Deposition Date
2019-04-12
Release Date
2019-04-24
Last Version Date
2024-10-16
Entry Detail
PDB ID:
6RF4
Keywords:
Title:
Crystal structure of the potassium-pumping S254A mutant of the light-driven sodium pump KR2 in the pentameric form, pH 8.0
Biological Source:
Source Organism(s):
Dokdonia eikasta (Taxon ID: 308116)
Expression System(s):
Method Details:
Experimental Method:
Resolution:
2.40 Å
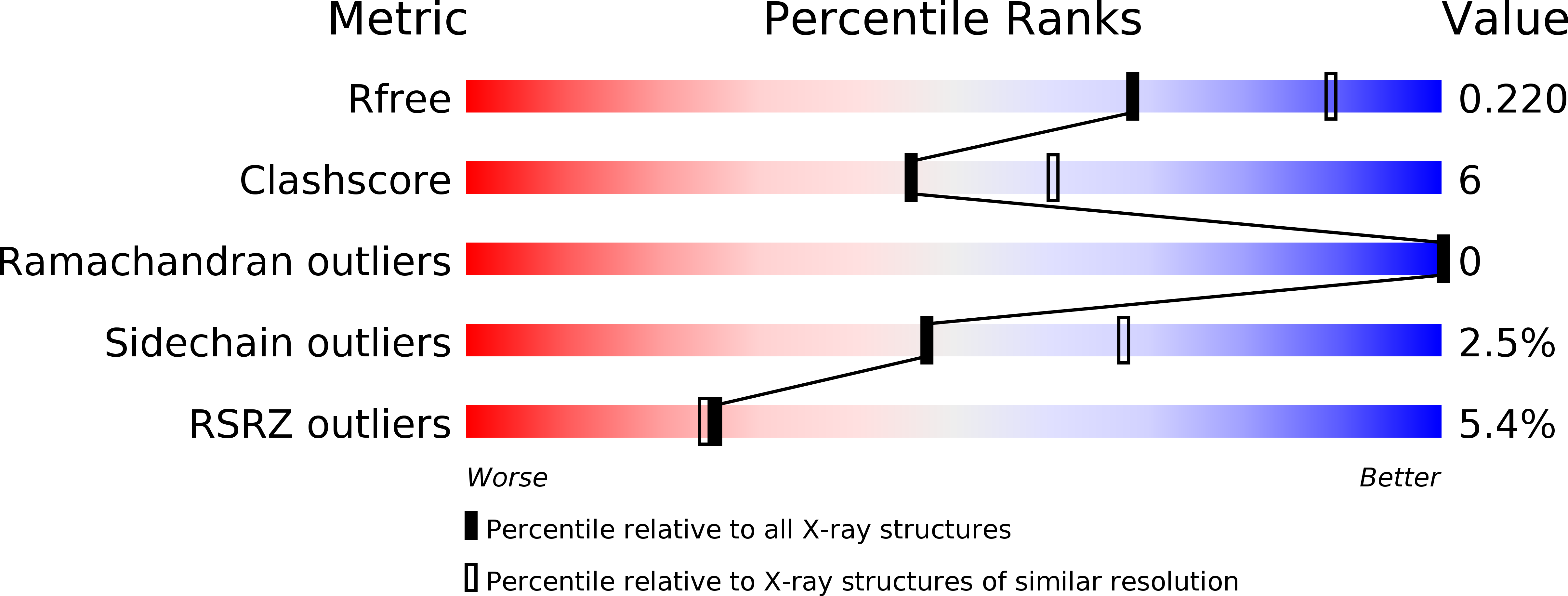
R-Value Free:
0.21
R-Value Work:
0.18
R-Value Observed:
0.18
Space Group:
C 2 2 21