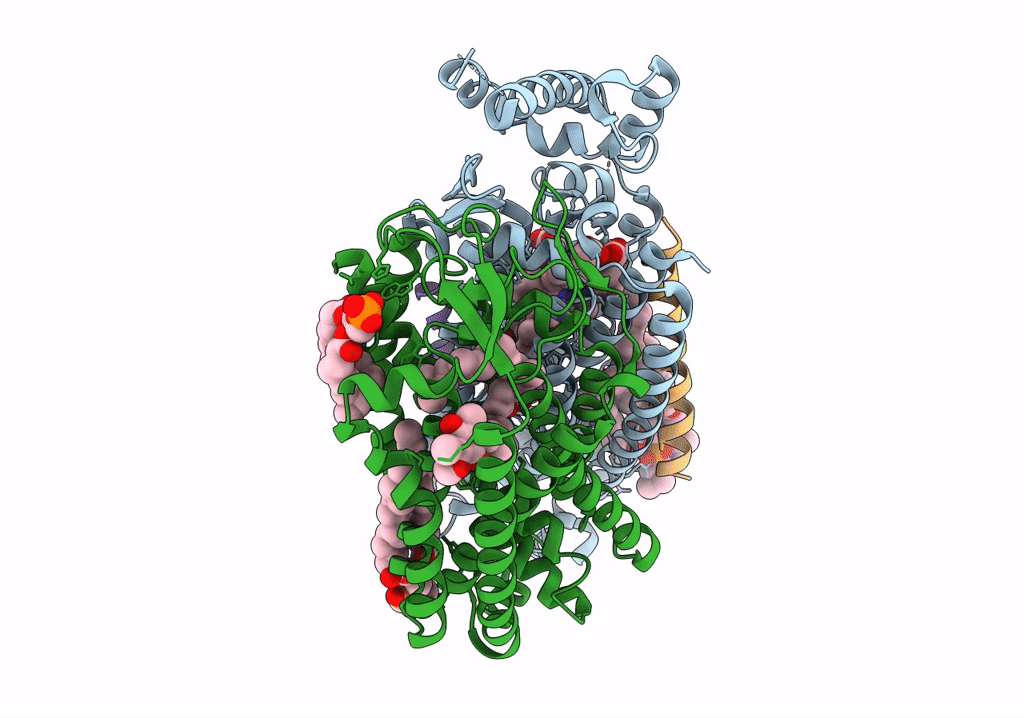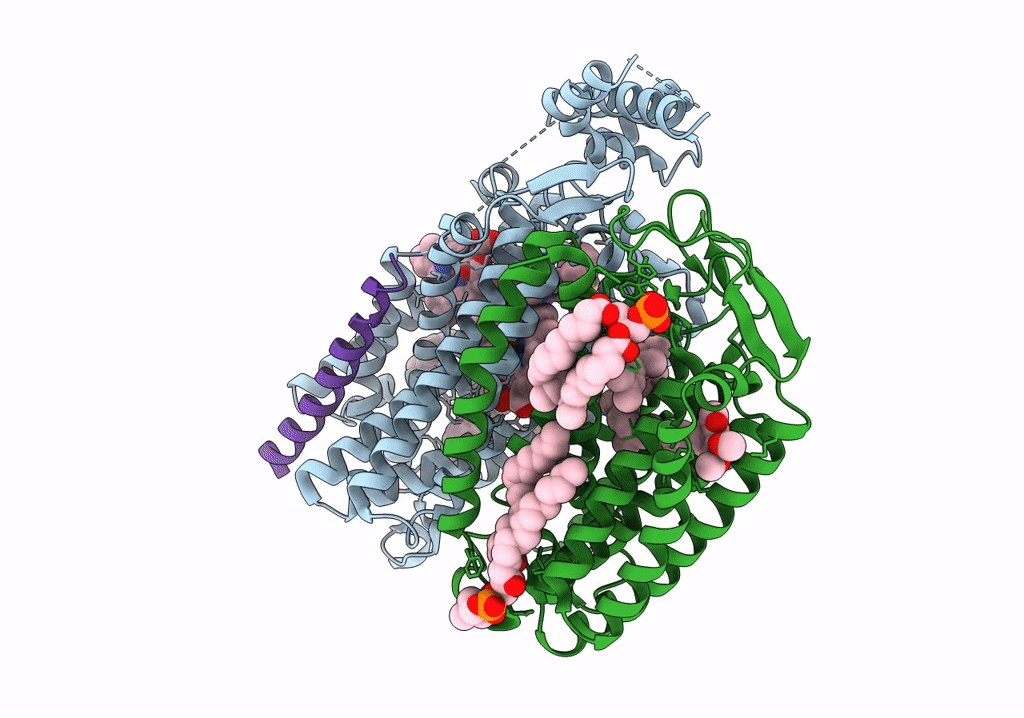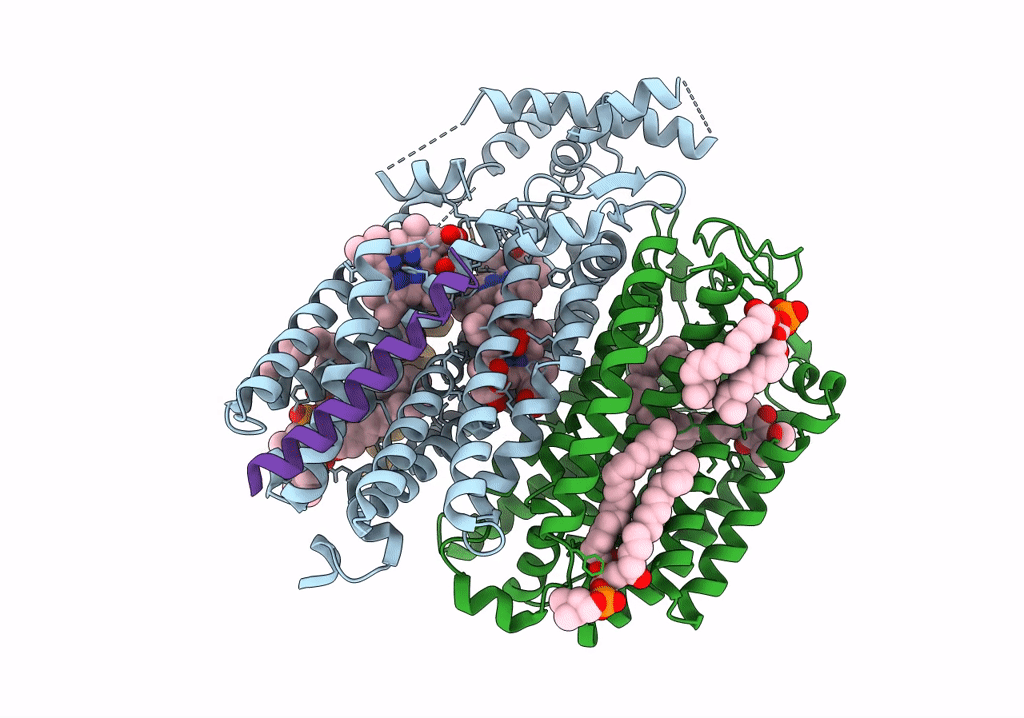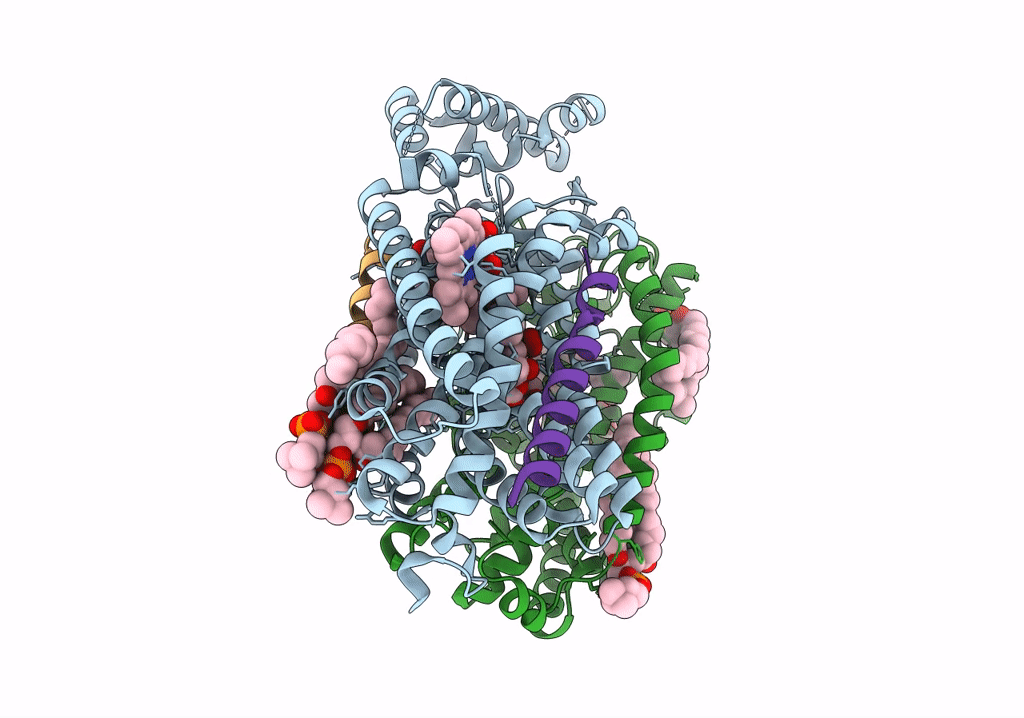
Deposition Date
2019-04-30
Release Date
2019-10-16
Last Version Date
2024-05-22
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6RKO
Keywords:
Title:
Cryo-EM structure of the E. coli cytochrome bd-I oxidase at 2.68 A resolution
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Escherichia coli (strain K12) (Taxon ID: 83333)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.68 Å
Aggregation State:
PARTICLE
Reconstruction Method:
SINGLE PARTICLE


