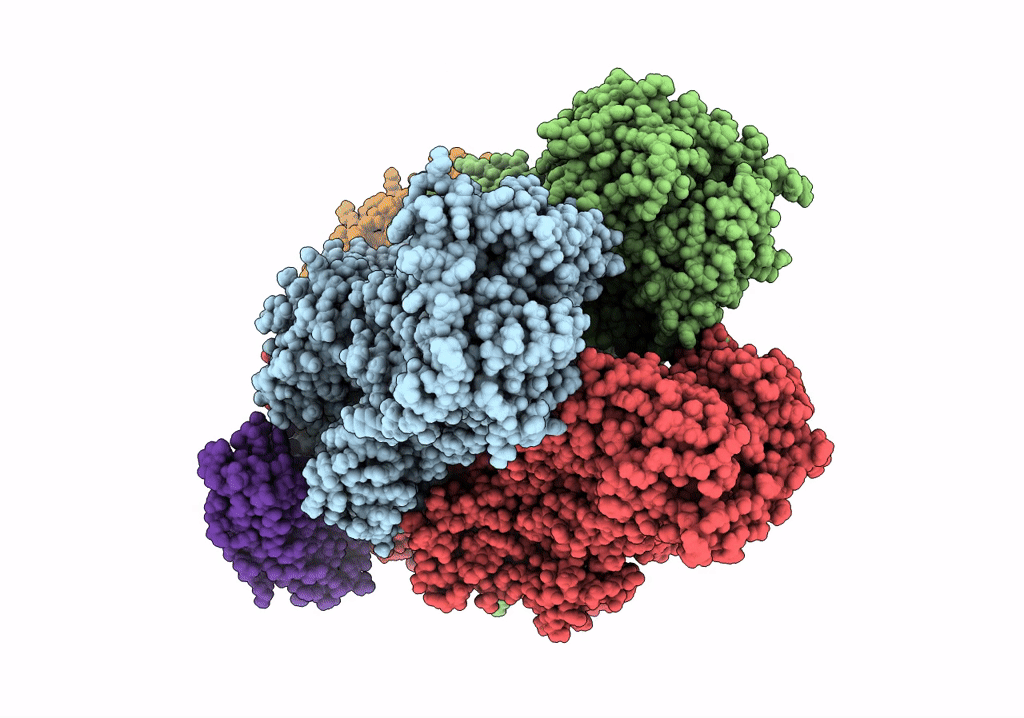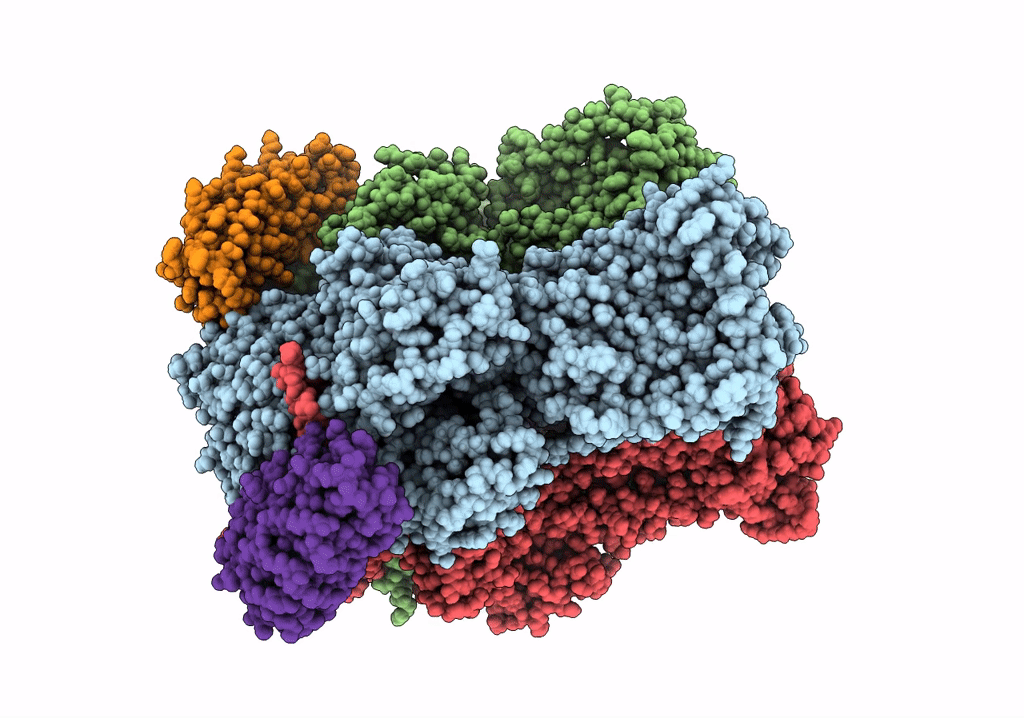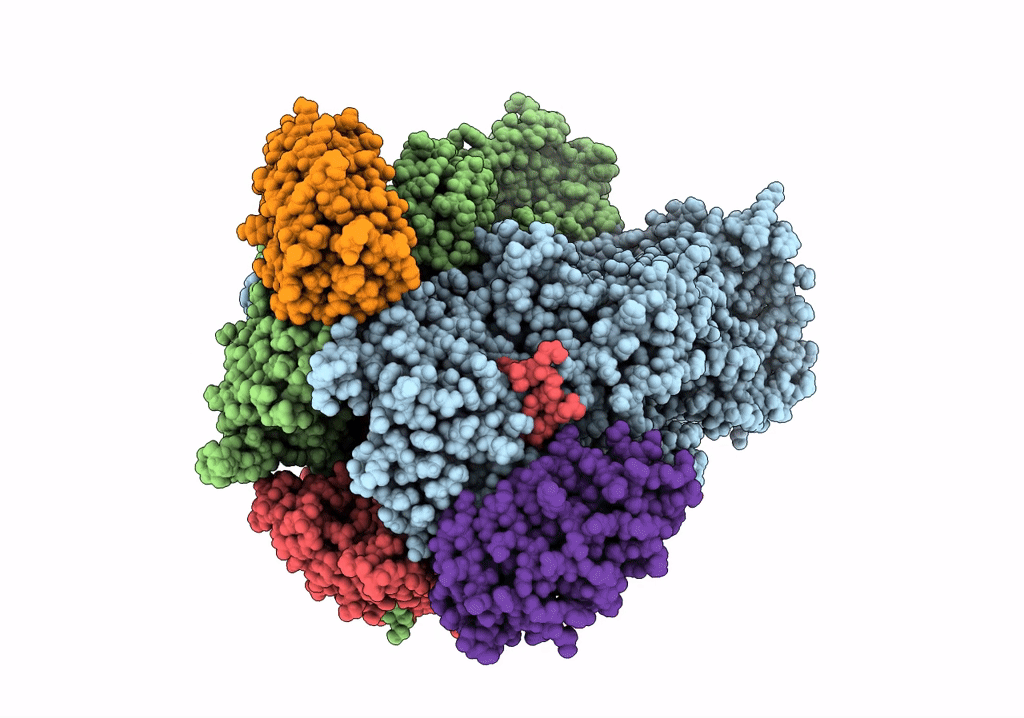
Cryo-EM structure of Escherichia coli AcrB and DARPin in Saposin A-nanodisc with cardiolipin
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli K12 (Taxon ID: 83333)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
synthetic construct (Taxon ID: 32630)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
3.46 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


