Deposition Date
2019-07-15
Release Date
2019-08-28
Last Version Date
2024-05-15
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6S9U
Keywords:
Title:
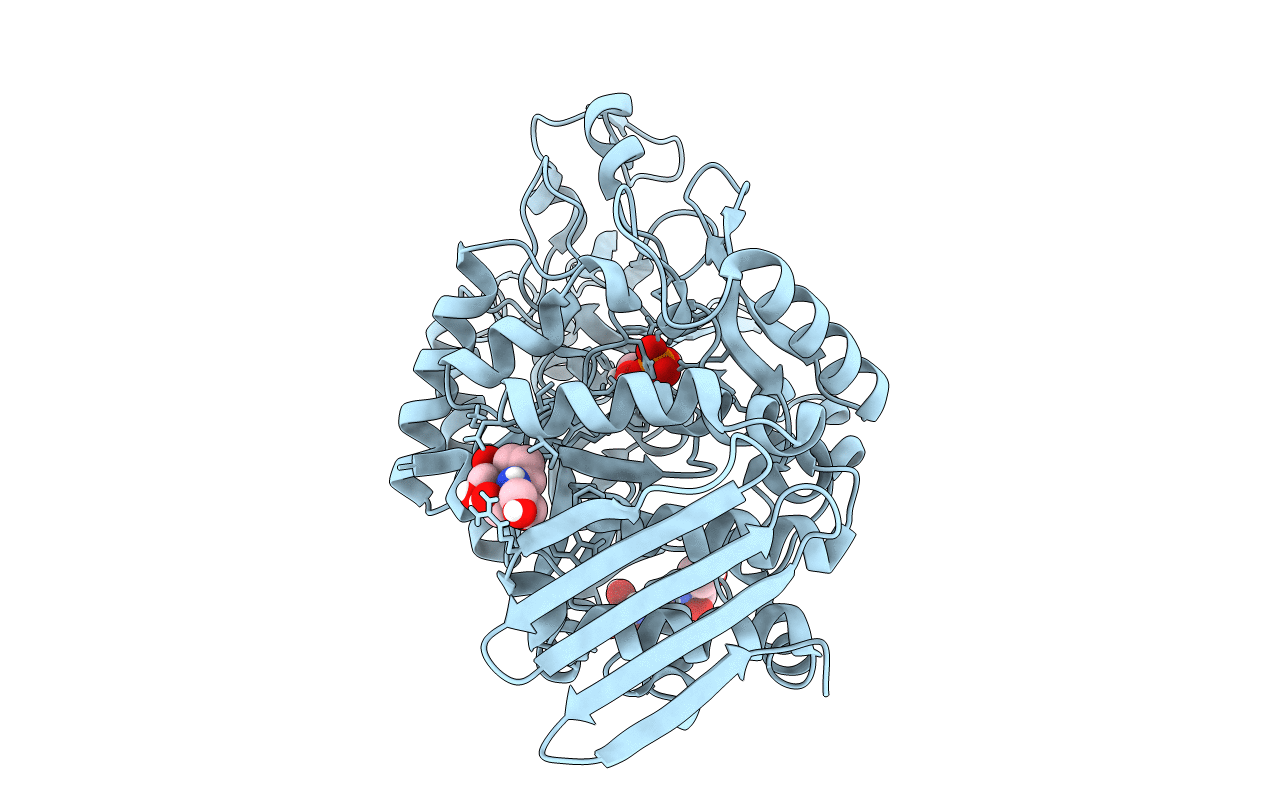
Crystal structure of sucrose 6F-phosphate phosphorylase from Ilumatobacter coccineus
Biological Source:
Source Organism:
Ilumatobacter coccineus YM16-304 (Taxon ID: 1313172)
Host Organism:
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
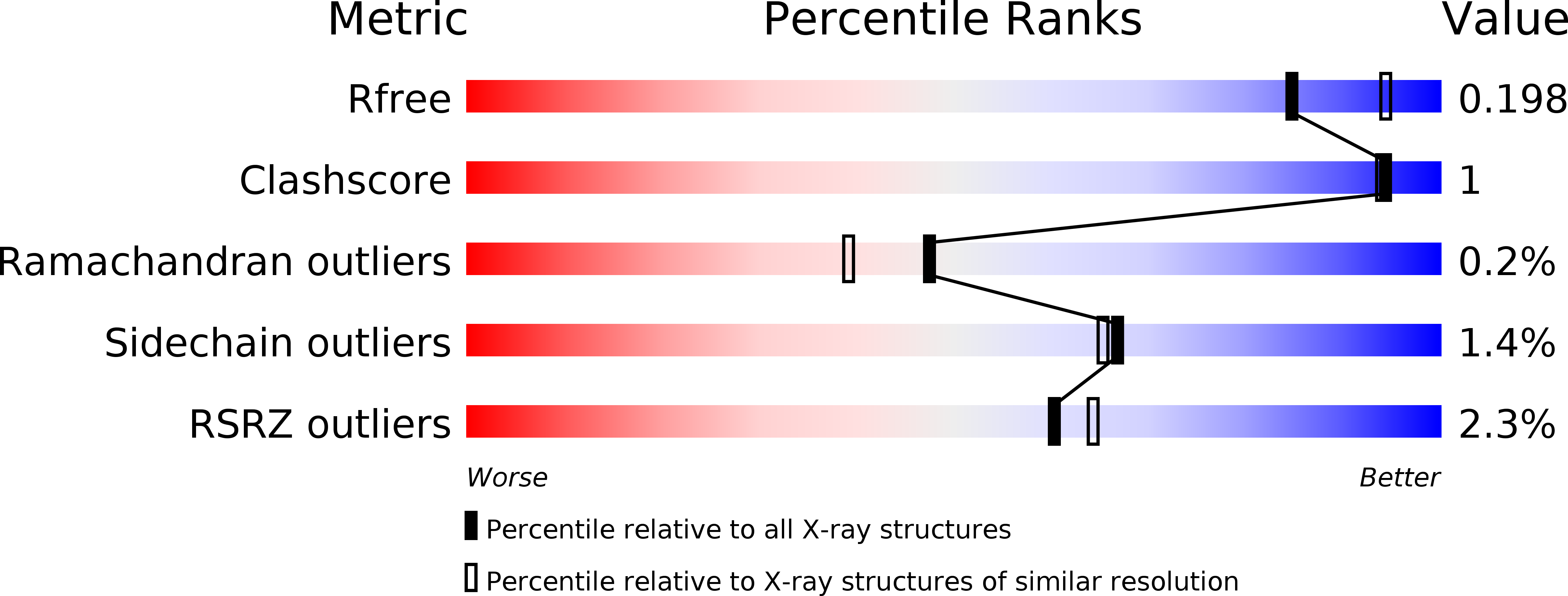
Resolution:
2.05 Å
R-Value Free:
0.19
R-Value Work:
0.16
R-Value Observed:
0.16
Space Group:
C 2 2 21