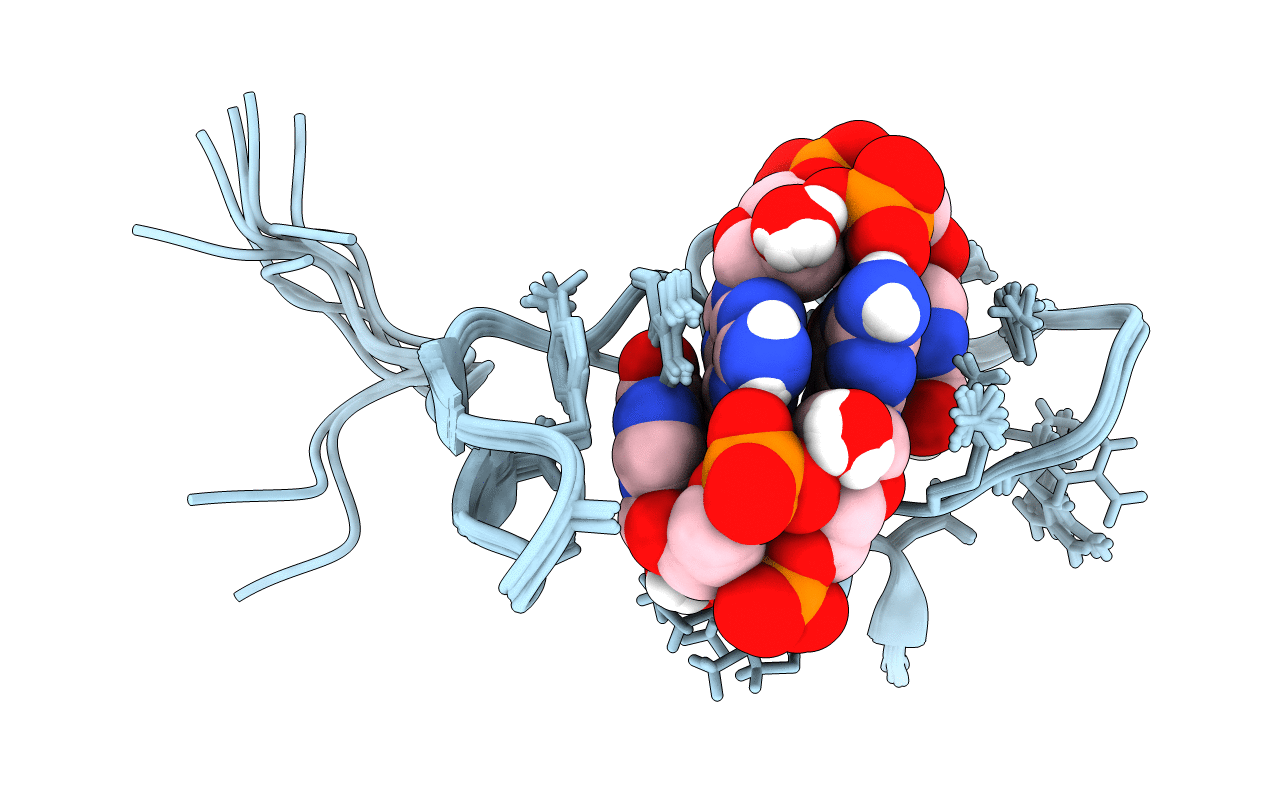
Deposition Date
2019-08-02
Release Date
2020-06-10
Last Version Date
2024-06-19
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6SFT
Keywords:
Title:
Solution structure of protein ARR_CleD in complex with c-di-GMP
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Caulobacter vibrioides (strain NA1000 / CB15N) (Taxon ID: 565050)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Conformers Calculated:
200
Conformers Submitted:
10
Selection Criteria:
structures with the lowest energy


